How To Build a GPS Tracking System For Fleet Management
Building a GPS tracking system for fleet management means understanding complex technologies, industry trends, and strategic implementation. Whether you manage a logistics company, delivery service, or transportation business, developing a reliable GPS tracker is crucial for operational efficiency, safety, and regulatory compliance.

If you’re wondering how to build a GPS tracking system that delivers real value, this comprehensive guide will walk you through every essential step.
We’ll explore the underlying technology, emerging trends, integration with IoT, key features, development procedures, and practical insights to help you create a GPS tracking system tailored to your fleet needs. Let’s begin by understanding the core technological landscape shaping vehicle tracking.
The Technology Behind GPS-Based Vehicle Tracking Systems
At the heart of every effective fleet management solution is a robust GPS technology foundation. The core components involve satellites, positioning algorithms, communication networks, and software systems. Understanding these elements is essential for designing a system that’s accurate, reliable, and scalable.
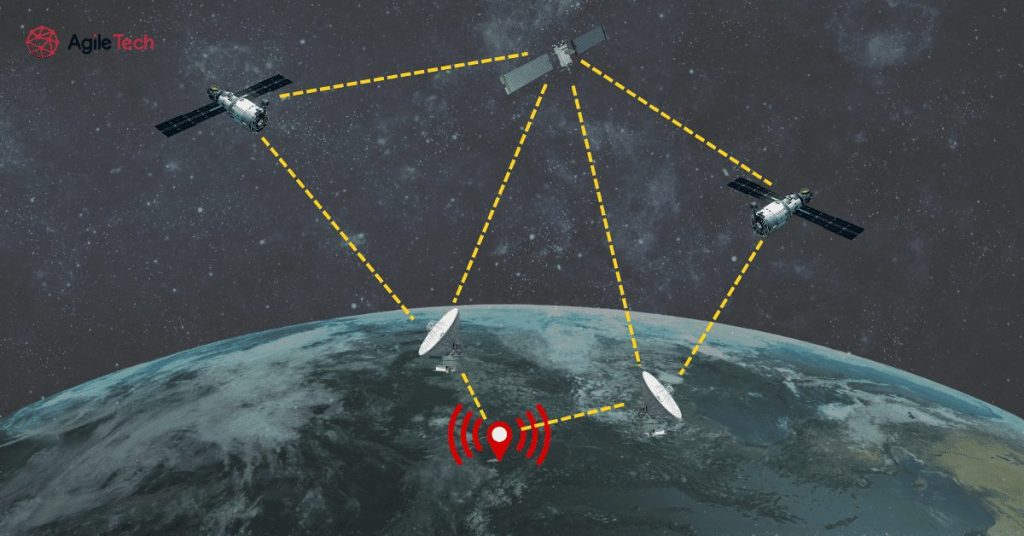
A GPS tracker works by receiving signals from multiple satellites orbiting Earth. Using advanced trilateration techniques, it calculates precise location coordinates. These coordinates are then transmitted to a central server via wireless communication channels like cellular networks or satellite communication. This real-time data forms the backbone of your entire fleet management system, providing insights into vehicle positions, routes, and operational status.
Much of the technology involved in building a GPS tracking system hinges on selecting the right hardware and communication protocols. For instance, integrating a high-quality GPS module ensures precise location detection, while choosing reliable cellular modules—such as 4G LTE or emerging 5G technology—guarantees consistent data transmission. Security protocols are also paramount, especially when dealing with sensitive fleet data, which means you need encryption standards and secure communication channels.
Furthermore, to create a scalable system, it’s vital to develop or adopt backend architectures that can handle massive data streams efficiently. Cloud-based solutions can facilitate scalable, secure, and AI-driven data processing, which is instrumental in offering advanced features like predictive analytics and automated alerts.
Emerging Trends Redefining Vehicle Tracking
The landscape of vehicle tracking is constantly evolving thanks to technological advancements and shifting industry needs. Here are the key trends transforming traditional GPS solutions into smarter, more adaptive systems:
- AI-driven analytics and machine learning: These technologies predict vehicle maintenance needs and analyze driver behavior patterns, which reduces costs and improves safety. Real-time data processing enables fleet managers to optimize routes dynamically, reducing fuel consumption and ensuring timely deliveries. This shifts the focus from mere location tracking to proactive fleet management.
