How Much Is the Cost of Implementing AI in Healthcare?
What is the cost of implementing AI in healthcare, and is it worth it? This is a pressing question for hospitals, clinics, and health-tech innovators worldwide. AI promises faster diagnostics, reduced administrative workloads, and highly personalized care—but the road to implementation can be filled with complex decisions, unpredictable expenses, and strategic missteps. In this guide, we’ll break down every layer of the cost of implementing AI in healthcare, from the obvious to the hidden, and help you evaluate whether AI is a sound investment for your healthcare institution. Whether you’re a healthcare executive, IT director, or operations lead, understanding the full financial picture is essential to making informed and impactful decisions.
- 1. What Is AI in Healthcare and How It’s Shaping Healthcare Systems
- 2. Key Cost Factors When Implementing AI in Healthcare Systems
- 3. Cost by Use Case
- 4. Hidden Costs of AI in Healthcare and Common Challenges
- 5. How to Reduce the Cost of AI Implementation in Healthcare
- 6. Conclusion
- FAQs: Understanding the Cost of Implementing AI in Healthcare
1. What Is AI in Healthcare and How It’s Shaping Healthcare Systems
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in healthcare refers to the use of advanced algorithms, machine learning models, and data-driven systems that assist in diagnosis, treatment planning, operational efficiency, and patient engagement. These systems analyze vast amounts of structured and unstructured medical data, recognize patterns, and offer insights or decisions that support human healthcare providers.
The benefits of AI in healthcare include improved diagnostic accuracy, reduced clinical workload, and enhanced patient outcomes. Applications of AI range from administrative automation, such as handling medical billing or appointment scheduling, to clinical roles like detecting abnormalities in radiology images or predicting patient deterioration in ICUs. AI-powered tools include chatbots for triage, robotic surgical assistants, and digital pathology systems.
What distinguishes AI in healthcare from other technologies is its ability to learn and adapt. With continuous data inputs, AI systems become more accurate over time, reducing reliance on static rules or manual intervention. As digital transformation accelerates across healthcare systems globally, AI has emerged as a foundational tool for modernizing patient care and operational processes.
Read more: AI Automation in Healthcare: From Hype to Real-World Applications
2. Key Cost Factors When Implementing AI in Healthcare Systems
Implementing AI in healthcare involves various direct and indirect costs that extend well beyond just purchasing software. It’s a comprehensive journey that includes data handling, infrastructure investment, staffing, training, compliance, and long-term support. Costs vary greatly depending on the scale of deployment, type of solution (custom-built vs off-the-shelf), geographic location, and maturity of the institution’s digital capabilities.
2.1. Discovery & Planning
The planning phase is crucial because it lays the groundwork for the entire project. During this phase, healthcare organizations need to map out objectives, select appropriate AI technologies, and create a roadmap aligned with clinical and administrative priorities. This phase often requires extensive workshops, interviews with clinical stakeholders, regulatory reviews, and procurement planning.
Consultants and technical advisors are often hired to conduct feasibility studies and ROI simulations. These preliminary tasks may cost anywhere from $25,000 to $100,000, depending on the organization’s complexity. It’s also essential to engage IT and clinical leadership early to secure buy-in and avoid costly delays during implementation.
2.2. Data Collection & Preparation
Data preparation remains one of the most labor-intensive and resource-consuming phases of AI deployment. Medical data, especially unstructured data like physician notes, handwritten prescriptions, and diagnostic images, requires cleaning, labeling, and standardization.
