Insurance App: Why Insurance Companies Need A Mobile App?
The insurance industry is experiencing a digital transformation, with mobile applications becoming essential tools for companies seeking to remain competitive and meet evolving customer expectations. As consumers increasingly rely on smartphones for daily activities, insurance companies must adapt their service delivery methods to match this digital-first mindset. Mobile apps represent more than just a technological upgrade, they’re a strategic necessity for insurance companies looking to enhance customer relationships, streamline operations, and capture new market opportunities.
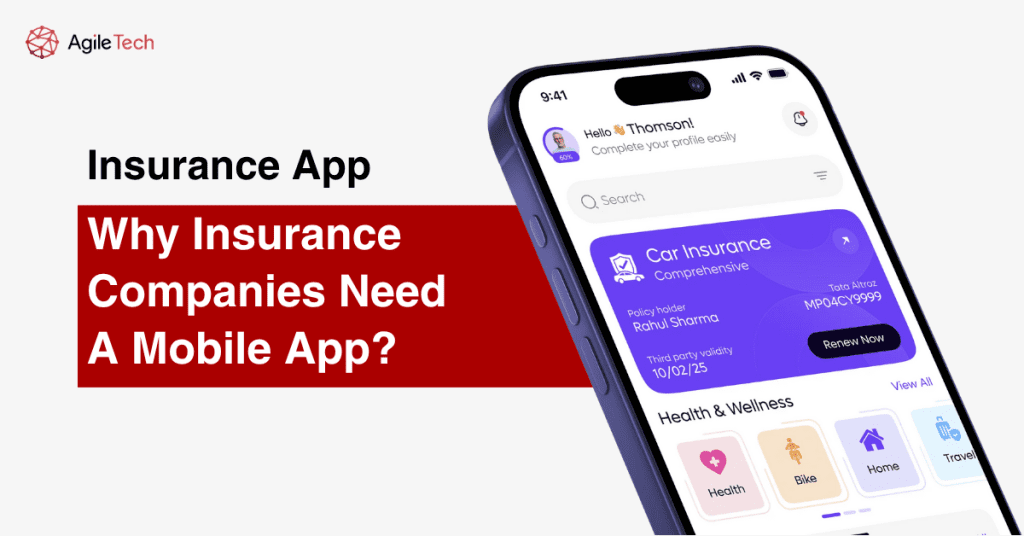
1. Top 4 Reasons Why an Insurance Company Needs a Mobile App
1.1. Enhanced Customer Experience and Accessibility
Mobile insurance apps provide unprecedented convenience, allowing customers to access their policies, file claims, and receive support 24/7 from anywhere. This constant availability eliminates the frustration of waiting for business hours or navigating complex phone systems. Customers can instantly view policy details, make payments, update personal information, and track claim status in real-time. The intuitive interface and user-friendly design make insurance services more approachable, particularly for younger demographics who expect seamless digital experiences.
1.2. Streamlined Claims Processing and Faster Resolution
Traditional claim processes often involve lengthy paperwork, multiple phone calls, and extended waiting periods. Mobile apps revolutionize this experience by enabling customers to submit claims instantly using their smartphone cameras to capture damage photos, automatically populate claim forms using GPS data, and upload supporting documents directly. This digital approach significantly reduces processing time, minimizes human error, and provides transparent tracking throughout the entire claims journey, leading to higher customer satisfaction and reduced operational costs.
1.3. Increased Customer Engagement and Retention
Mobile apps create direct communication channels between insurance companies and their customers, fostering stronger relationships through personalized notifications, policy reminders, and relevant insurance tips. Push notifications can alert customers about payment due dates, policy renewals, or important updates, reducing policy lapses and improving retention rates. The app becomes a valuable touchpoint for cross-selling additional coverage options, sharing safety tips, and providing educational content that demonstrates the company’s commitment to customer welfare beyond just policy coverage.
1.4. Competitive Advantage and Market Differentiation
In an increasingly crowded insurance marketplace, mobile apps serve as powerful differentiators that can attract new customers and retain existing ones. Companies with robust mobile platforms appear more modern, trustworthy, and customer-focused compared to competitors relying solely on traditional service channels. The app becomes a showcase for the company’s technological capabilities and commitment to innovation, particularly important when targeting tech-savvy millennials and Gen Z consumers who prioritize digital-first experiences when choosing service providers.
