How to Build an EMR App: A Complete Step-by-Step Guide 2025
Building an EMR app is essential for healthcare providers looking to digitize patient records and improve efficiency. These systems enable medical staff to securely access, update, and manage patient information in real time. This guide outlines how to build an EMR app from start to finish — covering key features, compliance, technology choices, and development best practices to help you create a secure, scalable, and efficient healthcare solution
What is an EMR Application?
An Electronic Medical Record (EMR) application replaces traditional paper-based medical records with digital systems designed for healthcare providers. It stores and manages patient demographic data, medical history, lab results, prescriptions, treatment documentation and more.
By digitizing records, EMR apps enhance efficiency, reduce human error, and enable seamless data sharing among authorized staff. These systems are now the foundation of healthcare IT infrastructure, empowering clinicians to make faster, more informed decisions and improving the overall quality of patient care.
Key Features of Modern EMR Systems
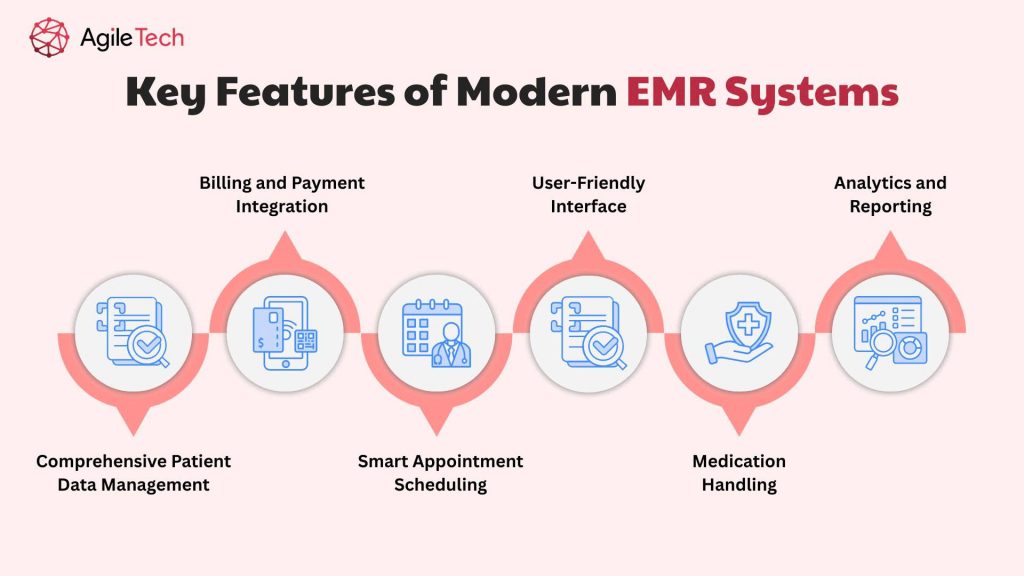
Comprehensive Patient Data Management
At the heart of every EMR system lies its ability to store, organize, and retrieve complete patient records efficiently. A centralized database consolidates all information, including:
- Personal demographics and contact details
- Medical history, allergies, and ongoing treatments
- Diagnostic results, lab reports, and clinical notes
- Immunization records and surgical history
An efficient data management module ensures that authorized healthcare professionals can access accurate, up-to-date patient information instantly. This minimizes administrative delays, improves coordination across departments, and supports informed clinical decisions.
Smart Appointment Scheduling
A smart appointment scheduling system helps medical practices optimize time and reduce patient wait times. The system should support:
- Automated booking and confirmation notifications
- Real-time availability tracking for doctors and rooms
- Reminders via SMS, email, or in-app notifications
- Digital queue management to prevent overlaps and idle time
Advanced EMR apps even integrate with patient portals, allowing patients to book, reschedule, or cancel appointments online. This not only improves operational efficiency but also enhances patient satisfaction through convenience and transparency.
Medication Handling
Prescription management is another cornerstone of modern EMR solutions. A secure e-prescription feature allows physicians to send prescriptions electronically to pharmacies, minimizing errors caused by illegible handwriting or manual entry.
Key capabilities include:
- Drug interaction checks and allergy alerts
- Medication dosage recommendations
- Refill tracking and expiration reminders
- Pharmacy integration for seamless order fulfillment
By digitizing this process, EMR apps promote safer prescribing practices, ensure better medication adherence, and enhance overall patient safety.