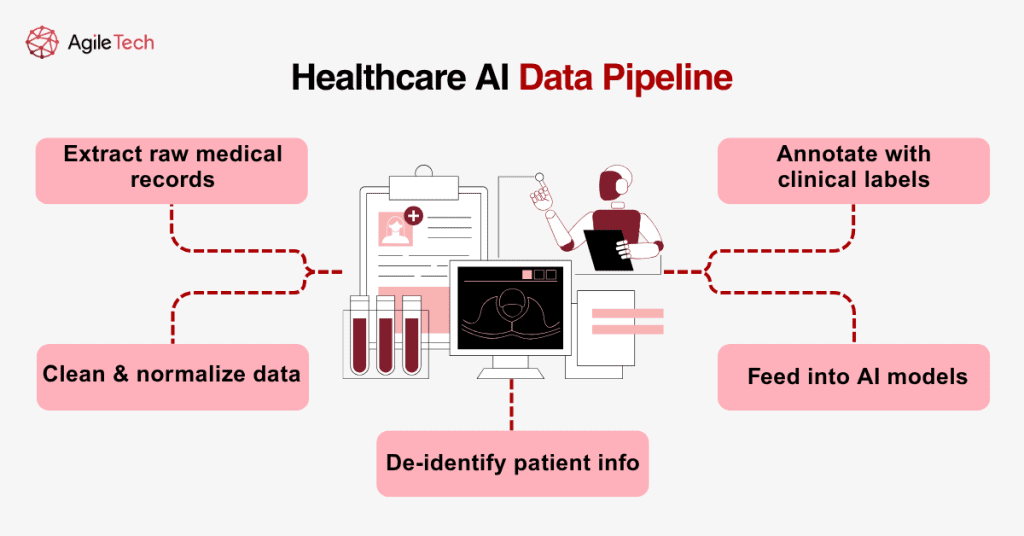
For example, building an AI model to detect pneumonia in chest X-rays requires thousands of labeled images, typically annotated by radiologists. A single expert-labeled image can cost $3 to $10, and large models may need up to 100,000 samples. That alone can add $300,000 to $1 million to a project’s total.
Data must also be anonymized to ensure patient privacy and comply with local and international regulations. Tools like FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) and SNOMED CT (Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine) are often used to structure and codify health data. These standards help AI tools communicate seamlessly with hospital systems, but the adaptation process can be lengthy and expensive.
2.3. AI Development
Developing AI in healthcare is far more complex than in many other sectors due to the critical and high-risk nature of decisions. Custom AI tools need to be trained on high-quality, domain-specific datasets, and they require rigorous validation.
Hospitals must either hire an in-house team (including data scientists, machine learning engineers, domain experts, and project managers) or work with AI vendors. Salaries alone for a competent team may exceed $500,000 annually. Training, validation, and deployment phases can take months or even years, depending on the model’s complexity.
Additionally, explainability is key. Clinicians and regulators must be able to understand why a model made a specific recommendation. This need for transparency often requires integrating interpretability tools, which adds to development time and cost.
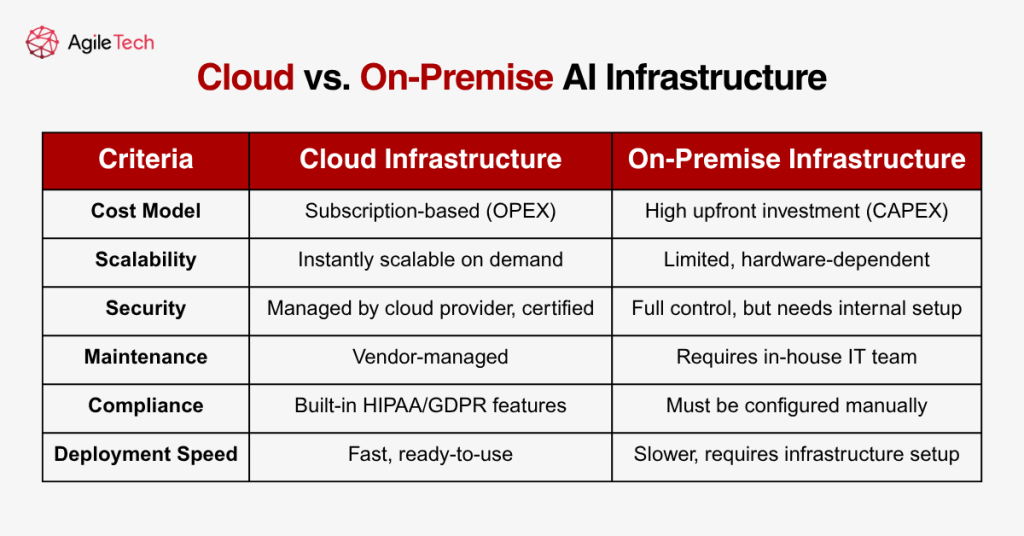
2.4. Infrastructure & Hosting
AI models typically require substantial computing power, especially during training. GPU servers, large-scale storage systems, and high-speed networking infrastructure are necessary. Hospitals must decide whether to use on-premise infrastructure or cloud-based solutions.
