Lean Software Development: Principles, Benefits, and Implementation in 2025
In an era where rapid delivery and efficiency are crucial, Lean Software Development (LSD) has emerged as a powerful approach for tech teams. Borrowing from lean manufacturing principles pioneered by Toyota, lean software development is a customer-centric methodology focused on reducing waste, improving productivity, and delivering high-quality software. As we move into 2025, LSD remains highly relevant, with agile and lean practices becoming cornerstones of modern software delivery.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the principles, benefits, challenges, and implementation strategies of lean software development to help businesses adapt and thrive in the competitive software landscape.
1. What Is Lean Software Development?
Lean software development is an agile-inspired methodology that focuses on maximizing value while minimizing waste. The core idea is to streamline the development process by eliminating non-value-adding activities, enabling teams to deliver better software faster.
Originating from lean manufacturing concepts developed by Toyota, LSD adapts those principles to the software industry. Waste in this context includes anything that does not directly contribute to delivering value to the customer, such as redundant features, excessive documentation, or inefficient processes.
The methodology encourages continuous improvement, rapid feedback, and collaboration across cross-functional teams. It aims to ensure high quality, early delivery, and alignment with customer needs.
2. The 7 Principles of Lean Software Development
2.1. Eliminate Waste
Waste in software development refers to unnecessary features, delays, handoffs, and miscommunications. Common forms include duplicate code, unused functionalities, and over-engineering. By removing these inefficiencies, teams can optimize their workflows and focus on creating real value.
Regular code reviews, backlog grooming, and minimizing context switching are practical steps to eliminate waste. Cross-functional teams should also align frequently to reduce misunderstanding and rework.
2.2. Build Quality In
Quality is not a final checkpoint; it’s built throughout the process. Lean development emphasizes writing clean, maintainable code and integrating testing early. This includes unit testing, test-driven development (TDD), and automated CI/CD pipelines.
Building quality also involves early validation of user stories, continuous integration, and peer collaboration. By embedding quality practices at every stage, defects are minimized and customer satisfaction increases.
2.3. Create Knowledge
Learning is continuous in lean development. Teams conduct experiments, collect feedback, and adapt their solutions accordingly. This iterative approach allows better decision-making and product evolution.
Knowledge sharing is encouraged through documentation, code comments, peer reviews, and retrospectives. Experimentation, such as A/B testing, drives innovation and helps validate ideas quickly.
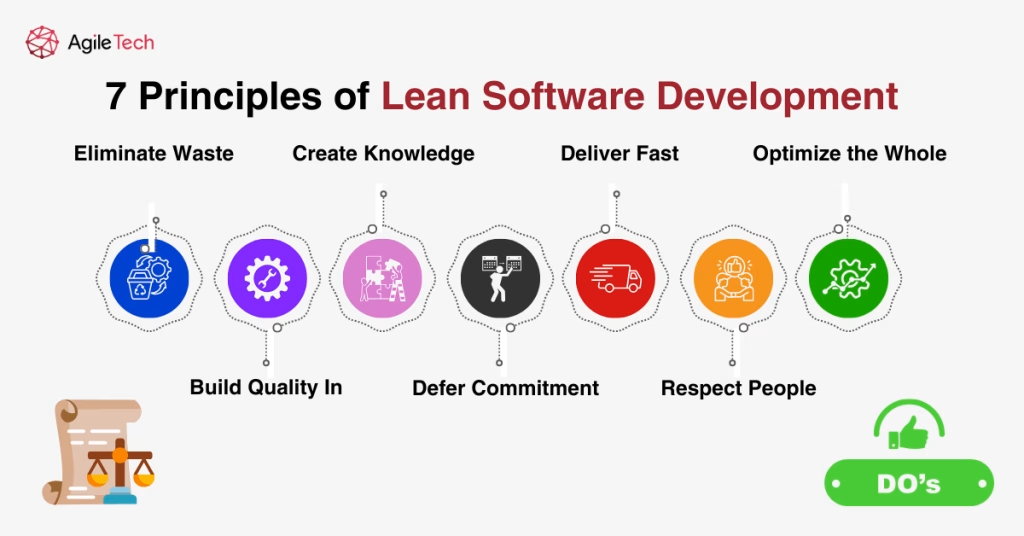
2.4. Defer Commitment
Lean encourages decisions to be made as late as responsibly possible. This enables more informed, context-aware choices and reduces the risk of rework. Instead of locking into early design decisions, teams collect feedback, validate assumptions, and adjust course as needed.
This principle is particularly valuable in uncertain environments where user needs evolve quickly. By keeping options open, development remains agile and responsive to change.
2.5. Deliver Fast
Rapid delivery enables early feedback and quick iteration. By shortening development cycles, teams can validate solutions sooner and reduce time-to-market. Frequent releases build trust with users and reveal improvement opportunities.
Practices like Scrum sprints, Kanban boards, and continuous delivery pipelines help teams achieve speed without sacrificing quality. Small batch sizes and MVPs are also core to delivering fast.
