Best Languages for Mobile App Development: Updated Guide for 2025
Choosing the right programming language is crucial to building a successful mobile app. With hundreds of languages available, it can be overwhelming to decide which one fits your app’s purpose, performance, and platform. In this updated guide, we explore the top 10 programming languages for mobile app development, each with strengths and real-world applications to help you build high-performance, cross-platform, or native apps.

1. JavaScript
Overview: JavaScript is one of the most widely used languages for web and hybrid mobile app development. It’s particularly powerful when combined with frameworks like React Native, Ionic, and Apache Cordova. As mobile and web increasingly converge, JavaScript continues to play a central role in cross-platform development.
Pros:
- Enables cross-platform development
- Supported by a large community and extensive libraries
- Works on both client and server sides
- Highly flexible for UI/UX development
Use Cases: Progressive Web Apps (PWAs), hybrid mobile apps, UI-rich applications, real-time apps (chat, collaboration tools)
Popular Apps: Facebook (React Native), Instagram, Uber, Discord
Best Frameworks: React Native, Ionic, Apache Cordova, NativeScript
Developer Insight: JavaScript enables fast prototyping and is ideal for startups needing quick MVP validation. With tools like Expo, you can build and deploy apps without touching native code.
Conclusion: JavaScript is a top choice for fast development cycles and cross-platform solutions, especially for apps where time-to-market and web integration are crucial.
2. Kotlin
Overview: Kotlin is the official programming language for Android development, replacing Java as the preferred choice by Google. Its concise syntax, null safety, and seamless Java interoperability have made it a favorite among Android developers worldwide.
Pros:
- Interoperable with Java libraries
- Safer code (null-safety and immutability)
- More concise than Java, reducing boilerplate
- Backed by JetBrains and Google
Use Cases: Android apps, backend services (via Ktor), modernizing legacy Java code, Jetpack Compose development
Popular Apps: Trello, Evernote, Coursera, Pinterest, Netflix (Android)
Best Tools: Android Studio, Ktor, Kotlin Multiplatform
Developer Insight: Kotlin is well-suited for teams looking to reduce technical debt while leveraging existing Java assets. It also supports functional programming patterns.
Conclusion: Kotlin is ideal for modern Android development, offering better readability, safety, and support for future Android SDKs.
3. Swift
Overview: Swift is Apple’s official language for iOS, iPadOS, watchOS, and macOS development. Designed to be safe, fast, and expressive, Swift has quickly replaced Objective-C as the go-to language for Apple ecosystems.
Pros:
- Cleaner and more readable than Objective-C
- Memory-safe and type-safe
- Actively maintained by Apple
- Interoperable with Objective-C codebases
Use Cases: Native iOS apps, iPad apps, Watch apps, macOS tools, augmented reality apps with ARKit
Popular Apps: Lyft, LinkedIn, Slack (iOS), Airbnb, Khan Academy
Best Tools: Xcode, Swift Playgrounds, ARKit, Core ML
Developer Insight: Swift is performance-oriented and easy to learn, making it accessible for both new developers and experienced Objective-C coders.
Conclusion: Swift is the go-to language for building high-performance, scalable, and secure iOS applications.
Read more: Top Benefits of Mobile Application Development Businesses Should Know
4. Dart
Overview: Dart is the language behind Google’s Flutter framework, which has taken the cross-platform app development world by storm. Dart focuses on UI creation, speed, and developer productivity, allowing a single codebase to serve Android, iOS, web, and desktop platforms.
Pros:
- Compiles to native ARM and JavaScript
- Supports hot reload for rapid iteration
- UI-centric programming model
- Excellent tooling and documentation
Use Cases: Cross-platform apps, real-time apps, admin dashboards, lightweight games
Popular Apps: Google Ads, Reflectly, Alibaba, eBay Motors
Best Tools: Flutter SDK, DartPad, Firebase + Flutter
Developer Insight: Flutter’s widget system lets developers create pixel-perfect UIs that look native on every platform. Dart’s learning curve is low for those familiar with JavaScript or Java.
Conclusion: Dart with Flutter is ideal for teams aiming for rapid development, beautiful UI, and seamless deployment across multiple platforms.
5. Java
Overview: Java has been the cornerstone of Android development for over a decade. While it’s been somewhat eclipsed by Kotlin, it remains vital due to its widespread usage, large ecosystem, and enterprise support.
Pros:
- Mature and stable
- Cross-platform capabilities with JVM
- Huge community and libraries
- Strong OOP foundation
Use Cases: Android apps, backend services, enterprise apps, IoT, large-scale mobile systems
Popular Apps: Twitter (early), Spotify, Signal, Uber (backend)
Best Tools: Android Studio, Spring Boot, Apache libraries
Developer Insight: Java is often the default for enterprise Android apps and legacy codebases. Developers also leverage Java for backend systems supporting mobile apps.
Conclusion: Java remains relevant for Android and enterprise mobile apps, especially in complex systems requiring scalability and security.
Read more: 10 Best Programming Languages for Website Development
6. C#
Overview: C# is a modern, object-oriented programming language developed by Microsoft. With Xamarin and .NET MAUI, C# enables cross-platform mobile development with native performance.
