How Much Does Telemedicine App Development Cost in 2025
The telemedicine industry has experienced unprecedented growth, with the global market projected to reach $659.8 billion by 2025. As healthcare organizations increasingly embrace digital transformation, understanding telemedicine app development cost becomes crucial for making informed investment decisions. Whether you’re a startup healthcare provider or an established medical institution working with telemedicine software providers, this comprehensive guide will help you navigate the complex landscape of telemedicine software development pricing.
From basic consultation platforms to enterprise-grade solutions with AI integration, telehealth app development varies significantly in complexity and cost. The investment required can range from $50,000 for a minimum viable product (MVP) to over $500,000 for a comprehensive enterprise solution. However, the exact telemedicine app development cost depends on numerous factors that we’ll explore in detail throughout this guide.
1. What is Telemedicine App Development
Telemedicine app development involves creating digital platforms that enable remote healthcare delivery through technology. These applications facilitate virtual consultations, remote patient monitoring, and seamless communication between healthcare providers and patients, eliminating geographical barriers and improving healthcare accessibility.
Modern telemedicine solutions integrate various technologies, including video conferencing, secure messaging, electronic health records (EHR), payment processing, and advanced analytics. The telemedicine software development process requires specialized expertise in healthcare regulations, data security, and user experience design tailored for medical environments.
Read more: What is emar in healthcare
1.1. Types of Telemedicine Applications
Synchronous Telemedicine Apps: Real-time communication platforms enabling live video consultations, instant messaging, and immediate medical guidance. Popular examples include Teladoc, Amwell, and Doctor on Demand. These telehealth software applications typically cost between $70,000 to $150,000 to develop, depending on feature complexity and integration requirements with various telemedicine software providers.
Asynchronous Telemedicine Solutions: Store-and-forward applications allow patients to submit medical information, photos, or symptoms for later review by healthcare providers. Solutions like 98point6 and HeyDoctor fall into this category, with telehealth app development costs ranging from $70,000 to $120,000.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) Apps: Comprehensive platforms that collect and analyze patient data from wearable devices and smart health monitors. Examples include Livongo and Omada Health, with telemedicine software development costs typically ranging from $90,000 to $200,000 due to complex integrations with IoT devices and advanced analytics requirements.
Hybrid Solutions: Modern telemedicine platforms often combine multiple approaches, offering both synchronous and asynchronous capabilities along with monitoring features. These comprehensive telehealth software solutions provide the most value but require higher initial investments, typically starting at $150,000.
1.2. Core Features and Functionalities
Patient-Facing Features: Essential patient features include user registration and profile management, doctor discovery and filtering, appointment scheduling, secure video calling, text messaging, prescription management, payment processing, and medical history access. These core features typically require 280-350 development hours in telemedicine software development.
Provider-Facing Features: Healthcare provider functionality encompasses comprehensive dashboards, patient management systems, appointment calendars, clinical documentation tools, prescription writing capabilities, billing integration, and reporting analytics. Provider-side features generally require 240-300 development hours due to their complexity in telehealth app development.
Administrative Features: Backend administrative capabilities include user management, content management systems, analytics dashboards, compliance monitoring, billing management, and system configuration tools. Administrative features typically add 150-200 development hours to the telemedicine app development cost project scope.
2. Key Cost-Influencing Factors
Understanding the factors that influence telemedicine app development cost is essential for accurate budget planning. These factors can significantly impact the final investment required, sometimes doubling or tripling initial estimates if not properly considered when working with telemedicine software providers.
2.1. Platform, Features and Design Complexity
Platform Selection Impact: Native iOS and Android development requires separate codebases, potentially costing $100,000 to $250,000 per platform. Cross-platform telehealth app development using React Native or Flutter can reduce costs by up to 50% while maintaining near-native performance. Web-based solutions offer the most economical approach but may have limitations in functionality.
Feature Complexity Levels: Basic features like user authentication and profile management require 10-15 hours each, while complex features like real-time video conferencing can take 70+ hours. Advanced AI-powered features such as symptom checkers or diagnostic assistance can add 100-200 development hours and $15,000 to $70,000 to the total telemedicine software development cost.