Billing and Payment Integration
Financial management is crucial for both private clinics and large hospitals. A robust EMR system integrates billing, claims processing, and payment management directly into the workflow.
Essential billing features include:
- Automated invoice generation linked to patient visits and procedures
- Insurance claims submission and tracking
- Payment reminders and transaction history
- Integration with accounting systems for real-time financial insights
This reduces manual paperwork, speeds up reimbursements, and minimizes billing errors — allowing healthcare providers to focus more on care delivery and less on administrative burdens.
User-Friendly Interface
Usability is one of the defining factors of a successful EMR app. A clean, intuitive interface ensures that doctors, nurses, and administrative staff can access information quickly without technical barriers.
A well-designed UI/UX should provide:
- Simple navigation with minimal clicks to complete key tasks
- Customizable dashboards for different roles (e.g., doctor, nurse, admin)
- Accessibility across desktop, tablet, and mobile devices
- Fast loading times and optimized layouts for real-time updates
An easy-to-use system not only saves time but also reduces training costs and enhances adoption rates among medical staff.
Analytics and Reporting
Modern healthcare organizations rely heavily on data analytics to drive decisions. A powerful EMR app should include built-in analytics and reporting tools to convert raw medical and operational data into meaningful insights.
Common analytics capabilities include:
- Performance dashboards showing patient flow, treatment efficiency, and physician productivity
- Clinical outcome reports for chronic disease tracking and preventive care
- Financial analytics to monitor revenue cycles and identify bottlenecks
- Compliance and audit reports to ensure adherence to healthcare regulations
By leveraging analytics, hospitals can identify trends, optimize resource allocation, and continuously improve the quality of care.
Regulatory Requirements and EMR App Compliance Standards
Healthcare software must comply with strict legal and regulatory frameworks to ensure data privacy and patient safety. In the United States, compliance with HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) is mandatory. Similar standards exist in other regions, such as GDPR in the EU and HITECH for digital health technology.
Compliance focuses on:
- Secure handling of Protected Health Information (PHI).
- Encrypted data storage and transmission.
- Access control and user authentication.
- Audit logs to track every system activity.
Adhering to these standards is not optional—it is vital for maintaining trust, avoiding penalties, and protecting patient data.
Step-by-Step EMR App Development Process
Building an EMR app is a complex process that requires careful planning, technical precision, and strict compliance with healthcare standards. Each phase — from research to deployment — plays a crucial role in ensuring that the final product is secure, user-friendly, and fully functional. Below is a detailed breakdown of the EMR app development process that healthcare organizations and software development teams should follow.
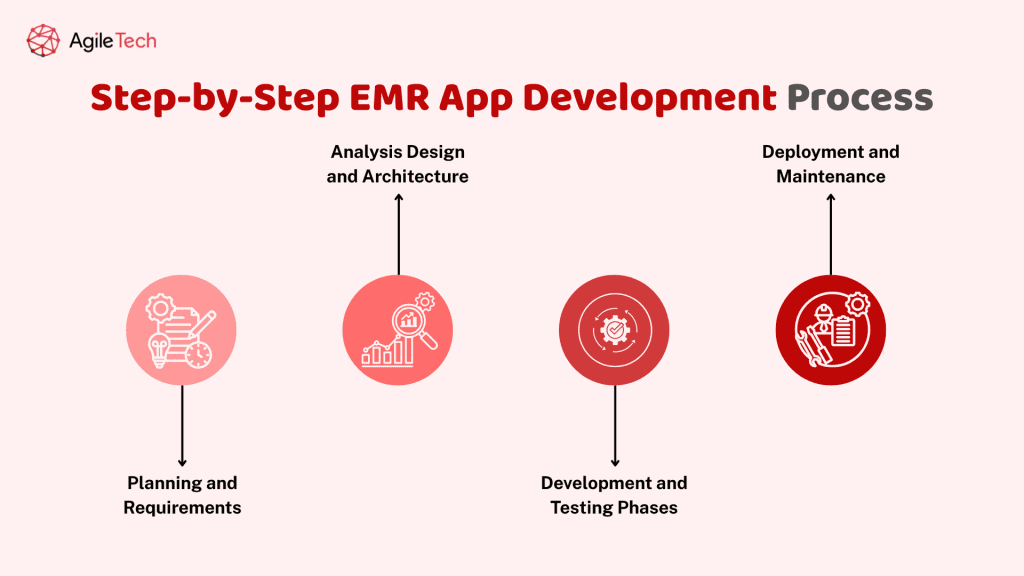
Planning and Requirements Analysis
The foundation of any successful EMR app lies in comprehensive planning. This stage defines the project’s scope, functional needs, and compliance requirements.