- Big Data analytics integration: Advanced data processing capabilities allow you to analyze massive amounts of fleet data in real-time. This means better decision-making based on current conditions rather than historical reports, leading to more efficient operations and reduced operational costs.
- Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity: Vehicle sensors, telematics devices, and environmental monitors now work seamlessly with GPS systems. This integration allows for touchless fleet management, enabling systems to automatically alert for issues like unauthorized usage or mechanical failures. As companies seek compliance with regulations like Hours of Service (HOS), these integrated systems further enhance compliance monitoring and reporting.
- Blockchain for secure data sharing: This emerging technology provides secure and transparent data sharing, especially relevant in industries with high compliance needs like logistics or pharmaceuticals. Blockchain ensures data integrity and creates tamper-proof records of vehicle movements and conditions.
These innovations are fundamentally changing how fleet management systems are built, kept secure, and leveraged for maximum ROI.
How Can IoT and GPS Tracking Go Hand in Hand?
The Internet of Things creates a powerful synergy with GPS technology by connecting vehicles, sensors, and management systems into a unified network. IoT enhances the capability of GPS by providing additional data points like vehicle health, fuel levels, cargo conditions, and driver activity, enabling a comprehensive view of fleet operations.
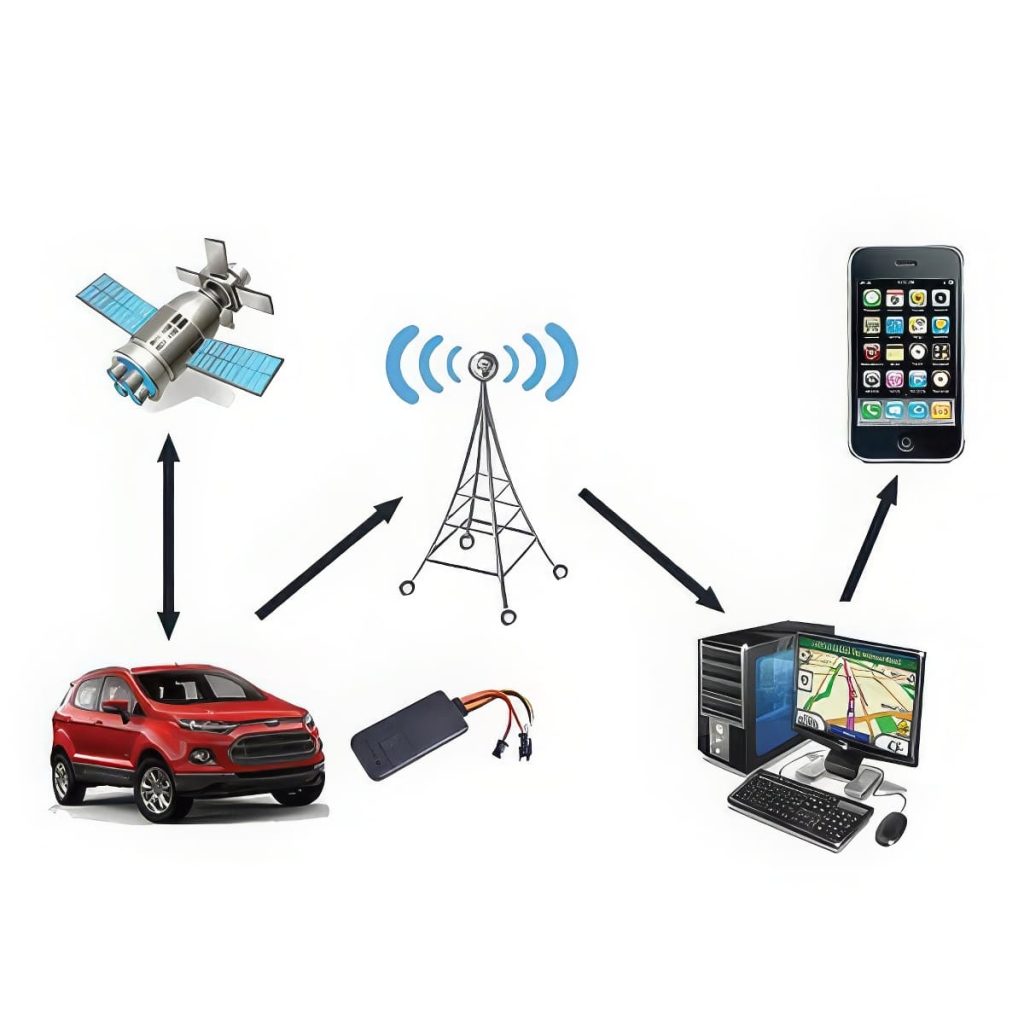

In practical terms, integrating IoT with GPS tracking allows fleet managers to automate many processes. For example, IoT sensors can monitor tire pressure or engine temperature, and this data can be correlated with location information to preempt maintenance or detect potential issues remotely. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and reduces operational costs.