Pros:
- Easy to read and maintain
- Native UI and hardware access via Xamarin
- Excellent IDE support (Visual Studio)
- Strong corporate support
Use Cases: Cross-platform apps, enterprise apps, mobile games (Unity)
Popular Apps: Storyo, Alaska Airlines, MRW Courier, UPS Mobile
Best Tools: Xamarin, .NET MAUI, Unity3D, Visual Studio
Developer Insight: C# is ideal for businesses using Microsoft Azure or needing apps for multiple platforms with shared code.
Conclusion: With strong tooling and enterprise capabilities, C# is a strategic choice for companies building cross-platform business or gaming apps.
7. Python
Overview: Python is rarely used to build native mobile apps but is widely adopted for backend development, data science, and automation. With frameworks like Kivy and BeeWare, Python can also be used for mobile front-end development.
Pros:
- Fast prototyping and development
- Huge library ecosystem
- Excellent for AI/ML integration
Use Cases: Backend APIs, AI-powered apps, mobile MVPs, automation scripts
Popular Apps: Instagram (backend), Reddit, Spotify (backend)
Best Tools: Django, Flask, Kivy, BeeWare, Chaquopy
Developer Insight: Python is unbeatable for startups building MVPs with AI or data analytics integration. It’s not ideal for production-level native mobile UIs, but great for the backend layer.
Conclusion: Python is powerful for backend services and prototyping, especially for data-driven mobile applications.
8. TypeScript
Overview: TypeScript brings static typing to JavaScript, improving code maintainability and developer productivity. It’s increasingly popular for mobile apps built with React Native or Ionic.
Pros:
- Adds strong typing and interfaces
- Scales better than plain JavaScript
- Supported by major JS frameworks
Use Cases: Cross-platform mobile apps, PWAs, large codebases
Popular Apps: Asana, Slack (web), Visual Studio Code
Best Tools: React Native, Ionic, Expo
Developer Insight: TypeScript reduces bugs in large-scale apps and improves IDE support, making it a safer option for long-term projects.
Conclusion: TypeScript is the smart evolution of JavaScript for mobile app teams looking for scale and reliability.
9. C++
Overview: C++ offers low-level memory control and high performance, making it a common choice in gaming and system-level mobile applications.
Pros:
- Extremely fast and powerful
- Ideal for graphics and heavy processing
- Portable across platforms
Use Cases: Game engines, embedded systems, high-performance apps
Popular Apps: Photoshop, PayPal, Google Chrome
Best Tools: Unreal Engine, Android NDK, Qt
Developer Insight: C++ is best for teams with expertise in systems programming or when integrating performance-critical components in mobile apps.
Conclusion: C++ is essential for performance-intensive mobile apps, especially games and rendering engines.
10. Ruby
Overview: Ruby is a dynamic, open-source language best known for its elegant syntax and the Ruby on Rails framework. While not used for mobile front-ends, Ruby excels in backend development and rapid prototyping.
Pros:
- Developer-friendly syntax
- Rapid development
- Mature web frameworks
Use Cases: Backend APIs, admin tools, mobile dashboards
Popular Apps: Airbnb, GitHub, Shopify
Best Tools: Ruby on Rails, Sinatra, Grape
Developer Insight: Ruby is ideal for startups building fast, scalable backends to support mobile apps.
Conclusion: Ruby accelerates backend development and remains a great choice for mobile-supporting services.
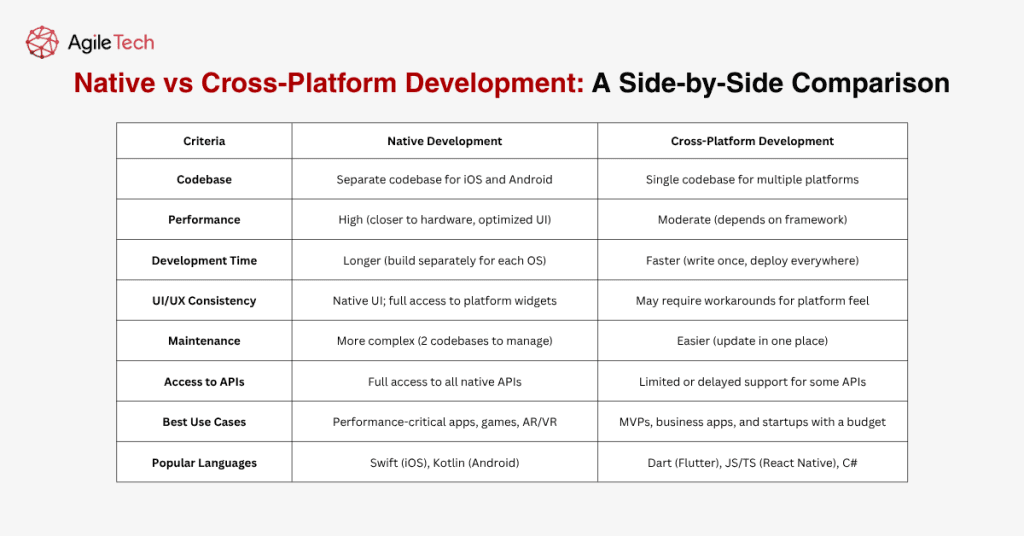
Conclusion
The mobile app development world is vast and dynamic. Your choice of programming language can shape your app’s performance, time-to-market, and maintainability. Native apps benefit from Swift (iOS) or Kotlin (Android), while cross-platform solutions thrive on Flutter (Dart), React Native (JavaScript/TypeScript), or Xamarin (.NET/C#).
When deciding, consider:
- Ecosystem and libraries
- Target platform(s)
- Performance requirements
- Developer expertise