Transforming Supply Chains: How IoT is Revolutionizing Transportation and Logistics in 2025
In 2025, the Internet of Things (IoT) will no longer be just a tech trend, it’s a game-changer in the transportation and logistics industry. From real-time fleet monitoring to predictive maintenance and smart inventory tracking, IoT is helping businesses streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance visibility across the entire supply chain. This article explores how IoT-driven solutions are transforming logistics workflows and why companies that adopt them are gaining a competitive edge.
- 1. The IoT Revolution in Transportation and Logistics
- 2. What is IoT in Logistics?
- 3. Key Benefits of IoT in Transportation and Logistics
- 3.1. Real-time Monitoring and Tracking Capabilities
- 3.2. Enhanced Inventory Management and Warehouse Optimization
- 3.3. Improved Supply Chain Visibility and Transparency
- 3.4. Operational Efficiency and Process Automation
- 3.5. Cost Reduction and Resource Optimization
- 3.6. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction and Service Quality
- 4. Real-world Applications of IoT in Logistics
- 5. Real-world Case Studies and Success Stories
- 6. Challenges and Considerations in IoT Implementation
- 7. Future Trends and Emerging Technologies
- 8. IoT Implementation Guide for Businesses
- Conclusion
1. The IoT Revolution in Transportation and Logistics
1.1. The Digital Transformation of Supply Chains
The landscape of global supply chains underwent a seismic shift in 2025, with Internet of Things (IoT) technology serving as the primary catalyst for unprecedented transformation. Traditional logistics operations, once characterized by manual processes and limited visibility, are now evolving into intelligent, interconnected networks that respond dynamically to real-time conditions. The integration of Internet of Things transportation solutions has fundamentally reimagined how goods move across the global economy.
IoT in logistics has accelerated supply chain digitization beyond industry predictions, driven by the convergence of advanced sensors, cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and 5G connectivity. Companies implementing Internet of Things in logistics solutions that once relied on periodic status updates and reactive problem-solving now operate with continuous monitoring and predictive capabilities. IoT in transportation enables proactive decision-making at every level of their operations, transforming traditional supply chain management.
1.2. Global IoT Logistics Market Overview and Growth Projections
The financial trajectory of Internet of Things transportation and logistics demonstrates the technology’s transformative impact on the industry. IoT in logistics market data shows explosive growth, with the global IoT in transportation market size estimated at USD 114.75 billion in 2024, growing to USD 139.64 billion in 2025 and predicted to surpass around USD 817.18 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 21.69% between 2024 and 2034.
More specifically for Internet of Things in logistics applications, the Global IoT Powered Logistics Market is projected to reach a value of around USD 809 billion by 2034, growing from USD 17.5 billion in 2024, at a CAGR of 46.72% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. This exponential growth in IoT in supply chain implementations reflects the critical role the Internet of Things and transportation technologies play in modernizing supply chain operations and the substantial return on investment companies are experiencing.
Regional market distribution shows North America maintaining its leadership position, though emerging markets are rapidly gaining ground. India is expected to register the highest CAGR from 2025 to 2030, indicating the global nature of this technological revolution.
1.3. Why IoT Matters for Modern Logistics Companies
IoT in logistics has become indispensable for logistics companies seeking a competitive advantage in an increasingly complex global marketplace. Internet of Things transportation solutions address fundamental challenges that have plagued the industry for decades: lack of real-time visibility, inefficient resource utilization, reactive maintenance approaches, and limited customer transparency. Modern consumers and business partners demand precise delivery windows, real-time tracking capabilities, and environmental accountability, all of which are enabled by comprehensive Internet of Things in logistics implementations.
2. What is IoT in Logistics?
2.1. Defining IoT in the Logistics Context
Internet of Things in logistics encompasses the deployment of interconnected devices, sensors, and systems throughout the supply chain to collect, transmit, and analyze data in real-time. IoT in transportation systems monitors everything from vehicle performance and cargo conditions to warehouse inventory levels and delivery routes. These smart devices create a comprehensive digital twin of physical logistics operations through Internet of Things and transportation integration, enabling unprecedented visibility and control over IoT in supply chain operations.