UI/UX Design Investment: Custom design tailored to healthcare environments typically costs $20,000 to $50,000, while basic template-based designs range from $10,000 to $20,000. Healthcare applications require specialized design considerations for accessibility, clinical workflows, and regulatory compliance, justifying higher design investments in telehealth software.
Accessibility and Compliance Design: Healthcare applications must comply with accessibility standards (WCAG 2.1) and provide interfaces suitable for users with disabilities. This specialized design work can add $5,000 to $15,000 to the telemedicine app development cost, but is essential for regulatory compliance and inclusive healthcare delivery.
2.2. Technology Stack and Integration
Backend Infrastructure Choices: Cloud-based solutions using AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud provide scalability but involve ongoing operational costs. The choice between serverless architecture, microservices, or monolithic approaches affects both development time and long-term maintenance costs. Enterprise-grade backend solutions typically add $20,000 to $50,000 to telemedicine software development costs.
Database and Storage Solutions: Healthcare applications require robust, secure database solutions capable of handling sensitive patient data. HIPAA-compliant database configurations, backup systems, and disaster recovery capabilities can add $10,000 to $25,000 to infrastructure costs when working with telemedicine software providers.
Third-Party Service Integrations: Basic integrations with payment gateways, email services, and scheduling systems cost $10,000 to $30,000. Complex integrations with EHR systems, laboratory information systems, or medical devices can range from $30,000 to $100,000, depending on the number and complexity of integrations required in telehealth app development.
API Development and Management: Custom API development for connecting various healthcare systems, supporting mobile applications, and enabling third-party integrations typically requires 200-400 development hours, adding $10,000 to $40,000 to telehealth software project costs.
2.3. Team Location and Development Model
Geographic Cost Variations: Development costs vary significantly based on team location. North American developers charge $60-$150 per hour, Western European developers $50-$120 per hour, while Eastern European telemedicine software providers offer competitive rates of $50-$95 per hour with high-quality deliverables.
Team Composition Requirements: A typical telemedicine software development team includes project managers, business analysts, solution architects, UI/UX designers, frontend and backend developers, QA engineers, and DevOps specialists. Team sizes can range from 5-8 professionals for simple projects to 12-15+ for enterprise solutions.
Development Model Choices: In-house development provides maximum control but requires significant upfront investment in talent acquisition and infrastructure. Outsourcing to telemedicine software providers offers cost savings and specialized expertise, while hybrid models combine the benefits of both approaches. Staff augmentation allows flexible team scaling based on project phases.
Communication and Management Overhead: Remote development teams require additional project management and communication overhead, typically adding 10-15% to total telemedicine app development cost. However, this investment ensures smooth collaboration and project success.
2.4. Compliance and Security Requirements
Regulatory Compliance Costs: HIPAA compliance implementation typically costs $10,000 to $30,000, including security assessments, policy development, and technical implementations. GDPR compliance for European markets adds another $5,000 to $15,000. FDA regulations for diagnostic features can significantly increase telemedicine software development costs and development timelines.
Security Implementation: Essential security measures include end-to-end encryption, two-factor authentication, biometric authentication, role-based access controls, secure data transmission protocols, and secure cloud storage. Comprehensive security implementation typically adds $15,000 to $40,000 to telehealth app development costs.
Audit and Certification Processes: Third-party security audits and compliance certifications can cost $10,000 to $25,000, but are essential for healthcare applications. These certifications provide credibility and may be required for partnerships with healthcare institutions and telemedicine software providers.
Ongoing Compliance Maintenance: Compliance is not a one-time cost but requires ongoing maintenance, monitoring, and updates. Annual compliance maintenance typically costs 10-20% of the initial compliance implementation investment in telehealth software.
3. Cost Breakdown by App Complexity
Understanding cost ranges based on application complexity helps in realistic budget planning and feature prioritization. Each complexity level serves different market needs and organizational requirements when working with telemedicine software providers.