2.6. Respect People
People are at the heart of lean development. Empowered teams perform better when they are trusted, respected, and given ownership. Respect fosters creativity, accountability, and motivation.
Lean teams encourage autonomy, cross-functional collaboration, and knowledge-sharing environments. Leaders play a supporting role, removing blockers rather than micromanaging.
2.7. Optimize the Whole
Rather than optimizing individual functions or departments, lean software development promotes system-wide optimization. Bottlenecks, dependencies, and handoffs across the entire workflow are examined to improve the holistic delivery pipeline.
Value stream mapping is one tool used to identify areas of inefficiency. Optimizing the whole leads to smoother handoffs, aligned goals, and better customer outcomes.
3. Benefits of Lean Software Development
3.1. Increased Efficiency
Lean principles reduce unnecessary steps and encourage automation, leading to faster release cycles. Teams spend more time delivering value and less time correcting errors or waiting on approvals. This streamlining makes lean development ideal for organizations under pressure to innovate rapidly.
3.2. Higher Product Quality
With quality built into every stage, lean software development reduces the risk of bugs, delays, and post-release issues. Practices like automated testing, early feedback loops, and pair programming result in more reliable software and fewer last-minute scrambles.
3.3. Improved Customer Satisfaction
Frequent iterations and short feedback loops allow teams to respond quickly to customer needs. This responsiveness ensures the product remains relevant and aligned with real-world demands, enhancing user experience and satisfaction.
3.4. Better Team Morale
Lean empowers teams to make decisions and take responsibility for outcomes. This autonomy promotes a sense of ownership, leading to more motivated, collaborative, and engaged developers.
3.5. Lower Development Costs
Lean software development avoids overproduction, unnecessary features, and costly delays. By focus
Read more: 12 Best Software Development Companies in 2025: Global Experts for Web, Mobile, and AI Solutions
4. Challenges in Applying Lean Software Development
4.1. Cultural Resistance
Transitioning to lean requires a mindset shift from top-down control to empowered teams. Organizations with entrenched hierarchies may struggle with this change, requiring strong leadership support and change management.
4.2. Misinterpretation of Lean
Superficial adoption of lean, such as emphasizing speed without quality, can be counterproductive. Teams must understand Lean’s deeper goals of delivering value, learning continuously, and eliminating waste.
4.3. Tooling and Integration Gaps
Successful lean development relies on automated pipelines, collaboration platforms, and real-time tracking. Outdated tools or siloed systems hinder efficiency and transparency.
4.4. Lack of Metrics and Feedback Loops
Without data on performance and outcomes, teams can’t identify improvement areas. Establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) like lead time, cycle time, and error rates is essential for lean optimization.
5. How to Implement Lean Software Development (Step-by-Step)
Step 1: Identify Customer Value
Begin by defining the value your software delivers from the end-user’s perspective. Clarify customer problems and prioritize features that directly contribute to solving them.
Step 2: Map the Value Stream
Use value stream mapping to document each step in your development process, from concept to delivery. Identify wasteful activities, bottlenecks, and areas where value is lost.
Step 3: Establish Cross-Functional Teams
Create small, autonomous teams that include all necessary roles: developers, QA, UX/UI, product managers, and DevOps. Cross-functional collaboration reduces silos and enhances decision-making.
Step 4: Apply Iterative Development
Break work into short, manageable cycles (sprints or iterations). Release MVPs or feature updates frequently to gather early feedback and make quick improvements.
Step 5: Build a CI/CD Pipeline
Set up continuous integration and delivery to automate building, testing, and deploying software. This ensures faster releases and quicker detection of defects.
Step 6: Visualize Work and Manage Flow
Use tools like Kanban boards or digital task trackers to make all work visible. Set WIP (Work In Progress) limits to avoid overloading team members and maintain smooth progress.
Step 7: Create a Learning Culture
Promote knowledge sharing, conduct regular retrospectives, and encourage safe experimentation. A learning-oriented culture helps teams adapt and grow over time.
Step 8: Monitor, Measure, and Optimize
Define metrics such as lead time, velocity, and error rates. Review performance data regularly, adapt based on insights, and strive for continuous improvement.
Read more: Lean Software Development: A Practical Implementation Guide
6. Lean vs Agile vs Waterfall: A Quick Comparison
| Methodology | Focus | Delivery Style | Flexibility | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lean | Waste reduction, flow | Continuous | High | Evolving projects, fast feedback |
| Agile | Iterative user feedback | Incremental sprints | High | Customer-driven feature delivery |
| Waterfall | Sequential phases | One-time release | Low | Well-defined, regulated projects |
Conclusion
Lean Software Development offers a powerful framework for building high-quality, efficient, and customer-focused software in today’s fast-paced world. By adopting its principles, eliminating waste, delivering fast, respecting people, and optimizing the whole team can deliver greater value with fewer resources.
For companies aiming to implement or scale lean development practices, choosing the right partner is crucial. At AgileTech, we help businesses embrace lean and agile methodologies to launch better products faster. With experience across diverse industries and a team of lean practitioners, we’re ready to help you optimize your software development journey.