2.2. Key IoT Components and Technologies
The foundation of Internet of Things transportation systems consists of several critical components working in harmony. Edge devices and sensors form the data collection layer, monitoring parameters such as temperature, humidity, shock, location, and security. IoT in logistics connectivity solutions, including 5G, LTE, satellite, and Wi-Fi networks, ensure reliable data transmission even in remote locations.
Cloud computing platforms process and store the massive volumes of data generated by the Internet of Things in logistics implementations, while analytics engines powered by artificial intelligence and machine learning extract actionable insights. User interfaces, including mobile applications and web dashboards, present IoT in transportation information in accessible formats for decision-makers at all organizational levels.
2.3. How IoT Systems Integrate with Supply Chain Operations
Internet of Things and transportation integration occur across multiple operational layers, from strategic planning to tactical execution. At the operational level, IoT in supply chain devices provides real-time feedback that enables dynamic route optimization, load balancing, and resource allocation. This Internet of Things in logistics integration extends to enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, warehouse management systems (WMS), and customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, creating a unified ecosystem of operational intelligence powered by IoT in transportation technologies.
Read more: Fleet Management Software Development: Development, Challenges, and Tech Stack
3. Key Benefits of IoT in Transportation and Logistics
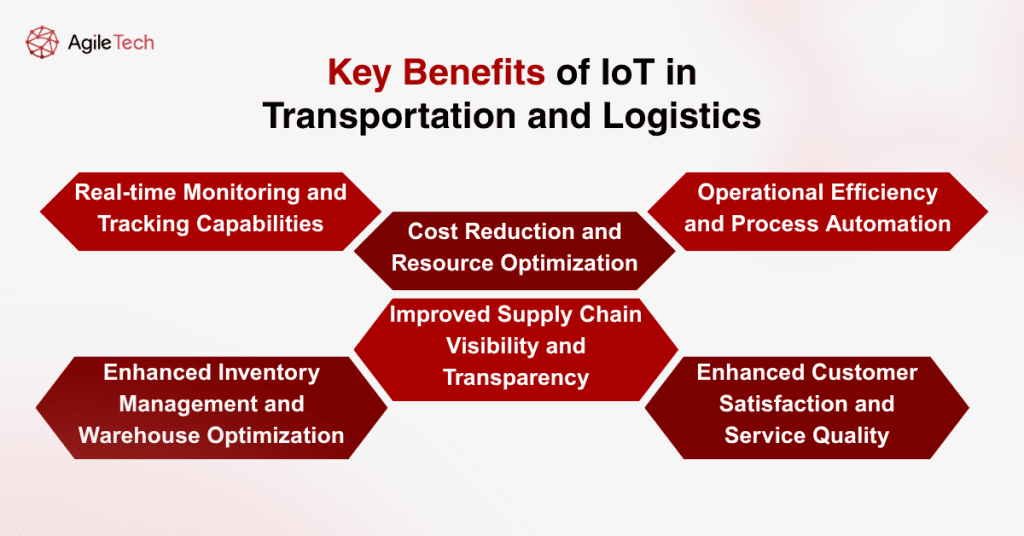
3.1. Real-time Monitoring and Tracking Capabilities
The cornerstone benefit of Internet of Things transportation implementation is the ability to monitor and track assets, inventory, and shipments in real-time. GPS-enabled devices provide precise location data, while environmental sensors monitor cargo conditions throughout the supply chain. IoT in logistics’ continuous monitoring capability eliminates the traditional “black holes” in logistics operations where shipments would disappear from visibility for hours or days.