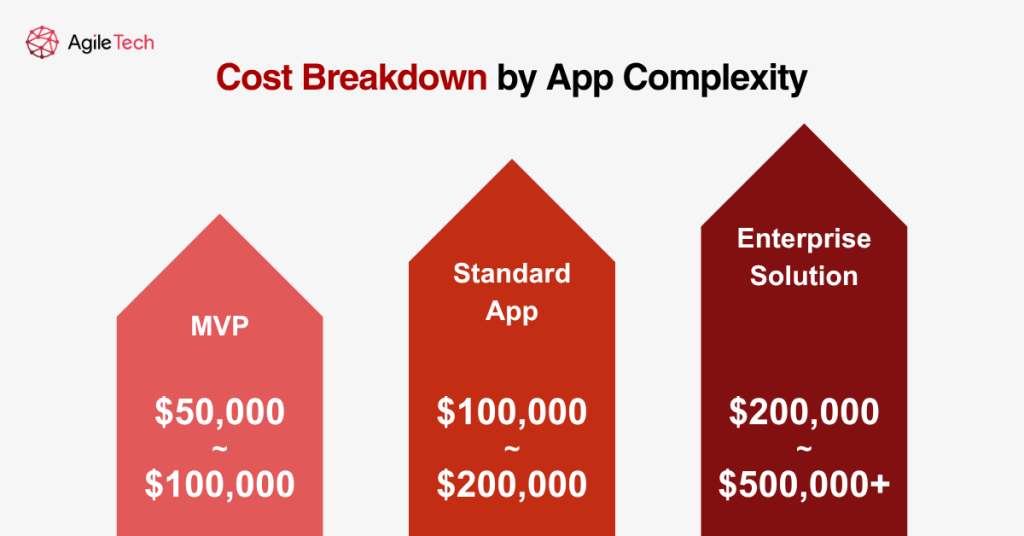
3.1. MVP ($50,000 – $100,000)
MVP Feature Set: A minimum viable product includes essential features such as user registration, basic profile management, simple appointment scheduling, basic video calling, text messaging, and fundamental security measures. MVP development typically requires 800-1,200 development hours in telemedicine app development cost planning.
MVP Benefits and Limitations: MVPs allow rapid market entry and user feedback collection while minimizing initial investment. However, they may lack advanced features needed for comprehensive healthcare delivery and may require significant additional investment for scaling with telemedicine software providers.
MVP Timeline: MVP development typically takes 3-6 months, depending on team size and feature complexity. This rapid telehealth app development approach allows for quick market validation and iterative improvement based on user feedback.
When to Choose MVP: The MVP approach is ideal for startups, proof-of-concept projects, or organizations wanting to test market demand before major investments in telemedicine software development. It’s also suitable for niche healthcare specialties with specific, limited requirements.
3.2. Standard App ($100,000 – $200,000)
Standard App Features: Standard applications include comprehensive patient and provider portals, advanced scheduling systems, integrated payment processing, basic EHR integration, prescription management, multi-platform support, and enhanced security features. Development typically requires 1,200-2,000 hours in telehealth software creation.
Target Market: Standard telemedicine apps serve small to medium healthcare practices, specialty clinics, and regional healthcare networks. They provide sufficient functionality for most routine healthcare delivery scenarios while remaining cost-effective when working with telemedicine software providers.
Scalability Considerations: Standard applications are designed to handle moderate user loads and can typically support 1,000-10,000 active users. They include basic scalability features but may require upgrades for significant growth in telemedicine app development cost planning.
Integration Capabilities: Standard apps support integration with popular EHR systems, payment processors, and basic third-party services. However, complex enterprise integrations may require additional development work with specialized telehealth software providers.
3.3. Enterprise Solution ($200,000 – $500,000+)
Enterprise Feature Set: Enterprise solutions include advanced analytics and reporting, AI-powered features, comprehensive EHR integration, multi-location support, advanced security and compliance features, custom workflows, API management, and extensive third-party integrations with multiple telemedicine software providers.
