Lean Software Development: A Practical Implementation Guide
In an age where speed and agility define success, lean software development (LSD) has emerged as a highly effective approach to building high-quality software efficiently. Originally rooted in lean manufacturing pioneered by Toyota, LSD emphasizes cutting waste, maximizing learning, and delivering customer value as fast as possible. This guide focuses on how to implement lean software development effectively in modern software environments.
- 1. Understanding Lean Software Development
- 2. Core Principles of Lean Software Development
- 3. A Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing Lean Software Development
- 4. Practical Tools for Lean Implementation
- 5. Common Pitfalls When Applying Lean (and How to Avoid Them)
- 6. Benefits of Lean Software Development
- Conclusion
1. Understanding Lean Software Development
Lean software development is a methodology that encourages organizations to reduce inefficiencies in software production. By emphasizing customer value, continuous learning, and fast delivery, LSD aligns technical practices with business goals. It minimizes resource waste, promotes transparency, and empowers teams to own and optimize their work. While inspired by manufacturing, lean adapts seamlessly to dynamic environments like software.
Read more: Lean Software Development: Principles, Benefits, and Implementation in 2025
2. Core Principles of Lean Software Development
Before diving into execution, it’s useful to review the foundational principles of lean software development. Each serves as a cornerstone for implementation:
Eliminate Waste: Remove anything that does not directly contribute to delivering value to the customer. This includes unused code, extra features, or inefficient handovers. Teams must regularly assess their workflow and eliminate practices that do not support the end-user’s needs.
Build Quality In: Shift left by integrating quality assurance into every development phase rather than treating it as an afterthought. This includes automated testing, code reviews, and continuous integration to catch issues early and frequently.
Create Knowledge: Embrace an iterative process where learning is constant. Teams test assumptions early through prototypes or MVPs, gather user feedback, and adjust accordingly. Knowledge documentation and cross-functional learning sessions are vital.
Defer Commitment: Avoid locking in decisions too early. Instead, delay important choices until the last responsible moment, allowing flexibility based on new data or feedback. This reduces rework and enhances decision quality.
Deliver Fast: Optimize for speed by reducing batch sizes, increasing automation, and continuously improving cycle time. Quick delivery encourages frequent user feedback and minimizes the time between idea and impact.
Respect People: Empower teams, encourage collaboration, and foster a culture of trust. Recognizing the value each person brings and giving them autonomy fosters innovation and accountability.
Optimize the Whole: Consider the end-to-end system, not just individual components. Improving local efficiency is meaningless if it creates bottlenecks elsewhere. Optimize entire value streams to maximize customer value.
Each of these principles interconnects, forming a cohesive philosophy for efficient, customer-focused software development.
3. A Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing Lean Software Development
Step 1: Identify Waste in Your Current Workflow
Conduct a lean audit using value stream mapping. Involve the team in identifying bottlenecks and delays. Common examples include:
Unclear requirements often result in rework. Clarify specifications early through user stories and examples. Long feedback loops delay course corrections. Introduce shorter sprints or continuous review practices. Feature bloat means investing in functionalities that users don’t need. Prioritize features with real user value. Work in progress (WIP) leads to task switching and context loss. Use WIP limits to encourage focus. Redundant handoffs between departments waste time. Cross-functional teams can eliminate unnecessary coordination layers.
Step 2: Define Customer-Centric Value
Use interviews, surveys, and analytics to understand your users. Don’t guess, ask. Define success through the lens of user impact, not just delivery milestones. Align team efforts to user journeys, ensuring every feature serves a purpose.
Step 3: Restructure into Cross-Functional Teams
Dismantle silos by forming autonomous, cross-functional teams. Each team should include members from product, engineering, QA, and operations. Foster a shared understanding of goals and accountability. Standups and retrospectives help maintain alignment.
