How To Build a Telemedicine App: An Ultimate Guide
Telemedicine is no longer just a response to the COVID-19 pandemic—it has evolved into a core pillar of modern healthcare. With growing demand for accessible, on-demand medical services, telemedicine apps have become essential tools for healthcare providers, patients, and clinics worldwide. From virtual consultations to e-prescriptions, remote diagnostics, and AI-assisted symptom checkers, today’s telemedicine platforms offer more comprehensive and personalized care than ever before.
As the digital health market continues to grow rapidly in 2025, building a telemedicine app is not just a competitive advantage—it’s a strategic necessity for healthcare organizations aiming to scale services, improve patient engagement, and streamline clinical operations. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about developing a successful telemedicine app—from must-have features and tech stack to estimated costs and compliance requirements—so you can confidently plan and launch a platform tailored to your business goals.
- 1. Overview of Telemedicine App
- 2. How does the Telemedicine App work?
- 3. Benefits of Building a Telemedicine App
- 4. Types of Telemedicine Apps
- 5. Essential Features of a Telemedicine App
- 6. Tech Stack
- 7. How to build a telemedicine app?
- 8. How much does it cost to Build a Telemedicine App?
- 9. How does Telemedicine App make money?
- Conclusion
1. Overview of Telemedicine App

According to “Introduction to the Practice of Telemedicine” by J. Craig and V. Patterson, the World Health Organization (WHO) defines telemedicine as:
“The practice of medical care using interactive audiovisual and data communications. This includes the delivery of medical care services, diagnosis, consultation, treatment, as well as health education and the transfer of medical data.”
In today’s digital age, there are multiple ways to apply technology in the field of telemedicine—and mobile apps are among the most effective. The rapid increase in smartphone adoption, improved internet infrastructure, and rising awareness of both physical and mental health have driven the widespread use of telemedicine mobile applications over the past few years.
These apps make it possible to perform a wide range of medical tasks—such as video consultations, live chat, appointment scheduling, remote monitoring, and even treatment planning—directly from a smartphone or tablet. With secure video calls, instant messaging, and digital medical records, telemedicine apps provide a seamless way to connect patients and healthcare professionals on a single platform.
Let’s explore some of the most recent trends shaping the telemedicine industry in 2025.
According to Grand View Research, the global mHealth app market was valued at USD 43.5 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.6% from 2023 to 2030. Meanwhile, a report published by Statista in early 2023 highlighted the ongoing rise in telemedicine adoption. Since 2021, the industry has seen steady growth across all key segments—particularly in:
- Live photo consultations
- Live video consultations
- Consultations via health apps and websites
This upward trend reflects increasing familiarity and trust in telemedicine among patients, doctors, and healthcare staff alike—making now an ideal time to invest in telemedicine app development.