3.2. Enhanced Inventory Management and Warehouse Optimization
Internet of Things in logistics sensors revolutionize inventory management by providing accurate, real-time stock levels and automated reorder triggers. Smart shelving systems equipped with weight sensors and RFID readers automatically track inventory movements, reducing human error and labor costs. Advanced analytics in IoT in supply chain implementations identify optimal storage configurations and predict demand patterns, enabling more efficient warehouse utilization through Internet of Things transportation integration.
3.3. Improved Supply Chain Visibility and Transparency
Complete supply chain visibility emerges as one of the Internet of Things’ most valuable contributions. Stakeholders at every level gain access to comprehensive operational data through IoT in transportation systems, from raw material sourcing to final delivery. This transparency, enabled by the Internet of Things and transportation technologies, enables better coordination between supply chain partners, faster issue resolution, and improved customer communication regarding shipment status and expected delivery times.
3.4. Operational Efficiency and Process Automation
IoT in logistics enables extensive process automation that reduces manual intervention and human error. Automated sorting systems in warehouses, dynamic route optimization for delivery vehicles, and predictive maintenance scheduling all contribute to significantly improved operational efficiency. These Internet of Things transportation automated processes operate continuously, making adjustments based on real-time conditions without requiring human oversight, demonstrating the power of IoT in supply chain operations.
3.5. Cost Reduction and Resource Optimization
The financial impact of the Internet of Things in logistics implementation extends across multiple cost categories. Fuel costs decrease through optimized routing and improved vehicle performance monitoring enabled by IoT in transportation systems. Labor costs decline as automated systems handle routine tasks more efficiently than manual processes. Maintenance costs drop significantly through predictive maintenance programs powered by the Internet of Things and transportation sensors that prevent costly equipment failures and extend asset lifecycles in IoT in supply chain operations.
3.6. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction and Service Quality
Internet of Things transportation directly improves customer experience through accurate delivery estimates, proactive communication about potential delays, and reduced damage rates for sensitive shipments. Customers gain access to detailed tracking information through IoT in logistics platforms and can plan their schedules around precise delivery windows. This enhanced service quality enabled by the Internet of Things in logistics translates into improved customer loyalty and competitive advantage.
4. Real-world Applications of IoT in Logistics
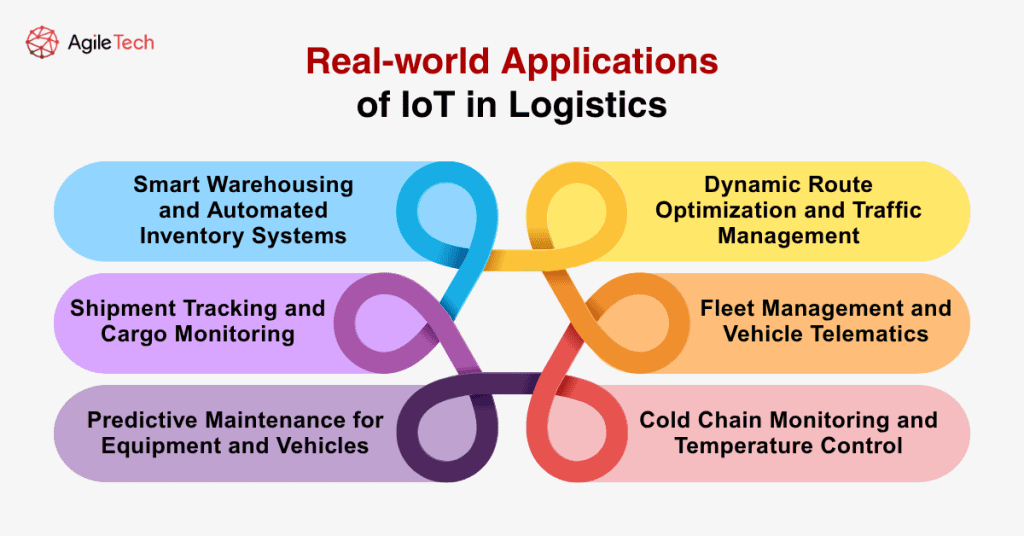
4.1. Shipment Tracking and Cargo Monitoring
Modern shipment tracking, powered by the Internet of Things and transportation, extends far beyond simple location monitoring. IoT in logistics-enabled tracking devices monitor cargo conditions, including temperature, humidity, shock, tilt, and security breaches. These Internet of Things in logistics devices send alerts when parameters exceed predefined thresholds, enabling immediate corrective action to prevent cargo damage or loss through advanced IoT in supply chain monitoring.