Scalability and Performance: Enterprise applications are designed to handle large user bases (10,000+ concurrent users), multiple healthcare facilities, and complex organizational hierarchies. They include advanced performance optimization, load balancing, and disaster recovery capabilities in telehealth app development.
Advanced Integration Requirements: Enterprise solutions require integration with existing hospital information systems, laboratory systems, imaging systems, billing platforms, and insurance networks. These complex integrations often account for 30-40% of total telemedicine software development costs.
Customization and Flexibility: Enterprise applications offer extensive customization options, configurable workflows, white-label capabilities, and API access for third-party developers. This flexibility requires additional architecture and development investment in telehealth software solutions.
Read more: Medical billing software prices
4. Feature Development Costs
Breaking down development costs by individual features helps in prioritizing functionality and managing budgets effectively when working with telemedicine software providers. Feature costs vary based on complexity, integration requirements, and security considerations.
4.1. Patient and Doctor Core Features
User Authentication and Management: Secure user registration, login systems, password recovery, and profile management typically require 120 development hours, costing approximately $6,000-$12,000. Healthcare applications require enhanced security measures, adding complexity to basic authentication systems in telemedicine app development cost calculations.
Appointment Scheduling System: Comprehensive scheduling functionality, including calendar integration, availability management, automated reminders, and rescheduling capabilities, requires 300 development hours, costing $15,000-$30,000. Advanced scheduling with multi-provider coordination adds additional complexity in telehealth software development.
Video Conferencing Integration: Real-time video communication with screen sharing, recording capabilities, and mobile optimization requires 420 development hours, costing $21,000-$42,000. Healthcare-specific features like vital sign integration during calls increase development requirements when working with telemedicine software providers.
Electronic Health Records Integration: Basic EHR integration for viewing and updating patient records requires 100-200 development hours, costing $5,000-$20,000. Comprehensive integration with multiple EHR systems can cost $30,000-$80,000, depending on the number and complexity of systems involved in telehealth app development.
Payment Processing System: Secure payment integration with insurance claim processing, copay collection, and financial reporting requires 150-200 development hours, costing $7,500-$20,000. Healthcare-specific billing requirements and insurance integrations add complexity to telemedicine software development.
4.2. Advanced Features and Integrations
AI-Powered Symptom Checker: Artificial intelligence features for symptom analysis and preliminary diagnosis require specialized expertise and extensive testing. Development costs range from $25,000-$75,000, including AI model training, integration, and compliance considerations in telehealth software solutions.
Remote Patient Monitoring Integration: Integration with wearable devices, IoT sensors, and health monitoring equipment requires 200-400 development hours, costing $20,000-$60,000. Real-time data processing and alert systems add additional complexity to telemedicine app development cost planning.
Prescription Management System: Electronic prescribing capabilities with drug interaction checking, pharmacy integration, and regulatory compliance require 250-350 development hours, costing $15,000-$35,000. Integration with prescription databases and pharmacy networks increases costs when working with telemedicine software providers.
Advanced Analytics and Reporting: Comprehensive analytics dashboards, clinical reporting, and business intelligence features require 300-500 development hours, costing $20,000-$50,000. Custom reporting requirements and data visualization add complexity to telehealth app development.
Multi-language and Localization: Supporting multiple languages and regional healthcare requirements requires 100-200 development hours per language, costing $5,000-$15,000 per language. Healthcare terminology translation requires specialized medical translation services in telemedicine software development.
5. Hidden Costs and Long-term Considerations
5.1. Compliance, Testing and Marketing
Regulatory Compliance auditing: Third-party compliance audits, penetration testing, and certification processes cost $15,000-$40,000 annually. These ongoing expenses are essential for maintaining healthcare industry credibility and regulatory compliance in telehealth software operations.
Quality Assurance and Testing: Comprehensive testing, including functional testing, security testing, performance testing, and user acceptance testing, typically costs 20-30% of development costs. Healthcare applications require additional clinical workflow testing and validation in telemedicine app development cost planning.
Marketing and User Acquisition: Digital marketing campaigns, content creation, SEO optimization, and user acquisition programs typically cost $50,000-$200,000 annually. Healthcare marketing requires specialized compliance knowledge and longer sales cycles when promoting telemedicine software solutions.