Read also: 6-Step Guide to Healthcare Mobile App Development for Businesses
2. How does the Telemedicine App work?
While each telemedicine app may have unique features and workflows, most follow a similar core process designed to deliver convenient, remote healthcare services. Here’s a step-by-step overview of how a typical telemedicine app works:
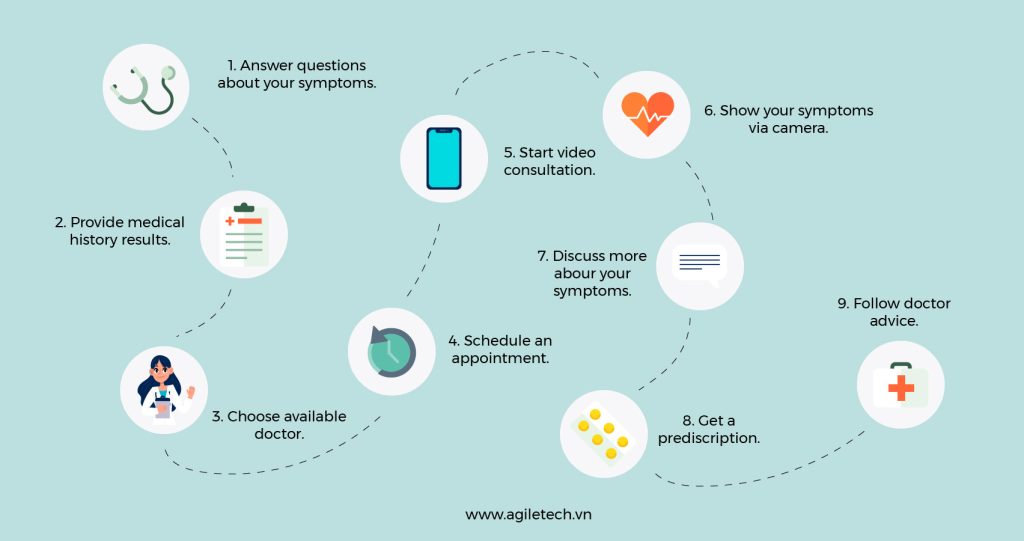
- User Registration and Symptom Submission
The patient begins by creating an account and logging into the platform. They are then prompted to describe their symptoms, upload relevant medical history, and select the type of care they’re seeking. - Smart Matching with Providers
Based on the user’s symptoms, location, and preferences, the app analyzes the input and recommends suitable clinics or nearby healthcare providers. Advanced apps may use AI to suggest the best-matched doctors based on specialization, availability, and user ratings. - Appointment Scheduling
The patient reviews the list of recommended doctors and selects one that fits their needs. Using the built-in calendar, they can book an appointment for a live video call, audio call, or secure chat session. The app may also allow sharing of images, voice notes, and documents ahead of the consultation. - Virtual Consultation
During the scheduled session, the doctor consults with the patient, reviews their symptoms, may request further information, and provides a diagnosis. If necessary, the doctor can order lab tests, prescribe medication, or refer the patient to a specialist. - Prescription and Payment
After the consultation, the patient receives a digital prescription and the doctor’s notes or recommendations. The app then facilitates secure payment through various integrated methods such as credit cards, e-wallets, or insurance coverage.
3. Benefits of Building a Telemedicine App
| Stakeholder | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Doctors | – Ability to treat more patients – Fewer cancellations and missed appointments – Convenient access to Electronic Health Records (EHR) – Easier collaboration with other professionals |
| Patients | – Easier access to healthcare services – On-demand consultations without traveling – Accessible on multiple devices – Reduced healthcare costs – Access to a wider range of specialists |
| Clinics / Hospitals / Businesses | – Operational cost savings – Broader patient/customer base – Lower staff turnover- Improved quality of patient care |
| Both Doctors & Patients | – Time-efficient consultations – Safer interactions, especially for vulnerable groups – Improved treatment outcomes through regular follow-ups |
4. Types of Telemedicine Apps
There are 3 different types of telemedicine services that you can provide. Take consideration of these types to decide what services you are able to provide when making a telemedicine app.
| Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Store-and-forward | This app will help patients send images, photos, forms, records, etc. to describe their medical conditions to doctors. Consequently, medical staffs and patients do not need to be available at the same time |
| 2 | Remote monitoring/ IoT-based telemedicine | This app allows healthcare providers to track health conditions of their remote patients. There are special devices used for measuring heart rate, blood pressure, levels of sugar, etc. These obtained information are automatically added to the medical records of the app to help doctors keep track of any changes in patients suffering. |
| 3 | Real-time interactive services | The type that includes phone and video calls for consultation, or call a medical specialists to visit patient at home, including: – Follow-up consultations after the patients is released from the hospital – Mental health therapy and neuropsychology – Pharmaceutical advice – Remote nursing consultations – Monitoring post-injury rehabilitation process |
Read more: Telemedicine App: How To Build Doctor On-Demand App For Healthcare?