4.2. Smart Warehousing and Automated Inventory Systems
Smart warehouses represent the pinnacle of the Internet of Things in logistics integration in logistics facilities. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) move inventory based on real-time demand signals from IoT in transportation systems, while robotic picking systems fulfill orders with unprecedented speed and accuracy. Environmental controls automatically adjust temperature and humidity based on stored products’ requirements through the Internet of Things and transportation sensors, ensuring optimal storage conditions while minimizing energy consumption in IoT in supply chain facilities.
4.3. Fleet Management and Vehicle Telematics
Internet of Things transportation vehicle telematics systems provide comprehensive insights into fleet performance, driver behavior, and operational efficiency. Real-time monitoring of engine performance, fuel consumption, and driver habits through IoT in logistics enables fleet managers to optimize operations and reduce costs. Integration with traffic management systems enables dynamic route adjustments through the Internet of Things in logistics that minimize delays and fuel consumption, showcasing the power of IoT in supply chain optimization.
4.4. Predictive Maintenance for Equipment and Vehicles
Internet of Things and transportation sensors continuously monitor equipment health, identifying potential failures before they occur. Vibration sensors on conveyor systems detect bearing wear, while engine monitoring systems, through IoT in logistics, track performance degradation that indicates upcoming maintenance needs. This predictive approach, enabled by the Internet of Things in logistics, reduces unexpected downtime by up to 40% and extends equipment lifecycles significantly in IoT in supply chain operations.
4.5. Dynamic Route Optimization and Traffic Management
Advanced route optimization systems process real-time traffic data, weather conditions, and delivery priorities to calculate optimal routes continuously. These systems adapt to changing conditions throughout the day, rerouting vehicles around traffic congestion or weather delays. The result is improved on-time delivery performance and reduced fuel consumption.
4.6. Cold Chain Monitoring and Temperature Control
Cold chain logistics benefits enormously from IoT monitoring, particularly for pharmaceutical and food products. Continuous temperature monitoring ensures product integrity throughout the supply chain, while automated alerts notify relevant personnel of any deviations. This monitoring extends to humidity, light exposure, and other environmental factors that can impact product quality.
Read more: IoT Fleet Management: A Step-by-Step Implementation Guide for Software Development
5. Real-world Case Studies and Success Stories
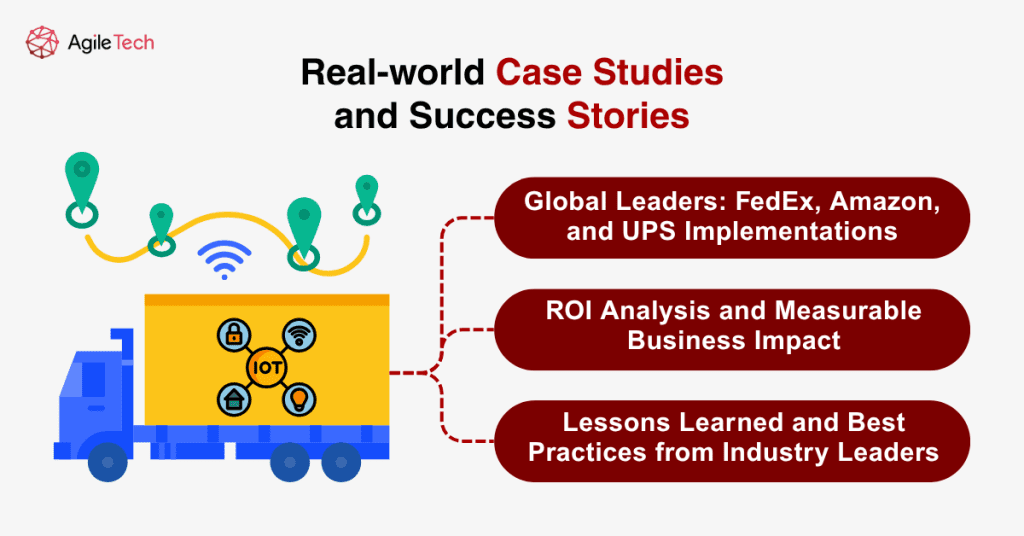
5.1. Global Leaders: FedEx, Amazon, and UPS Implementations
Leading logistics companies have invested heavily in IoT technologies with remarkable results. FedEx is utilising IoT technology through its SenseAware platform to enhance fleet management, especially for monitoring high-value and sensitive shipments. The system allows customers to monitor the condition of their packages from origin to destination and receive real-time updates on their route.