On-premise solutions offer more control but involve high capital expenditure. Costs include purchasing and maintaining servers, hiring dedicated IT staff, and ensuring physical security. In contrast, cloud solutions offer scalability, reliability, and compliance-ready features, often at a lower upfront cost but higher long-term subscription fees.
For example, AWS’s HIPAA-compliant AI services or Google Cloud’s Healthcare Data Engine offer comprehensive solutions, with prices ranging from a few hundred to thousands of dollars per month based on usage.
2.5. System Integration
Seamless integration with existing hospital systems is non-negotiable for any AI application. AI tools must pull data from EHRs, send alerts to care teams, and sometimes trigger automated responses such as medication refills or discharge planning.
This often requires building secure APIs and working with third-party vendors. Hospitals must ensure interoperability while minimizing workflow disruptions. Middleware platforms like Mirth Connect or HL7-based integration engines are commonly used to support this process. Testing and rollout across departments can take several weeks and cost anywhere from $50,000 to $250,000.
2.6. Validation & Compliance
AI systems in healthcare must comply with both technical performance and regulatory standards. Clinical validation involves comparing AI-generated insights with actual outcomes and conducting controlled trials.
In the U.S., FDA clearance is required for AI systems classified as medical devices. This process includes documentation, audits, and trial results, which may cost hundreds of thousands. Compliance with GDPR and HIPAA also adds legal review fees, consent management systems, and documentation requirements.
2.7. Maintenance
Maintaining an AI system in production involves much more than bug fixes. Over time, clinical practices evolve, and patient populations change. This phenomenon, called “model drift,t,” requires periodic retraining and performance reevaluation.
Hospitals may also need to expand their models, add new use cases, or integrate feedback mechanisms. Long-term support may involve cybersecurity upgrades, patch management, and integration with newer systems. Maintenance costs can reach up to 20%–25% of the original investment per year.
Read more: Harnessing Computer Vision in Healthcare: Transforming Patient Care and Clinical Workflows
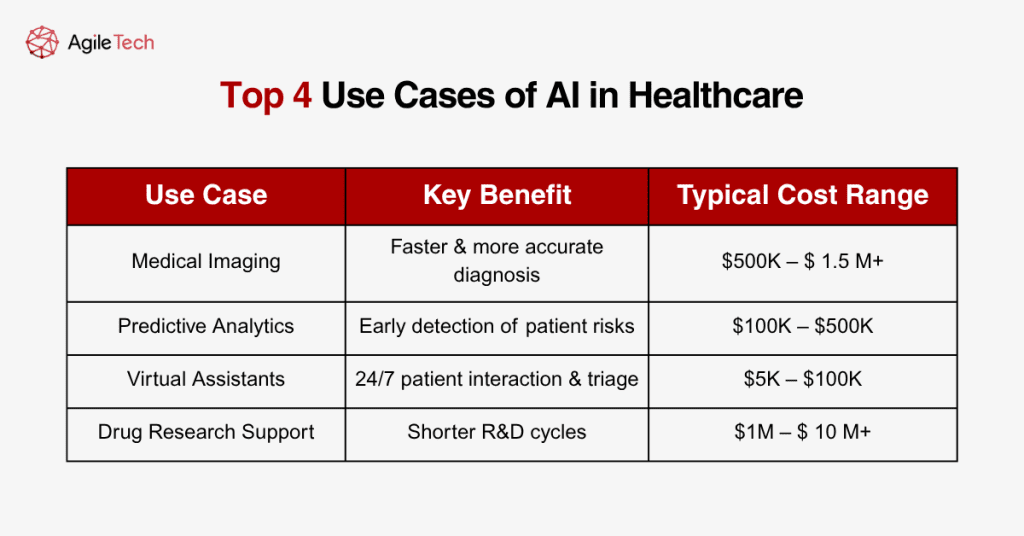
3. Cost by Use Case
The cost of implementing AI in healthcare varies significantly depending on the use case. Each type of application requires different levels of technical complexity, data requirements, integration depth, and clinical validation. In this section, we examine four major use cases where AI has shown strong adoption and discuss the typical costs, benefits, and deployment considerations associated with each.