2. Types of Mobile Insurance Apps
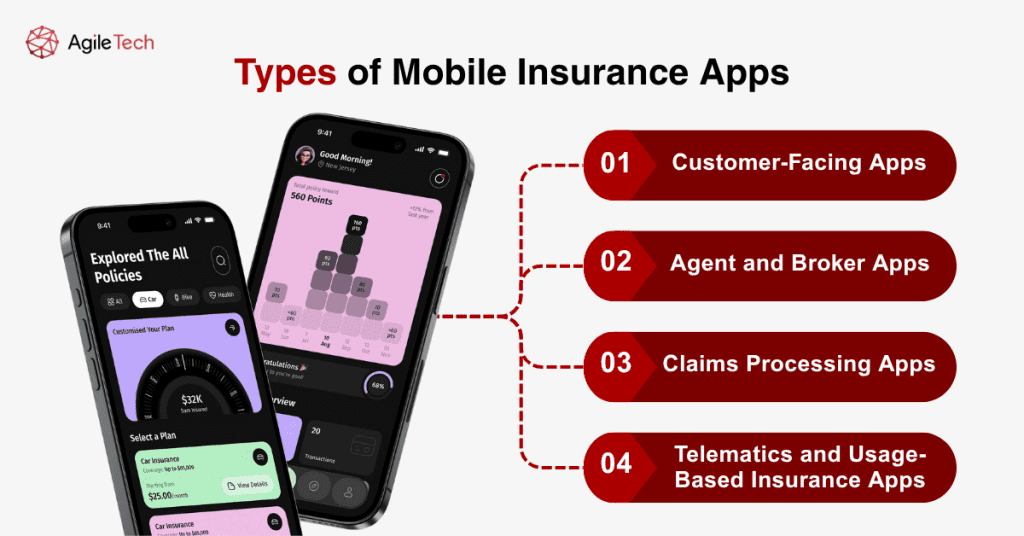
2.1. Customer-Facing Apps
These applications serve policyholders directly, providing comprehensive self-service capabilities including policy management, premium payments, claim submissions, and customer support access. Customer-facing apps typically feature document storage, coverage calculators, emergency assistance contacts, and personalized dashboards showing policy status and coverage details.
2.2. Agent and Broker Apps
Designed for insurance professionals, these applications enable agents to access customer information, generate quotes, process applications, and manage their client portfolios while in the field. These apps often include CRM functionality, commission tracking, lead management tools, and real-time access to company resources and product information.
2.3. Claims Processing Apps
Specialized applications focused specifically on streamlining the claims process, featuring advanced capabilities like AI-powered damage assessment, fraud detection algorithms, and automated estimation tools. These apps often integrate with third-party services for repair shop networks, medical provider directories, and settlement processing systems.
2.4. Telematics and Usage-Based Insurance Apps
These applications collect real-time data about user behavior, such as driving patterns for auto insurance or health metrics for life insurance. The apps analyze this data to offer personalized premiums, safety recommendations, and risk assessment insights, creating more accurate pricing models and encouraging safer behaviors.
Read more: How To Define Mobile App Development Budget In 3 Steps!
3. Basic Features for an Insurance App
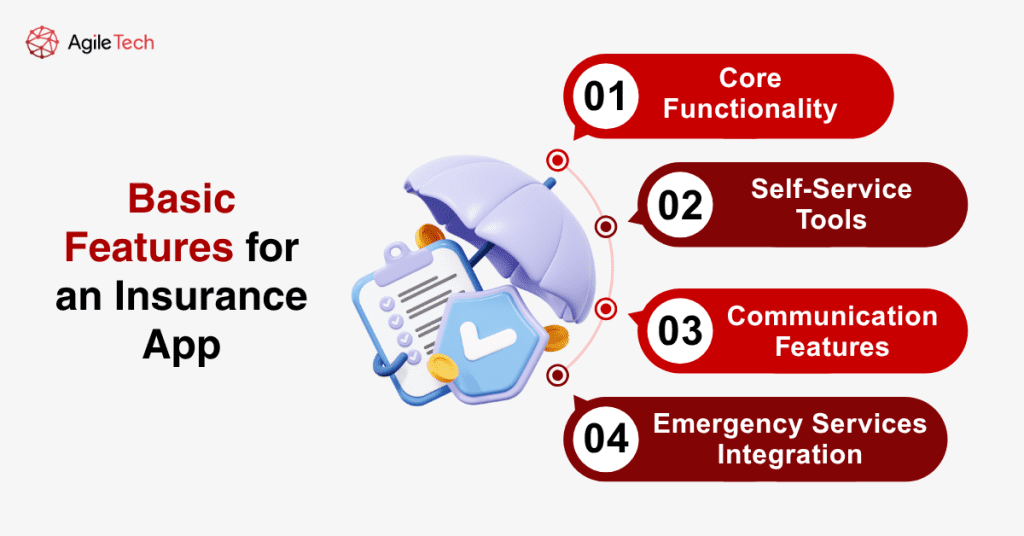
3.1. Core Functionality
Every insurance app should include essential features such as secure user authentication, policy overview dashboards, premium payment processing, and claim submission capabilities. Document management allows users to store and access important insurance documents digitally, while push notifications keep customers informed about critical updates, payment reminders, and claim status changes.