Collaborative Research
Begin with extensive consultations involving doctors, nurses, healthcare administrators, and IT specialists. Their insights help you understand real-world workflows — such as patient intake, diagnosis recording, medication management, and billing — to ensure your EMR solution aligns with clinical operations.
Requirement Gathering
Clearly define:
- Core functionalities: Patient records management, appointment scheduling, prescription handling, and billing automation.
- User roles: Identify permissions for doctors, nurses, administrative staff, lab technicians, and patients.
- Access controls: Establish rules for who can view, modify, or approve specific types of medical data.
Documentation
Create detailed technical and functional documentation. This includes:
- Workflow diagrams for user journeys.
- Data flow mapping for information exchange.
- Compliance documentation referencing HIPAA, GDPR, or regional standards.
A well-documented plan ensures all team members share the same understanding and helps maintain alignment between business objectives and technical execution.
Design and Architecture
This stage shapes the structure, user experience, and performance of your EMR system. A strong architectural design ensures the app remains scalable, maintainable, and compliant with data protection regulations.
System Architecture
Adopt a modular or microservices architecture, where each service (e.g., patient records, billing, scheduling) functions independently but communicates through secure APIs. This allows flexibility for future upgrades, easy maintenance, and better performance distribution.
UI/UX Design
Design the interface with healthcare professionals in mind:
- Simple, intuitive layouts that minimize clicks.
- Role-based dashboards showing the most relevant data for each user type.
Clear color coding and accessibility features (for example, large text or high-contrast modes) to support usability under clinical conditions.
Database Design
Design data models that support complex relationships between patients, physicians, diagnoses, and treatments. The database must allow for:
- Fast retrieval of large data sets.
- Support for multiple file types (scans, lab reports, images).
- Versioning of records to maintain historical accuracy.
Cross-Platform Compatibility
Modern healthcare workflows span across multiple devices — desktops in offices, tablets in wards, and mobile phones for on-the-go access. Your EMR app should be responsive and device-agnostic, ensuring consistent functionality and security on all platforms.
Compliance by Design
Embed HIPAA and GDPR compliance into the architecture itself. This means enforcing secure authentication, encrypted communication, audit trails, and automatic logouts from the very beginning of design, not as an afterthought.
Development and Testing Phases
Core Development Stages
Start by developing and testing the core modules that form the backbone of the EMR system:
- Patient Registration and Profile Management: Create functionalities for onboarding new patients, verifying credentials, and maintaining demographic and medical data.
- Electronic Medical Records Module: Implement features for documenting medical history, clinical notes, lab results, and imaging data.
- Appointment and Scheduling System: Automate scheduling, reminders, and doctor availability tracking.
- Billing, Insurance, and Payment Integration: Develop financial modules that link directly to patient visits, generating invoices and insurance claims automatically.
User Management and Access Control: Set up multi-level authentication, user roles, and session management for enhanced security.
Testing should begin early and continue throughout development. Key testing approaches include:
- Functional Testing: Validate that each feature works as intended across different user roles and workflows.
- Security Testing: Conduct vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, and API security validation to safeguard sensitive patient data.
- Performance Testing: Simulate heavy loads and concurrent access to ensure the app performs efficiently under hospital-scale usage.
- Usability Testing: Gather feedback from healthcare professionals using prototypes to improve interface design and workflow logic.
Integration Testing: Verify seamless communication between EMR modules and external systems like lab databases, pharmacy APIs, or payment gateways.
Deployment and Maintenance
Staged Deployment
Start with a pilot implementation in a single clinic or department. This allows your team to collect real-world feedback, identify usability issues, and fine-tune performance before system-wide release. Once stabilized, scale deployment to the entire organization or network of facilities.
User Training
Training is critical for successful EMR adoption. Provide workshops, user manuals, and video tutorials for staff to familiarize themselves with the system. Role-specific training ensures each department understands how to use the app efficiently and securely.
Technical Support and Monitoring
Establish a dedicated support and monitoring system to address any issues quickly. Monitor performance metrics such as response time, uptime, and error rates. Logging tools and analytics dashboards can help identify technical bottlenecks and user pain points.