The combination also enhances tracking accuracy and gives real-time insights into operational conditions. For instance, if a truck’s temperature sensor detects an abnormal reading in refrigerated cargo, the system can automatically trigger alerts, reroute the vehicle, or notify relevant personnel. Building such an integrated system requires thoughtful hardware choices, including IoT sensors compatible with your vehicle fleet, along with robust connectivity options.
Developing or customizing a GPS system that integrates with IoT devices may involve using specialized platforms that support blockchain-enabled, secure, and scalable solutions. This integration elevates traditional vehicle tracking to a smarter, more resilient fleet management ecosystem.
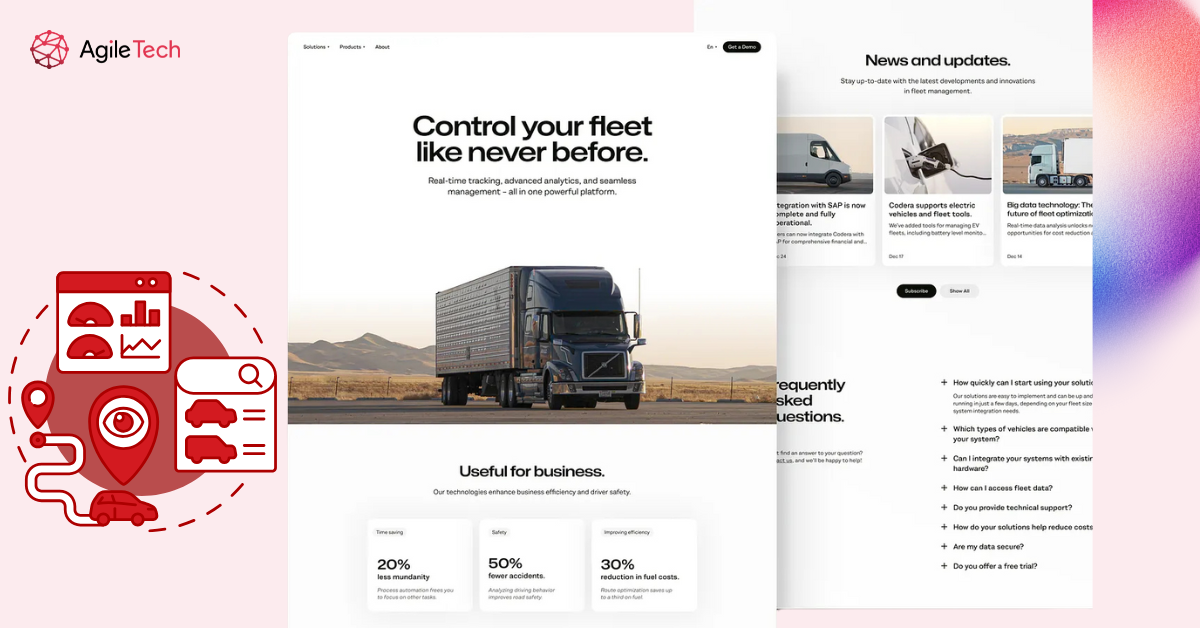
Key Benefits of Real-Time Vehicle GPS Tracking
Implementing real-time GPS tracking offers a multitude of benefits that span operational efficiency, cost savings, compliance, and safety. The immediate visibility of vehicle locations allows fleet managers to respond swiftly to unexpected events, optimize routes dynamically, and improve customer service.
One of the most direct advantages is enhanced route planning and optimization. By constantly monitoring vehicle positions, fleet managers can prevent delays, reduce fuel consumption, and improve delivery schedules. This not only boosts customer satisfaction but also results in significant cost savings for transportation-intensive businesses. Accurate ETAs and improved truck dispatching further streamline operations.