3.1. Medical Imaging
AI in medical imaging is one of the most advanced and commercially mature applications. These systems use deep learning models to analyze radiological scans such as X-rays, CTs, MRIs, and mammograms. They assist radiologists by detecting anomalies, highlighting areas of concern, and offering second opinions.
The development of such tools often involves training on massive image datasets, sometimes comprising millions of scans requiring expert labeling, high-end computing resources, and extensive validation. Integration into Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) is also required.
Costs include:
- Licensing fees for commercial models: $100,000–$500,000/year
- Custom development: $500,000–$1.5 million
- Validation and compliance: $100,000–$300,000
- Integration and training: $50,000–$150,000
Despite the high initial investment, hospitals benefit from faster diagnoses, reduced radiologist fatigue, and improved diagnostic accuracy, leading to better patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
3.2. Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics models in healthcare are designed to anticipate events such as patient deterioration, hospital readmission, disease onset, or treatment response. These tools use patient history, vital signs, lab results, and demographic data to predict risks and trigger early interventions.
Such models vary in complexity. Basic risk scoring models can be developed using regression or decision trees, while advanced systems use ensemble models and neural networks. Cost drivers include data quality, integration with real-time monitoring systems, and ongoing model updates.
Estimated costs:
- Development and testing: $100,000–$400,000
- Data preparation and compliance: $50,000–$150,000
- Integration with EHR and alert systems: $30,000–$100,000
Predictive analytics tools help reduce emergency incidents, optimize ICU resources, and lower overall care costs. Studies show predictive models can reduce hospital readmission rates by up to 15%, leading to both financial savings and improved care quality.
3.3. Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
These AI applications are designed to improve patient engagement and automate front-desk operations. Chatbots answer patient queries, schedule appointments, provide medication reminders, and assist with administrative forms.
Implementation is relatively straightforward. Most systems leverage natural language processing (NLP) models integrated with messaging platforms or hospital websites. Customization for medical terminology and patient personas is essential to ensure relevance and usability.
Typical costs:
- Basic chatbot: $5,000–$20,000
- Advanced NLP-enabled assistant: $50,000–$100,000F
- Integration with EHR and patient portals: $10,000–$30,000
These systems reduce administrative burden on staff and offer 24/7 service to patients, improving satisfaction and reducing phone traffic by up to 60% according to some hospital case studies.
3.4. Drug Research and Development Support
AI is revolutionizing drug discovery by predicting molecule behavior, simulating clinical trials, and identifying candidates for repurposing. These applications require massive investment but offer long-term payoff through shortened R&D cycles and higher success rates.
Costs can reach millions:
- AI platforms for drug design: $500,000–$2 million per license
- Custom pipelines using deep learning: $1 million–$10 million+
- Infrastructure and compliance: $500,000+
Pharmaceutical firms and biotech startups leverage these tools to reduce average drug development time from 10–15 years to 5–7 years. Successful applications by companies like DeepMind, Insilico Medicine, and Atomwise illustrate the massive economic potential of AI in pharma.