Regular Maintenance and Updates
Ongoing maintenance is essential for compliance and performance optimization. Schedule periodic updates to:
- Patch security vulnerabilities.
- Add new features based on user feedback.
- Ensure compatibility with updated healthcare data standards like HL7 FHIR.
Feedback and Continuous Improvement
Encourage healthcare teams to share feedback post-launch. Their insights help improve workflows, fix usability challenges, and shape future development iterations. Continuous feedback loops ensure your EMR system evolves with the needs of the medical facility.
Professional EMR App Development Solutions
Benefits of Custom EMR App Development
Many healthcare providers opt for custom EMR app development to tailor solutions to their workflows, departments, and specific needs.
Benefits include:
- Personalized Features: Custom modules like specialty templates, custom dashboards, and analytics reports.
- Enhanced Productivity: Medical staff work with tools aligned to their daily operations.
- Scalability: Easily expand the app as the organization grows.
Custom EMR systems offer better usability, stronger integration, and higher adaptability compared to off-the-shelf solutions.
Technical Requirements for EMR App Development
Choosing the right technology stack is one of the most important decisions in building an EMR app. It directly impacts the system’s performance, scalability, security, and ease of maintenance. Because healthcare applications handle massive volumes of sensitive data and require real-time responsiveness, selecting modern, stable, and secure technologies is crucial from the start.
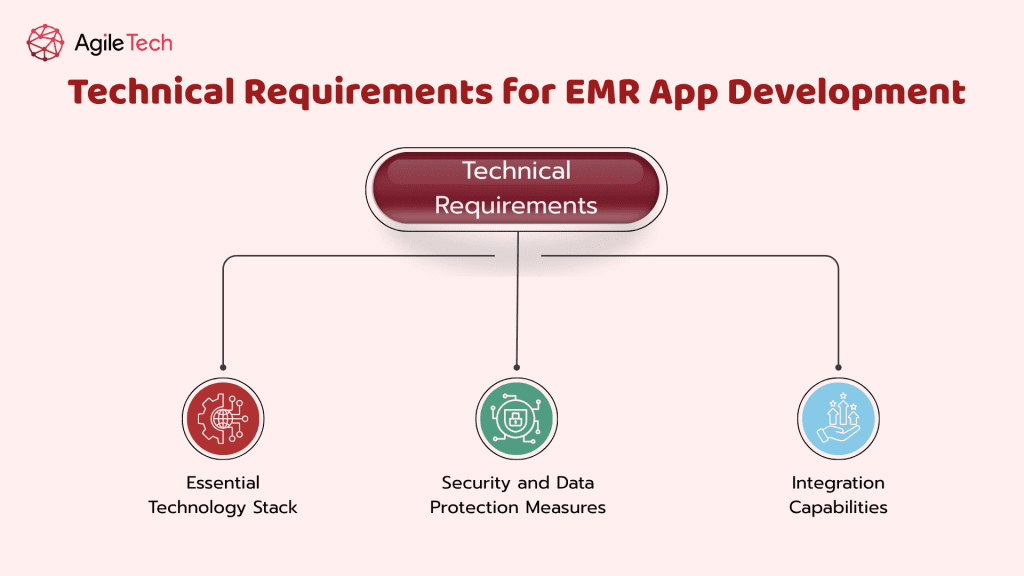
Essential Technology Stack for EMR System
Backend Technologies
The backend is the backbone of the EMR system — responsible for handling data processing, business logic, and communication between the database and frontend.
Two of the most widely used backend technologies are:
- Node.js: A JavaScript runtime environment known for its speed and scalability, making it ideal for building asynchronous, event-driven applications like EMR systems. It supports real-time data exchange, enabling instant updates to patient records, appointment statuses, or lab results.
- Django (Python): A high-level web framework that emphasizes security and rapid development. Django includes built-in tools for authentication, ORM, and admin interfaces, making it especially useful for healthcare projects where compliance and data integrity are priorities.
Both frameworks can be extended with RESTful or GraphQL APIs to enable integration with third-party systems such as laboratory software, pharmacy databases, or insurance platforms.
Database Systems
Healthcare data comes in many forms — from structured tables (like patient demographics) to unstructured documents (like scanned reports or imaging data). Hence, a combination of relational and NoSQL databases is often used.