Real-time tracking also enhances safety and security. Fleet managers can monitor driver behavior like speeding or harsh braking, allowing targeted training or interventions. Additionally, real-time alerts on unauthorized vehicle usage serve as deterrents against theft or misuse, protecting assets and personnel. This quick response capability is especially crucial in emergency situations or when deviations from planned routes occur.
Furthermore, compliance with governmental regulations, such as Hours of Service (HOS), is simplified. Many GPS solutions enable automated logging and reporting, ensuring fleets meet legal requirements without manual paperwork. The cumulative impact of these benefits underscores the importance of investing in a reliable GPS tracking system that delivers real ROI.
Use Cases That Prove GPS Tracking Is More Than Just Location Data
GPS tracking systems are undeniably powerful, but their true value lies in the diverse use cases they enable beyond basic location monitoring. These practical applications help fleet managers leverage data for strategic decision-making, compliance, security, and customer engagement.
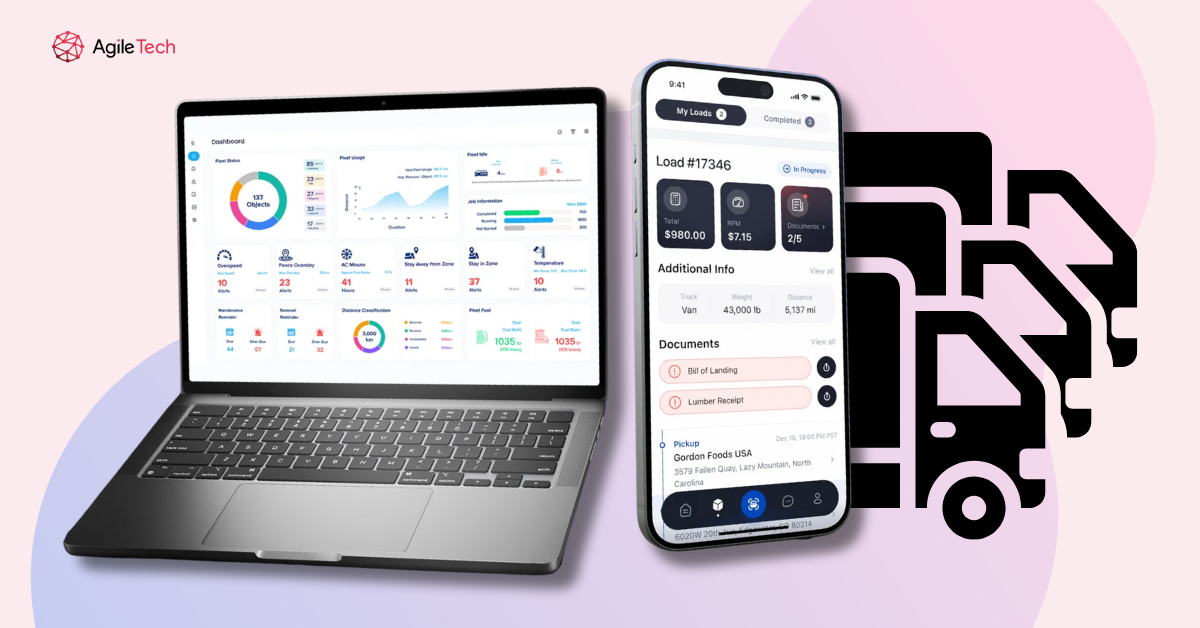
One compelling use case is fleet maintenance prediction. By analyzing vehicle telematics data over time, companies can predict when parts may fail or require servicing, minimizing unplanned downtime. Integrating this with GPS data reveals patterns such as increased wear in vehicles that frequently make certain routes or drive in specific conditions.
In logistics and delivery services, real-time tracking enhances customer communication. Customers can receive accurate ETA updates, and businesses can proactively inform them of delays or issues. Similarly, GPS data supports dynamic rerouting in response to traffic congestion or accidents, optimizing fleet productivity.
Finally, in shipment security, GPS tracking plays a pivotal role in theft prevention and recovery. Advanced systems incorporate geofencing and real-time alerts, enabling rapid response if a vehicle deviates from its authorized route or enters restricted areas. These applications demonstrate that GPS systems are vital tools for holistic fleet management, not just location tracking.
Key Features Every Real-Time GPS Tracking System Must Include
Designing an effective fleet management GPS system requires incorporating features that address the core operational challenges. These features should enhance accuracy, efficiency, security, and compliance, delivering a comprehensive solution that meets modern needs.