5. Essential Features of a Telemedicine App
5.1. For Patients
Registration & Sign-in
Patients can create a personal account using an email address, phone number, or third-party platforms like Google or Facebook. Two-step authentication via SMS or email is highly recommended to enhance security. A registered account allows users to access personalized services such as health tracking, in-app appointment calendars, and automated reminders—making the process more seamless than relying on memory.
Profile Management
After signing up, patients complete a profile form that includes basic personal details (e.g., name, gender, age) and relevant medical information such as past treatments or chronic conditions. This data helps doctors better understand the patient’s health history and tailor care accordingly. Patient profiles are kept confidential and accessible only to authorized medical professionals.
Health Tracking Dashboard
The app should feature a dashboard that presents key health data in visual formats such as graphs, charts, and progress bars. This allows both patients and healthcare providers to monitor changes, receive alerts, and track ongoing treatment outcomes in real time.
Search & Filter Options
To help patients find the right doctor, the app should include smart filters based on specialization, language, availability, user ratings, and reviews.
Video Consultations
Video calls are essential for most remote diagnoses, as they allow doctors to visually assess symptoms. This feature significantly improves diagnostic accuracy compared to audio- or text-only options.
Secure Messaging
For non-urgent cases, patients can send text messages to their doctors. This asynchronous communication is ideal for follow-ups or minor concerns. Support for attachments (photos, medical reports, etc.) enhances the usefulness of chat.
Appointment Calendar
An integrated calendar allows patients to view, schedule, or reschedule appointments. Any changes are sent to the doctor for confirmation. Automatic notifications remind patients of upcoming sessions to reduce missed appointments.
Payment Integration
The app should support secure payment options—either via custom-built systems or trusted third-party gateways. While third-party services offer fast deployment and PCI compliance, custom systems offer greater control and flexibility when developed by experienced providers.
Doctor Reviews & Ratings
After a consultation, patients can rate their doctors and leave feedback. These reviews help future users make informed choices and encourage quality service from providers.
Push Notifications
Real-time notifications keep patients informed about upcoming appointments, new messages, prescriptions, app updates, and health tracking reminders.
Read more: What is eMAR in Healthcare: Definition and Core Functions
5.2. For Doctors
Professional Profile
Doctors create a detailed profile that highlights their specialization, credentials, experience, and areas of expertise. A well-structured profile helps establish trust and attracts the right patients.
Appointment & Calendar Management
Doctors can manage their availability through an in-app calendar. If patients request changes to scheduled appointments, doctors can approve or suggest alternatives with just a few clicks.
Access to Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
To make informed decisions, doctors must be able to view patients’ health histories, treatment records, lab results, and current conditions through secure access to EHRs.
Messaging and Video Calls
Just like patients, doctors need robust communication tools. Real-time messaging and video consultations enable them to provide timely care, follow up with patients, and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Patient Ratings & Feedback
Doctors can also leave feedback on patient behavior, such as missed appointments or late arrivals. This two-way review system encourages accountability and enhances the reliability of the platform for all users.
6. Tech Stack
Here, we give you a rough list of technology for telehealth app development, depending on your choice of what features you want to implement, the tech stack might change to meet your needs.
- Front-end development: ReactJS, Angular,
- Back-end development: Node.js, Phyton, PHP, ; database – Postgres, MongoDB, MySQL,
- Mobile development: iOS – Swift, Android – Java,
- Web development: Javascript, HTML, CSS, Vue.js, React.js
- Databases: Firebase, MySQL, MongoDB,
- Multiple payment modes: PayPal, Braintree, Stripe
- User location tracking and map integration: MapKit, Google Maps API, CoreLocation
- Push notifications: Twilio, Push.io
- In-app messaging and calling: Twilio
- Audio/ Video call: Web RTC, RTMP
- Calendar: Google Calendar API
- Cloud environment: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google, Microsoft Azure.
7. How to build a telemedicine app?
Once you need to build a telemedicine app, you first need to decide who will actually do this. There are 2 common options for you:
- The first option is hiring an in-house team, which may cost a lot of money and time to find the developers with the right skills. But it allows you to completely control the project, decreases the data leaks and self-reliance.