4. Hidden Costs of AI in Healthcare and Common Challenges
While many organizations plan extensively for the direct costs of implementing AI in healthcare, hidden costs often emerge after deployment begins. If not anticipated, these indirect expenses can hinder progress, cause budget overruns, and delay impact realization.
One of the most frequently overlooked aspects is workforce adaptation. Successful integration of AI tools requires that medical staff, administrators, and IT teams be trained not only in how to use the systems but also in understanding their limitations, ethical considerations, and interpretation of results. These training sessions, often repeated due to staff turnover or role shifts, carry cumulative costs over time in terms of money and reduced productivity during onboarding periods.
Legal and compliance-related costs also tend to escalate. Healthcare providers must ensure that data privacy regulations such as HIPAA (in the U.S.) and GDPR (in Europe) are adhered to at all times. This involves setting up complex consent management workflows, retaining legal counsel, and sometimes building data-sharing frameworks that meet jurisdictional laws. These activities are rarely budgeted with precision in early phases, yet they are essential to avoid legal risks.
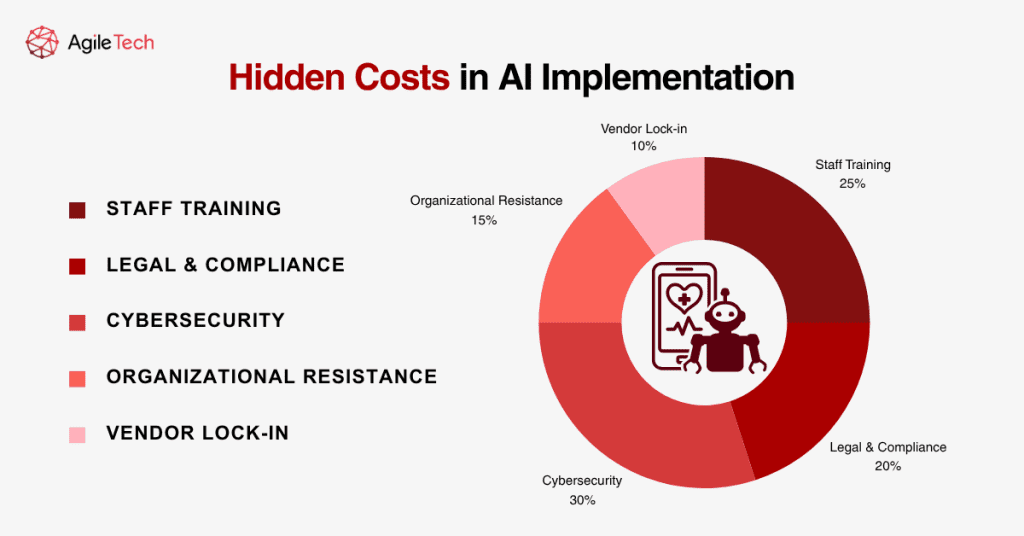
Another significant hidden cost lies in cybersecurity. AI tools often connect to multiple data sources and systems, increasing the organization’s digital footprint. This makes them attractive targets for cyberattacks. Robust cybersecurity measures such as firewalls, encryption, anomaly detection systems, and staff awareness programs must be implemented and maintained. The cost of failing to do so can be devastating, not only financially but also in terms of patient trust.
Resistance to change is a human factor that has real financial implications. If staff feel threatened by AI, perceive it as replacing their roles, or distrust its recommendations, adoption can slow dramatically. In some cases, hospitals have had to launch internal campaigns, hold regular town halls, and even employ behavioral experts to manage this transformation, costs that are seldom part of initial AI budgets.
Vendor lock-in represents another long-term challenge. AI solutions that rely on proprietary formats or ecosystems can limit future flexibility and incur high switching costs if the hospital wants to transition to another vendor. To mitigate this, institutions must negotiate exit strategies and data portability clauses from the outset, legal services that also add cost.