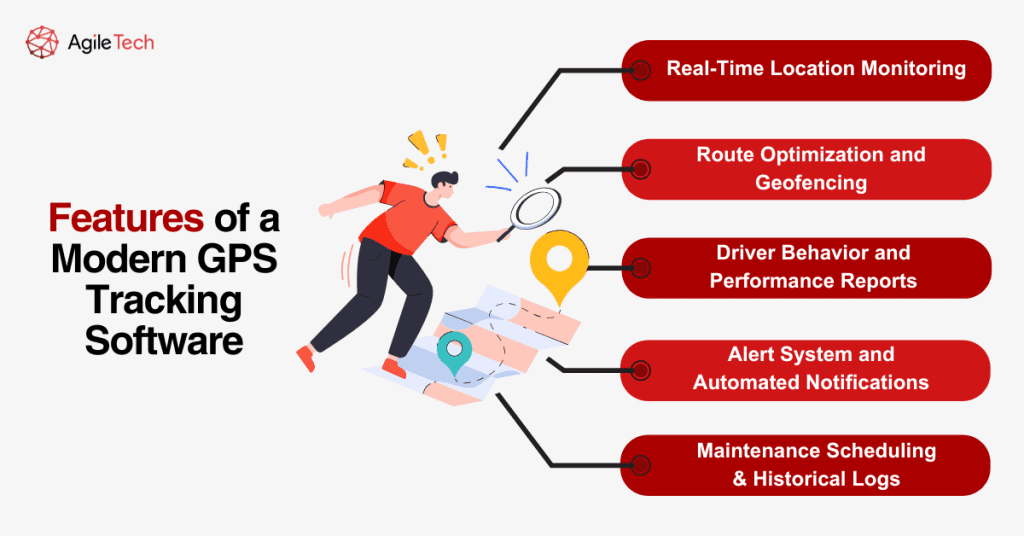
Real-time Location Monitoring
Your GPS system needs to pinpoint vehicles within feet of their actual position, even in challenging environments like urban canyons or tunnels. Multi-constellation receivers (GPS, GLONASS, Galileo) deliver the precision you need for confident decision-making. When your dispatchers can trust the location data they’re seeing, they make smarter routing decisions, respond faster to customer requests, and eliminate costly errors that come from outdated tracking.
Route Optimization and Geofencing
The best GPS systems don’t just tell you where vehicles are—they actively help you manage where they should go. By leveraging AI and real-time data, your system suggests optimal routes based on traffic, weather, and delivery priorities, then automatically reroutes when conditions change. Add geofencing capabilities that alert you when vehicles enter or exit designated areas, and you’ve got a powerful tool for preventing unauthorized stops, ensuring compliance, and catching potential theft before it becomes a problem.
Automated Mileage Tracking
Manual mileage logs are time-consuming and error-prone. Automated tracking captures precise trip data as vehicles operate, creating detailed records that flow seamlessly into your accounting or ERP systems. Beyond administrative efficiency, this feature provides the analytics foundation you need to identify cost-saving opportunities and ensures compliance in jurisdictions requiring accurate logs.
Alert System and Automated Notifications
Proactive fleet management depends on knowing about problems before they become expensive disasters. Your alert system should notify you immediately about scenarios that matter—unauthorized movement, route deviations, excessive idling, speeding, or mechanical issues. When alerts are configured thoughtfully, they empower your managers to intervene at exactly the right moment, preventing breakdowns and keeping customers informed.
Maintenance Scheduling & Historical Logs
Unplanned downtime kills profits, but predictive maintenance turns that equation around. By tracking vehicle usage patterns, mileage, and telematics data over time, your GPS system alerts you when parts are likely to fail or service is due—before you’re dealing with a roadside breakdown. Historical logs provide the detailed records you need for warranty claims, compliance audits, and identifying patterns that cause accelerated wear.
Step-by-Step Guide to Building a Real-Time GPS Tracking System That Delivers ROI
Creating a successful GPS tracker from scratch requires meticulous planning, technical expertise, and ongoing management. This step-by-step guide outlines a proven approach to develop a scalable, secure, and effective fleet management system that maximizes ROI.