- The second way is hiring a dedicated software development team, either onshore or offshore. It could be cheaper and easier to connect to qualified and skilled IT professionals, and capitalise on the experience of the vendors. However, if you choose to outsource from an unreliable vendor, it will take more time, over-budget and difficult interaction.
As you can see, each option has its pros and cons, you can choose the most suitable one or even combine the two based on your demands and budget. The two ways will follow a basic process:
7.1. Research & Analytics
The first thing you should do is to identify your project that meets demands. You should conduct research about your target customer, market and competitor to make sure that your idea is worth implementing. This stage is a basic step to let you know which problems you are facing and how to solve them quickly and effectively. When researching your rivals in the telehealth industry, pay attention to their prices, platforms and user reviews to know exactly their strengths and weaknesses.
7.2. Prototyping
There are many prototypes in the process of telemedicine app development. They are all necessary to ensure your app development. Firstly, creating a sketch of the fundamental functionality first to ensure your developers know what should be done. Then, the UI/UX designers will add more details and functionality to fulfil the prototypes.
7.3. Test
You need to test almost everything before you launch the app for users, from the design to the features. After each test, the developers will receive feedback, make changes and improvements, and finally fix bugs.
7.4. MVP Development
After creating a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) which only has necessary features with barely UI Design, you will gather user feedback and conduct the final test. Having more user feedback, fewer bugs are fixed and redesigned at later stages.
7.5. Deployment & Maintenance
When all the features are implemented, remember to run the final product and give your app the project-related data. After all, your mobile app with all the features available is ready to launch on app marketplaces.
Finally, don’t forget to keep a maintenance team that monitors system health and provides necessary updates.
8. How much does it cost to Build a Telemedicine App?
The cost and time of developing a Telemedicine App will depend on many factors like:
- Tech stack
- Platform choices (iOS, Android, website…)
- Functionality
- Design
- Team size
- Hourly rates
- Developer’s qualifications
We’ll look at the telemedicine app development cost by location of the development team, it varies from $45,000 to $280,000. It can be seen that choosing a dedicated team from South Asia would help you reduce a lot in building your telemedicine app.
| Location | Average Cost (unit: US dollars) |
|---|---|
| Australia | 160,000 |
| The US | 280,000 |
| The UK | 180,000 |
| Western Europe | 150,000 |
| Eastern Europe | 75,000 |
| South Asia | 45,000 |
Read more: Save Costs, Scale Faster: Offshore Staffing or Outsourcing?
9. How does Telemedicine App make money?
Regardless of the business model, Telemedicine App can have a variety of monetisation options, such as
- Subscription: A subscription model allows access to the full content of a given app. They can be either available on a monthly, quarterly or yearly basis.
- One-time purchases: This work best for intermittent services or urgent support
- In-app advertisement: Ads are an excellent way to generate revenue. It could be a full-screen banner or just a widget. The widget can be put in the sidebars or footers.
- Freemium: A standard offer allows customers to use limited services with no fee, if your customers want more, offer them with freemium to make them pay for extra services.
- External links: Apps can provide links to services and products in any format, such as a book, an MP3 file or a podcast.
Conclusion
Telemedicine is a valuable technology in linking hospitals, clinics and medical businesses with patients to prove beneficial to them, such as, minimising the doctors’ and patients’ travel time, increasing the quality of healthcare facilities, expanding access to remote areas, etc. The market trends indicate that the need for telemedicine apps is increasing in the global market. So, it’s the right time to create a telemedicine app now! Become one of the first to benefit from telemedicine app development!
If you want to choose a reliable technology partner in Asia to build your telemedicine app, contact us to start together today! AgileTech is an experienced technology outsourcing company that has intense experience in this market, so we can help you with building web and mobile products and creating a clear picture for your business to succeed. Maybe your product will be outstanding in the telemedicine app industry.