FedEx Dataworks, an initiative started in early 2020, epitomizes the organization’s dedication to data-driven insights, predictive analytics, and customer-centric solutions. The company has leveraged IoT alongside artificial intelligence and machine learning to create predictive logistics capabilities that anticipate and prevent delivery delays.
Amazon’s implementation of IoT spans its entire fulfillment network, from warehouse automation to last-mile delivery optimization. The company’s IoT-enabled robotic systems in fulfillment centers have reduced order processing times while improving accuracy rates. Similarly, UPS has deployed IoT sensors across its vehicle fleet and package handling facilities to optimize operations and improve service quality.
5.2. ROI Analysis and Measurable Business Impact
Companies implementing comprehensive IoT solutions report significant returns on investment. Operational cost reductions typically range from 15-25% within the first year of implementation, driven primarily by improved fuel efficiency, reduced maintenance costs, and enhanced labor productivity. Customer satisfaction improvements often exceed 30% due to better delivery reliability and enhanced visibility.
5.3. Lessons Learned and Best Practices from Industry Leaders
Successful IoT implementations share common characteristics: phased rollout strategies that minimize operational disruption, comprehensive employee training programs, and robust data security measures. Industry leaders emphasize the importance of selecting IoT platforms that integrate seamlessly with existing enterprise systems and provide scalable architectures for future expansion.
6. Challenges and Considerations in IoT Implementation
6.1. Data Security and Cybersecurity Concerns
The implementation of IoT requires robust measures to secure the vast amount of data collected from IoT devices. End-to-end encryption, stringent access controls, and regular security updates are essential to protect sensitive information from cyber threats and unauthorized access. The interconnected nature of IoT systems creates multiple potential entry points for malicious actors, requiring comprehensive security strategies.
6.2. System Interoperability and Integration Issues
Legacy systems integration presents significant challenges for many organizations. IoT platforms must communicate effectively with existing warehouse management systems, transportation management systems, and enterprise resource planning platforms. Ensuring seamless data flow between these systems requires careful planning and often significant customization.
6.3. Scalability and Infrastructure Requirements
IoT implementations must be designed for scalability from the outset. The infrastructure supporting IoT systems must handle exponential data growth as more devices come online. Cloud computing platforms provide scalable solutions, but organizations must plan for bandwidth requirements and data storage costs as their IoT networks expand.
6.4. Regulatory Compliance and Data Privacy
Data privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA impact how companies collect, store, and use IoT-generated data. Cross-border shipments add complexity as different regions have varying regulatory requirements. Companies must implement comprehensive data governance programs that ensure compliance while enabling operational benefits.
6.5. Initial Investment Costs and Budget Planning
IoT implementation requires significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and system integration. However, the rapid payback period typically justifies these costs within 12-18 months. Organizations should develop detailed business cases that account for both direct cost savings and revenue enhancement opportunities.