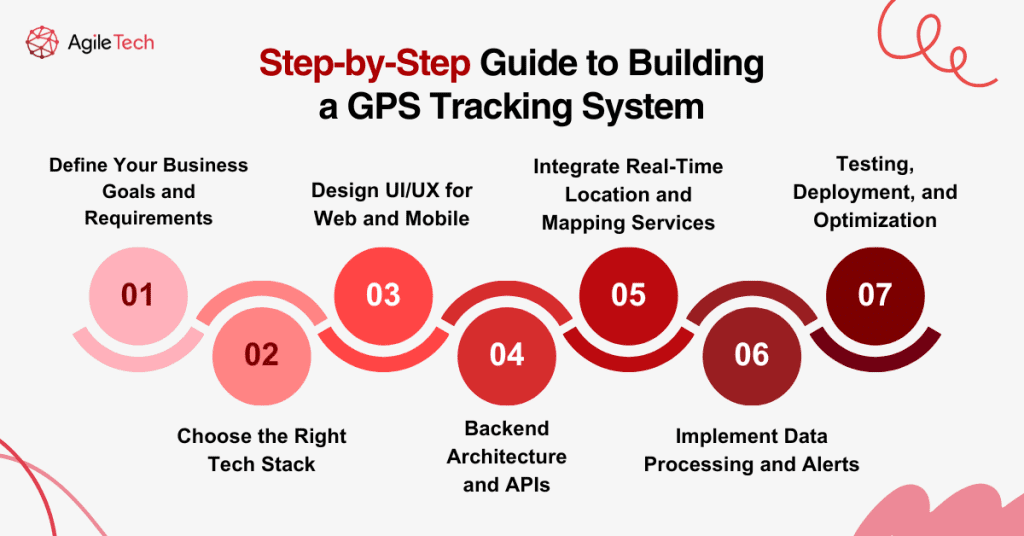
1. Define Your Business Goals and Requirements
Start by identifying the specific operational challenge your GPS system will solve—whether it’s reducing fuel costs, improving driver safety, ensuring regulatory compliance, or optimizing delivery routes. Engage your stakeholders (drivers, dispatchers, IT teams) to understand their pain points and document current metrics like fuel consumption, delivery times, or violation rates. Clear goals keep your development focused on features that deliver measurable results, not just technical bells and whistles that look impressive but don’t move your bottom line.
2. Choose the Right Tech Stack
Your technology choices make or break system performance and scalability. Select high-precision GPS modules that work reliably in urban environments, pair them with 4G LTE or 5G cellular modules for consistent data transmission, and add IoT sensors for comprehensive vehicle monitoring. On the software side, cloud platforms like AWS or Azure provide the scalability you need, while AI algorithms enable predictive analytics that transform raw data into actionable insights. The key decision here is build versus buy—custom development offers perfect fit but costs more, while off-the-shelf platforms deploy faster with some feature compromises.
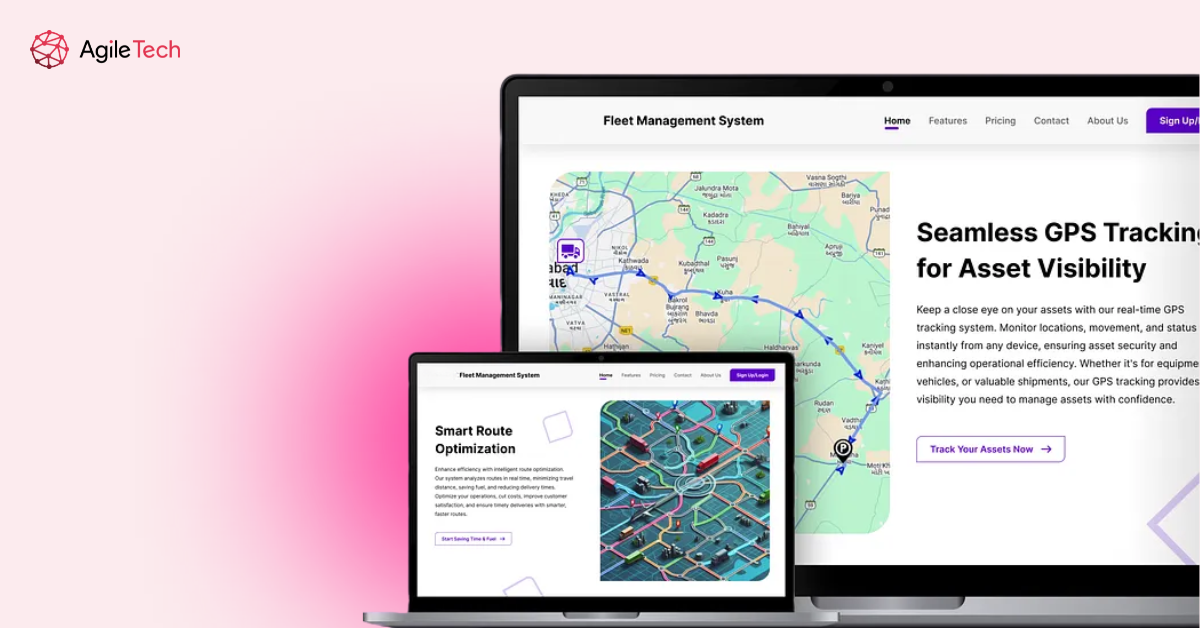
3. Design UI/UX for Web and Mobile
Your system is only valuable if people actually use it, which means intuitive interfaces for different user roles. Dispatchers need real-time dashboards with quick vehicle location access and route management tools. Drivers need simple mobile apps that don’t distract from driving but allow easy communication and task updates. Managers need executive views with KPIs, alerts, and analytics. Invest in usability testing early—a clunky interface tanks adoption rates no matter how powerful your backend is.