- PostgreSQL: A robust, open-source relational database system ideal for structured data management. It supports advanced data integrity features, transactions, and indexing, ensuring reliability and compliance for mission-critical medical data.
- MongoDB: A NoSQL document-based database suitable for handling large, complex, and flexible data sets such as lab reports, clinical notes, and treatment histories. Its schema-less nature provides flexibility for evolving EMR structures.
Some EMR apps use a hybrid architecture, where PostgreSQL manages structured patient and billing data while MongoDB stores unstructured medical documents, images or logs.
To further enhance performance, caching tools such as Redis or Memcached can be integrated to reduce query time and improve system responsiveness.
Frontend Frameworks
The frontend is the interface through which users — doctors, nurses, and administrators — interact with the EMR system. It needs to be responsive, intuitive, and lightweight, offering a seamless experience across devices.
Popular frontend technologies include:
- React: A JavaScript library by Meta, ideal for building dynamic and interactive user interfaces. React’s component-based architecture allows modular development, easier maintenance, and faster updates.
- Angular: A powerful TypeScript-based framework developed by Google. It offers built-in data binding, dependency injection, and routing, making it suitable for enterprise-level EMR applications that require complex workflows and multiple modules.
Both frameworks support cross-platform development and can be paired with React Native or Flutter to create complementary mobile EMR apps for iOS and Android devices.
Cloud Platforms and Infrastructure
Modern EMR systems benefit immensely from cloud computing, which provides flexibility, scalability, and enhanced security without the need for extensive on-premise infrastructure.
Leading cloud service providers for EMR hosting include:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): Offers HIPAA-compliant infrastructure, scalable storage, and advanced data encryption. Services like AWS Lambda and EC2 enable flexible deployment and automated scaling.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Provides healthcare-focused tools such as the Cloud Healthcare API for FHIR and HL7 data exchange, making interoperability easier.
- Microsoft Azure: Known for strong enterprise integration and compliance capabilities, Azure supports secure virtual machines, cloud databases, and built-in analytics services.
Cloud hosting ensures 24/7 uptime, global accessibility, and disaster recovery, all essential for mission-critical healthcare environments. It also allows healthcare organizations to expand their infrastructure as they grow, without heavy upfront investment.
Security and Data Protection Measures in EMR Apps
When building an EMR app, data security is paramount. Patient information is one of the most sensitive forms of data and must be protected through multiple security layers.
Key practices include:
- Data Encryption: Encrypt both stored and transmitted data using strong cryptographic algorithms
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Adds a secondary layer of identity verification for users.
- Role-Based Access Control: Restrict access to sensitive modules based on user roles and responsibilities.
- Protected APIs: Use secure APIs with authentication tokens and proper endpoint validation.
- Zero Trust Architecture: Verify every access request, regardless of its origin, to minimize internal risks.
By combining these methods, healthcare systems can reduce vulnerabilities and maintain patient trust.
Integration Capabilities of an EMR App
A robust EMR system must integrate seamlessly with other medical and administrative tools. Integration enhances efficiency and ensures a unified flow of information across platforms.
Common integrations include:
- Laboratory Information Systems (LIS): Automatically import test results into patient records.
- Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS): View X-rays, MRI scans, and other imaging results directly within the EMR.
- Pharmacy Management Systems: Handle prescriptions, inventory, and drug tracking.
- Insurance and Billing Systems: Manage claims, payments, and financial records.
Supporting healthcare data exchange standards like HL7 and FHIR ensures interoperability and scalability for the EMR app.
AgileTech – Experienced Partner in EMR App Development
With over a decade of experience in software development, AgileTech has worked on a wide range of web and mobile solutions, including healthcare, finance, and education projects. The team focuses on building reliable, secure, and user-friendly applications that meet industry-specific standards and compliance requirements.
Drawing on years of practical experience, AgileTech applies agile methodologies and modern technologies to deliver healthcare solutions that are efficient, scalable, and adaptable to real-world needs. This expertise enables the company to support healthcare organizations in developing EMR systems that enhance data management, workflow efficiency patient care and explore our project.
Great insights! As AI adoption grows, user awareness and digital hygiene are becoming just as important as innovation itself.
At AgileTech, we’ve seen how easily users can fall into subscription traps from unofficial “AI apps.”
The key is transparency — always confirm the source before downloading or subscribing.