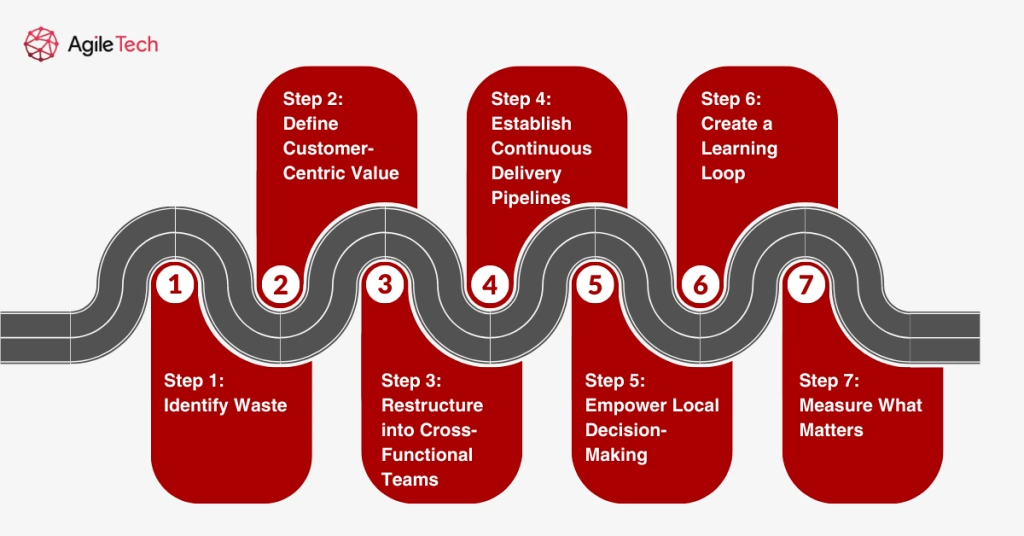
Step 4: Establish Continuous Delivery Pipelines
Automate the path from code to production. Begin with CI tools like Jenkins or GitHub Actions, and progress toward full CD. This improves release frequency and reduces manual error. Focus on small, safe, frequent deployments.
Step 5: Empower Local Decision-Making
Encourage developers and teams to make decisions about their work. Provide guardrails such as architectural principles, but avoid micromanagement. Clear goals and trust in execution foster ownership and speed.
Step 6: Create a Learning Loop
Install mechanisms for continuous improvement. These include retrospectives, post-mortems, and daily syncs. When an issue arises, use tools like the 5 Whys to uncover root causes. Share findings in a transparent knowledge base.
Step 7: Visualize Work and Limit WIP
Use Kanban boards or digital equivalents (e.g., Jira, Trello) to visualize workflow. Set limits on WIP to prevent multitasking and promote completion. Visual status boosts accountability and coordination.
Step 8: Measure What Matters
Track lean-relevant KPIs like:
- Cycle Time: Time from task start to completion
- Lead Time: Total time from idea to release
- Throughput: Completed units over time
- Deployment Frequency: How often code is shipped
- Change Failure Rate: Percentage of deployments causing failure. Use this data to guide improvements, not as blunt performance tools.
4. Practical Tools for Lean Implementation
To reinforce lean principles, integrate the following tools into your development process:
- Version Control: GitHub, GitLab – Manage code collaboratively and transparently.
- CI/CD Automation: Jenkins, GitHub Actions, CircleCI – Enable fast, reliable delivery.
- Project Management: Jira, Trello, Notion – Organize tasks and track WIP.
- Monitoring & Logging: Datadog, Prometheus, Sentry – Improve observability and response.
- Team Collaboration: Slack, Confluence, Miro – Support asynchronous communication and documentation.
The right tooling reduces friction and supports transparency, speed, and collaboration.
Read more: Top 14 Software Development Tools in 2025: A Comprehensive Guide
5. Common Pitfalls When Applying Lean (and How to Avoid Them)
Misidentifying Waste
Not all non-coding activities are wasteful. Strategic planning, design thinking, or user research adds essential value. Clearly define what constitutes waste and involve the team in assessments.
Over-Standardization
Too many rules stifle innovation. Frameworks should offer guidance, not rigidity. Leave space for team discretion and adaptation.
Chasing the Wrong Metrics
Measuring velocity without context can mislead teams. Prioritize metrics like cycle time or customer feedback instead. Tie all metrics to customer value.
Undervaluing Culture
Process cannot substitute culture. A team without psychological safety will not embrace experimentation. Invest in trust, collaboration, and recognition.
Neglecting Continuous Feedback
Skipping retrospectives, ignoring user input, or delaying testing breaks the lean cycle. Implement frequent, low-friction feedback loops across stakeholders.
6. Benefits of Lean Software Development
- Faster Time-to-Market: Small, frequent releases shorten the path from idea to impact.
- Improved Product Quality: Continuous testing and iteration reduce defects.
- Lower Development Costs: Focusing on essential features reduces overhead.
- Enhanced User Alignment: Frequent feedback ensures solutions meet real needs.
- Stronger Teams: Autonomy and shared goals increase satisfaction and performance.
Conclusion
Lean software development isn’t just about tools or frameworks, it’s a mindset that prioritizes continuous learning, team empowerment, and customer-centric delivery. By eliminating waste, building quality into every step, and focusing on iterative improvement, teams can unlock greater agility and innovation.
At AgileTech, we specialize in helping companies implement lean software practices at every stage of the development lifecycle. Whether you need coaching, pipeline setup, or custom development, our experts are ready to support your journey.