4. Backend Architecture and APIs
Build your backend with scalability in mind from day one because retrofitting is expensive. Your architecture needs to handle massive data streams with minimal latency while maintaining data integrity and security. Implement RESTful APIs that enable seamless integration with your existing ERP, CRM, or compliance systems. Consider microservices architecture for flexibility—it lets you update or scale individual components without touching the entire system. Don’t forget authentication, encryption, and access controls at this stage.
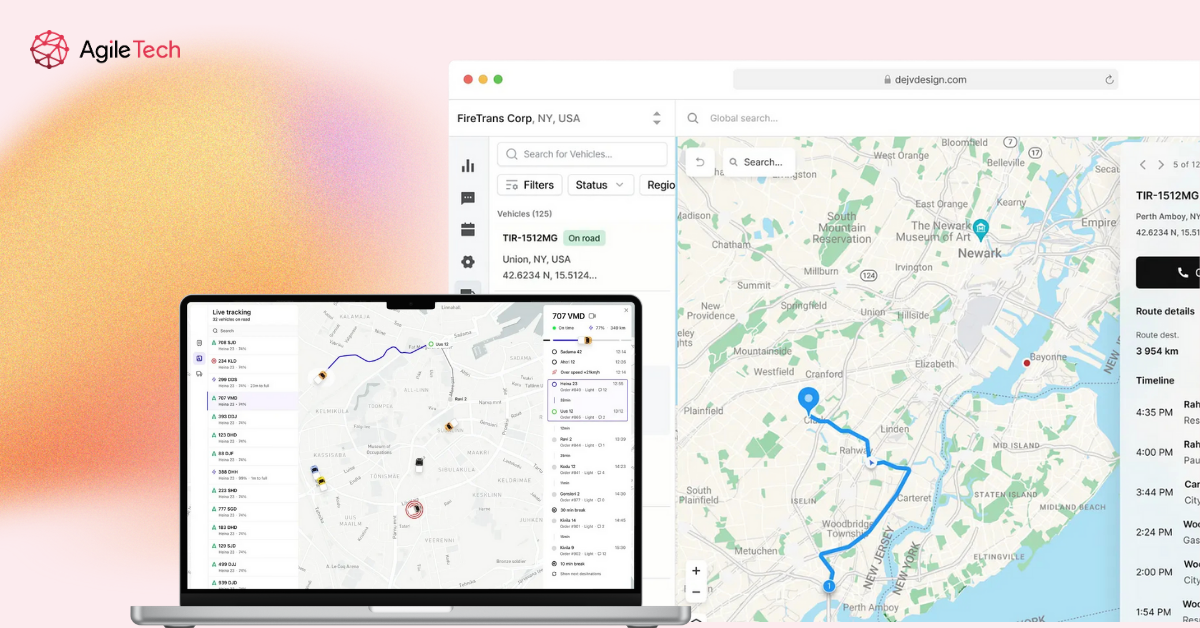
5. Integrate Real-time Location and Mapping Services
This is where your GPS data becomes visually useful. Integrate mapping services like Google Maps, Mapbox, or OpenStreetMap that display vehicle positions in real-time. Implement geofencing capabilities that trigger alerts when vehicles enter or exit designated zones. Build route visualization that shows planned versus actual paths, helping you identify inefficiencies. The integration should update smoothly without lag—nothing frustrates users more than watching dots jump around a map or seeing stale location data.