Training and Change Management: Staff training programs, user documentation, and change management initiatives cost $10,000-$50,000, depending on organization size. Healthcare providers require extensive training on new technologies and workflows from telemedicine software providers.
5.2. Maintenance and Updates
Ongoing Maintenance Costs: Annual maintenance typically costs 15-25% of initial development investment, covering bug fixes, security updates, performance optimization, and minor feature enhancements. Healthcare applications require more frequent updates due to regulatory changes in telehealth app development.
Infrastructure and Hosting: Cloud hosting costs for healthcare applications range from $2,000-$20,000 monthly, depending on user base and data storage requirements. HIPAA-compliant hosting solutions command premium pricing but are essential for telemedicine software development applications.
Third-party Service Costs: Ongoing costs for third-party services, including video conferencing APIs, payment processing, SMS services, and integrations, typically range from $1,000-$10,000 monthly. These costs scale with usage and user base growth in telehealth software solutions.
Security Monitoring and Updates: Continuous security monitoring, vulnerability assessments, and security updates cost $5,000-$20,000 annually. Healthcare applications require enhanced security monitoring due to sensitive data handling requirements when working with telemedicine software providers.
6. Cost Optimization Strategies
Smart cost optimization strategies can significantly reduce development expenses while maintaining quality and functionality. These approaches help organizations maximize return on investment and achieve sustainable growth in telemedicine app development cost management.
6.1. MVP Approach and Outsourcing
Phased Development Strategy: Implementing a phased development approach allows organizations to spread costs over time while generating revenue from early phases. Start with core functionality and gradually add advanced features based on user feedback and business growth in telehealth app development.
Offshore Development Benefits: Partnering with reputable offshore telemedicine software providers can reduce costs by 40-60% while maintaining quality. Eastern European and South American development teams offer excellent technical expertise at competitive rates.
Open Source Integration: Leveraging open-source technologies and frameworks can reduce development time and costs. However, healthcare applications require careful evaluation of open-source components for security and compliance considerations in telemedicine software development.
Code Reusability and Standardization: Implementing standardized development practices, reusable components, and modular architecture reduces long-term maintenance costs and enables faster feature development for future enhancements in telehealth software solutions.
6.2. ROI and Revenue Models
Subscription-Based Revenue: Monthly or annual subscription models provide predictable revenue streams while distributing costs over time. Typical healthcare SaaS applications charge $50-$500 per provider per month, depending on features and user base, when working with telemedicine software providers.
Transaction-Based Revenue: Per-consultation or per-transaction pricing models align costs with usage and can generate significant revenue. Transaction fees typically range from 2-8% of consultation fees, depending on payment processing and platform features in telehealth app development.
Freemium Models: Offering basic functionality for free while charging for premium features can accelerate user acquisition. However, healthcare applications must carefully balance free features with premium offerings to ensure sustainable business models in telemedicine software development.
Enterprise Licensing: Large healthcare organizations often prefer enterprise licensing models with annual contracts ranging from $50,000-$500,000+. These models provide predictable revenue while offering comprehensive feature access through telemedicine software providers.
ROI Timeline Expectations: Well-executed telemedicine applications typically achieve break-even within 18-36 months, depending on market adoption, pricing strategy, and operational efficiency. Revenue growth of 100-300% annually is common for successful healthcare technology companies utilizing effective telehealth software solutions.
Conclusion
Telemedicine app development cost in 2025 ranges from $50,000 for MVP solutions to over $500,000 for enterprise platforms. Key factors influencing costs include platform complexity, regulatory compliance, team location, and feature requirements when selecting telemedicine software providers.
Success lies in balancing functionality with budget constraints. Starting with an MVP approach enables market validation while minimizing risk, allowing organizations to scale based on user feedback and business growth in telehealth app development. With proper planning and experienced telemedicine software development teams, telemedicine investments typically achieve break-even within 18-36 months, positioning healthcare organizations for long-term success in digital healthcare delivery through comprehensive telehealth software solutions.