3.2. Self-Service Tools
Comprehensive self-service options empower customers to handle routine tasks independently, including policy modifications, beneficiary updates, coverage adjustments, and address changes. Interactive tools like coverage calculators, risk assessment questionnaires, and premium estimators help customers make informed decisions about their insurance needs.
3.3. Communication Features
Built-in communication tools facilitate seamless interaction between customers and insurance representatives through in-app messaging, video calls, and callback scheduling. Knowledge bases, FAQ sections, and chatbot integration provide immediate answers to common questions, reducing the burden on customer service teams while improving response times.
3.4. Emergency Services Integration
Critical emergency features include one-touch access to emergency services, roadside assistance, medical helplines, and disaster reporting tools. GPS integration enables location-based services, automatic accident detection, and faster emergency response coordination.
Read more: Location Based App: How To Build a Geolocation App [Full Guide]
4. Insurance App for Employees
4.1. Internal Operations Management
Employee-focused insurance apps streamline internal operations by providing staff with mobile access to customer databases, policy management systems, and claims processing tools. These applications enable field agents to conduct business remotely, access real-time customer information, and complete transactions without returning to the office.
4.2. Training and Compliance Tools
Comprehensive training modules, compliance checklists, and certification tracking help ensure employees stay current with industry regulations and company procedures. These apps can deliver mandatory training content, track completion rates, and maintain compliance documentation for regulatory audits.
4.3. Performance Monitoring and Analytics
Advanced analytics dashboards provide managers with insights into employee performance, customer satisfaction metrics, and operational efficiency indicators. Real-time reporting capabilities enable quick decision-making and identification of areas requiring improvement or additional training.
4.4. Collaboration and Communication
Internal messaging systems, file sharing capabilities, and video conferencing integration facilitate seamless collaboration between different departments and remote team members. These features are particularly valuable for coordinating complex claims investigations or customer service escalations.
5. How Much Does It Cost to Develop an Insurance App?
5.1. Basic Insurance App Development
Entry-level insurance apps with fundamental features like policy viewing, payment processing, and basic claim submission typically cost between $50,000 to $100,000. These applications include essential security measures, basic user interfaces, and integration with existing insurance management systems. Development timelines usually range from 4-6 months, depending on complexity and customization requirements.
5.2. Mid-Range Insurance App Development
Comprehensive insurance apps with advanced features such as AI-powered chatbots, telematics integration, advanced analytics, and multi-platform compatibility generally cost between $100,000 and $300,000. These applications require more sophisticated backend infrastructure, third-party integrations, and enhanced security protocols. Development periods typically extend to 6-12 months, including thorough testing and regulatory compliance verification.
5.3. Enterprise-Level Insurance App Development
High-end insurance applications with cutting-edge features like machine learning algorithms, blockchain integration, IoT connectivity, and comprehensive analytics platforms can cost $300,000 to $800,000 or more. These enterprise solutions often require custom development, extensive third-party integrations, and ongoing maintenance contracts. Development timelines can extend beyond 12 months, particularly for companies requiring multiple app versions or complex regulatory compliance across different markets.
5.4. Ongoing Costs and Considerations
Beyond initial development costs, insurance companies must budget for ongoing expenses, including app store fees, hosting costs, security updates, feature enhancements, and regulatory compliance maintenance. Annual maintenance costs typically range from 15-25% of the initial development investment, while marketing and user acquisition efforts require additional budget allocation to ensure successful app adoption and customer engagement.
The investment in mobile app development represents a strategic decision that can significantly impact an insurance company’s competitive position, customer satisfaction levels, and operational efficiency. Companies should carefully evaluate their specific needs, target audience requirements, and long-term growth objectives when determining the appropriate level of investment in mobile app technology.
Conclusion
In an increasingly digital and mobile-first world, developing a dedicated insurance app is no longer optional, it’s a strategic imperative. From improving customer experience and accelerating claims processing to strengthening internal operations and gaining a competitive edge, mobile apps offer immense value to insurance companies of all sizes. By investing in the right features, targeting both customers and employees, and understanding the full development lifecycle and costs, insurers can future-proof their operations and build stronger, more trusted relationships with tech-savvy consumers. As the insurance landscape continues to evolve in 2025 and beyond, those who embrace mobile innovation will be best positioned to lead.