6. Implement Data Processing and Alerts
Raw GPS coordinates mean nothing until you process them into actionable intelligence. Build data pipelines that analyze location data alongside speed, idle time, harsh braking events, and other telematics inputs. Configure customizable alert thresholds for scenarios critical to your operations—unauthorized movement, speeding, maintenance needs, or HOS violations. Ensure alerts reach the right people through their preferred channels (SMS, email, push notifications) and include enough context for quick decision-making.
7. Testing, Deployment, and Optimization
Start with pilot testing on a small fleet subset to identify bugs and gather real-world feedback before full rollout. Train your staff thoroughly—even the best system fails without proper adoption. Monitor performance continuously after launch, tracking system uptime, data accuracy, and user satisfaction. Plan for regular updates that address user feedback, patch security vulnerabilities, and add features that respond to evolving business needs. Treat deployment as the beginning of your journey, not the end.
The Proven Tech Stack Powering AgileTech’s Leading GPS Vehicle Tracking Solutions
A robust GPS tracking system relies on an intelligent tech stack combining hardware components, communication protocols, cloud infrastructure, and AI capabilities. AgileTech Vietnam leverages this integration to deliver secure, scalable, and AI-driven solutions ideal for SMEs and startups.
Web Development
Django
Drupal
CakePHP
Testing and Automation
Appium
Katalon
UIPath
US Compliance & Data Privacy: The Requirement You Cannot Skip
Navigating U.S. data privacy laws and fleet compliance standards is essential when developing a GPS tracking system. The regulatory landscape is complex and varies by industry, but non-compliance isn’t an option—violations result in hefty fines, legal liability, and damaged reputation.
FMCSA ELD Mandate (For Freight)
If you operate commercial freight vehicles, the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration’s Electronic Logging Device mandate requires you to automatically record driving time and Hours of Service compliance. Your GPS tracking system must integrate ELD functionality that captures duty status, engine hours, vehicle movement, and miles driven. The data must be readily accessible for roadside inspections and stored securely for at least six months. This isn’t just about avoiding fines—it’s about creating verifiable records that protect your business in disputes and audits.
HIPAA Compliance (For Medical Transport)
Medical transport fleets handle protected health information (PHI), which means your GPS system falls under HIPAA regulations. You need end-to-end encryption for all data transmission, secure access controls that limit who can view patient-related information, and comprehensive audit trails tracking every data access. Business Associate Agreements with your technology providers are mandatory, and your system must allow for data breach notifications within the required timeframes. The stakes are high here—HIPAA violations start at $100 per record and can reach millions in penalties.
FERPA Compliance (For School Buses)
School bus fleets must protect student information under the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act. Your GPS tracking system should never expose individual student pickup or drop-off locations publicly, and access to route data containing student information must be strictly controlled. Implement role-based permissions ensuring only authorized school personnel can access sensitive location data. Many districts also require parental consent before tracking systems that could identify specific students, so build consent management into your workflow from the start.
Data Protection Standards
Beyond industry-specific regulations, your GPS system must implement foundational data protection practices. This means encrypting data both in transit and at rest using industry-standard protocols (AES-256 minimum), implementing multi-factor authentication for system access, conducting regular security audits and penetration testing, and maintaining detailed logs of all data access and modifications. Consider obtaining SOC 2 certification to demonstrate your commitment to data security—many enterprise clients won’t work with vendors who lack this credential.
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
If you track vehicles in California or handle data from California residents, CCPA gives drivers and employees significant rights over their personal data. Your system must allow individuals to request what data you’ve collected about them, delete their personal information upon request, and opt out of data sale (if applicable). You need clear privacy notices explaining what data you collect, why you collect it, and how long you retain it. The law also requires reasonable security measures and notification of data breaches within specific timeframes.
New York SHIELD Act
The Stop Hacks and Improve Electronic Data Security Act requires any business handling New York residents’ private information to implement reasonable data security measures. This means administrative safeguards (security policies, employee training), technical safeguards (encryption, secure authentication, monitoring), and physical safeguards (access controls to servers and devices). If you experience a data breach, you must notify affected individuals without unreasonable delay. The Act’s broad definition of “private information” includes location data combined with names, making it directly applicable to GPS tracking systems.