Read more: The True Cost of Telehealth Implementation and How to Lower It
5. How to Reduce the Cost of AI Implementation in Healthcare
Despite these challenges, healthcare organizations can adopt strategic measures to contain costs without sacrificing quality or outcomes. A phased implementation approach is often the most effective starting point. Rather than deploying AI across all departments, hospitals should select a single, high-impact use case, such as automating appointment scheduling or using AI to detect patient deterioration. Demonstrating early success builds stakeholder confidence and justifies future investment.
Utilizing open-source frameworks can significantly reduce development costs. Tools such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Apache MXNet offer extensive functionality and active communities. By building on these foundations, organizations can focus resources on model customization and integration rather than core architecture.
Healthcare-specific platforms offered by vendors like IBM Watson Health, Google Cloud Healthcare, and Amazon HealthLake can also streamline implementation. These platforms come with built-in data handling, compliance, and API integrations, minimizing the need for complex custom development. Choosing these pre-vetted solutions helps avoid reinvention and accelerates time to value.
Cloud computing offers another major opportunity for cost reduction. Hosting AI models on platforms like Microsoft Azure, AWS, or Google Cloud enables hospitals to scale resources on demand, pay only for what they use, and eliminate costly infrastructure maintenance. Moreover, these platforms typically offer security and compliance certifications that meet healthcare requirements, easing regulatory burden.
Cross-training internal staff is another high-leverage tactic. Rather than outsourcing maintenance and retraining of AI models indefinitely, healthcare organizations can invest in upskilling their current teams. Collaborations with academic institutions or participation in online AI certification programs can help clinical and IT staff develop foundational knowledge, creating a sustainable support model.
Additionally, organizations should explore partnerships and funding opportunities. Many governments, NGOs, and global health bodies offer grants for AI research and digital health innovation. Tapping into these external resources can dramatically offset development and deployment expenses.
Finally, establishing a governance framework early in the process ensures that AI projects align with institutional goals, stay within scope, and adapt to evolving regulations. This framework should define ownership, set performance benchmarks, and outline a review cadence. Governance helps prevent the uncontrolled expansion of AI initiatives, a common source of cost creep, and creates organizational discipline that pays off in long-term efficiency and scalability.
6. Conclusion
The cost of implementing AI in healthcare is multifaceted, encompassing both direct and hidden expenses. From data preparation and model development to integration, maintenance, and compliance, each phase carries its own challenges and resource demands. However, when approached strategically, these costs can be controlled, and the long-term benefits of AI in healthcare can far outweigh the investment.
AI brings measurable improvements to patient care, administrative efficiency, diagnostics, and treatment personalization. It addresses chronic challenges in the healthcare sector, from staff shortages to operational inefficiencies. Institutions that invest wisely, starting with targeted pilots, choosing flexible solutions, and upskilling their teams, can position themselves as future-ready healthcare providers.
Ultimately, the true value of AI in healthcare lies not only in its ability to save money but in its potential to save lives. With careful planning, ongoing evaluation, and commitment to ethical implementation, AI can revolutionize care delivery while remaining cost-effective and sustainable.
FAQs: Understanding the Cost of Implementing AI in Healthcare
Before wrapping up, let’s address some of the most common questions healthcare organizations have when considering the implementation of AI. These questions are often raised during internal board discussions, planning workshops, or consultations with vendors, and answering them clearly can help clarify direction, avoid common pitfalls, and inspire confident decision-making.
Looking to bring the power of AI into your healthcare organization? Whether you’re just exploring your first pilot project or ready to scale AI across clinical and administrative systems, AgileTech Vietnam can support you every step of the way. From early discovery to post-deployment optimization, our team specializes in healthcare-specific AI development, ensuring data privacy, scalability, and measurable ROI. Contact us today to explore how we can help you launch high-impact healthcare AI systems that are secure, scalable, and cost-effective.