Read more: Unlocking the Power of IoT in Fleet Management System 2024
7. Future Trends and Emerging Technologies
7.1. AI and Machine Learning Integration with IoT
The convergence of AI and IoT creates unprecedented opportunities for autonomous logistics operations. Machine learning algorithms analyze IoT data streams to identify patterns and make predictions that enable proactive decision-making. This integration enables autonomous route optimization, predictive maintenance scheduling, and dynamic inventory management without human intervention.
7.2. Blockchain Technology in IoT Supply Chains
Blockchain technology enhances IoT implementations by providing immutable records of supply chain transactions and conditions. This combination creates tamper-proof audit trails that improve transparency and trust between supply chain partners. Smart contracts executed on blockchain platforms can automatically trigger payments and other actions based on IoT sensor data.
7.3. 5G Networks and Enhanced IoT Connectivity
5G networks enable new IoT applications that were previously impossible due to connectivity limitations. Ultra-low latency communications support real-time control of autonomous vehicles and robotic systems. Enhanced bandwidth supports high-resolution video monitoring and complex sensor arrays that provide unprecedented operational visibility.
7.4. Sustainability and Green IoT Solutions
Environmental sustainability drives the development of green IoT solutions that minimize energy consumption while maximizing operational efficiency. Solar-powered sensors, energy-efficient edge computing devices, and optimized routing algorithms that reduce carbon emissions represent growing areas of innovation.
8. IoT Implementation Guide for Businesses
8.1. Assessment and Planning Phase
Successful IoT implementation begins with a comprehensive assessment of current operations and identification of specific use cases that provide maximum value. Organizations should conduct pilot programs that demonstrate ROI before committing to full-scale implementation. This assessment phase should include evaluation of existing infrastructure, identification of integration requirements, and development of detailed implementation timelines.
8.2. Technology Selection and Vendor Evaluation
Technology selection requires careful evaluation of IoT platforms, device capabilities, and vendor support services. Organizations should prioritize solutions that offer open architectures, robust security features, and proven scalability. Vendor evaluation should include assessment of technical capabilities, industry experience, and long-term viability.
8.3. Phased Implementation Strategy and Timeline
Phased implementation strategies minimize operational risk while enabling organizations to learn and adapt throughout the deployment process. Initial phases should focus on high-impact, low-risk applications that demonstrate clear business value. Subsequent phases can expand functionality and coverage based on lessons learned from initial deployments.
8.4. Performance Measurement and ROI Tracking
Comprehensive performance measurement programs ensure that IoT implementations deliver expected benefits. Key performance indicators should include operational metrics such as on-time delivery rates, cost reduction achievements, and customer satisfaction improvements. Regular assessment enables organizations to optimize their IoT investments and identify opportunities for additional improvements.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things transportation revolution in transportation and logistics represents a fundamental transformation of how goods move through global supply chains. With market projections showing explosive growth and industry leaders demonstrating substantial returns on investment, the Internet of Things in logistics has moved from emerging technology to essential business capability.
The comprehensive benefits of IoT in logistics implementation, from real-time visibility and cost reduction to enhanced customer satisfaction and sustainability improvements, justify the initial investment and ongoing operational commitments required. As emerging technologies such as 5G, AI, and blockchain mature, the potential for even greater transformation through the Internet of Things and transportation continues to expand.
Organizations that embrace IoT in supply chain technology today position themselves for sustained competitive advantage in an increasingly complex and demanding marketplace. The question is no longer whether to implement the Internet of Things in logistics operations, but rather how quickly and comprehensively organizations can transform their supply chains to capture the full potential of this revolutionary IoT in transportation technology.
Success requires careful planning, phased implementation, and commitment to continuous improvement, but the rewards of operational excellence, cost optimization, and customer satisfaction make IoT implementation an essential strategic priority for logistics organizations in 2025 and beyond.