The True Cost of Telehealth Implementation and How to Lower It
Healthcare organizations investing in telehealth face complex cost structures beyond initial software purchases. Understanding these expenses and implementing strategic cost-reduction approaches can significantly improve return on investment while delivering quality patient care.
- 1. Understanding Telehealth Software and Services
- 2. Key Drivers of Telehealth Software Cost
- 3. How Much Does Telehealth Cost Overall?
- 4. Hidden Cost of Telehealth Implementation
- 5. Smart Ways to Cut Down Telehealth Implementation Costs
- 6. AgileTech’s Role in Cost-Effective Telehealth Integration
- 7. Conclusion
1. Understanding Telehealth Software and Services
What Telehealth Software Encompasses
The telehealth industry has experienced unprecedented growth, transforming how healthcare providers deliver patient care. The cost of telehealth implementation varies significantly based on the scope, features, and deployment model organizations choose. Modern telehealth software encompasses video conferencing capabilities, electronic health record integration, patient scheduling systems, and secure messaging platforms that collectively create comprehensive virtual care solutions.
Telehealth Service Cost Models
Telehealth service cost structures typically fall into three primary categories: subscription-based models, per-encounter pricing, and custom enterprise solutions. Subscription models offer predictable monthly or annual fees ranging from $50 to $500 per provider, depending on feature sets and user volumes. Per-encounter pricing charges healthcare organizations between $5 and $25 for each patient consultation, making it attractive for practices with variable patient volumes. Enterprise solutions require custom pricing negotiations based on organizational size, integration requirements, and specialized functionality needs.
Software versus Comprehensive Services
The distinction between telehealth software and comprehensive telehealth services is crucial for accurate cost planning. Basic telehealth software provides core video conferencing and communication tools, while full-service platforms include patient engagement features, clinical documentation systems, billing integration, and ongoing technical support. Organizations must evaluate whether they need simple communication tools or comprehensive digital health platforms that support entire patient care workflows.
Deployment Models and Their Cost Implications
Healthcare providers should also consider the difference between cloud-based and on-premises telehealth solutions. Cloud-based platforms typically offer lower upfront costs but involve ongoing subscription fees, while on-premises systems require significant initial capital investment but provide greater long-term cost control. The choice between these deployment models significantly impacts the overall cost of telehealth implementation and ongoing operational expenses.
Integration Capabilities and Cost Considerations
Integration capabilities represent another critical factor influencing telehealth software cost considerations. Platforms that seamlessly connect with existing electronic health records, practice management systems, and billing software often command premium pricing but deliver substantial efficiency gains. Organizations must weigh the higher initial investment against long-term operational savings when evaluating integrated versus standalone telehealth solutions.
2. Key Drivers of Telehealth Software Cost
User Capacity and Licensing Models
Several fundamental factors determine how much telehealth costs for healthcare organizations. Software licensing represents the most visible expense, but multiple underlying elements significantly influence total implementation costs. Understanding these drivers enables organizations to make informed decisions about platform selection and deployment strategies.
User capacity requirements directly impact telehealth software cost structures. Most vendors price their solutions based on concurrent users, licensed providers, or total organizational size. Small practices with fewer than ten providers might spend $2,000 to $10,000 annually on telehealth software, while large health systems could invest $50,000 to $500,000 or more, depending on their scale and requirements. Organizations must carefully assess their actual usage patterns to avoid over-provisioning expensive licenses.
Feature Complexity and Functionality
Feature complexity and functionality breadth significantly affect pricing models. Basic video conferencing solutions cost substantially less than comprehensive platforms offering advanced clinical documentation, automated patient reminders, prescription management, and analytics dashboards. Healthcare organizations should prioritize essential features initially and plan phased implementation approaches to manage costs while building telehealth capabilities progressively.
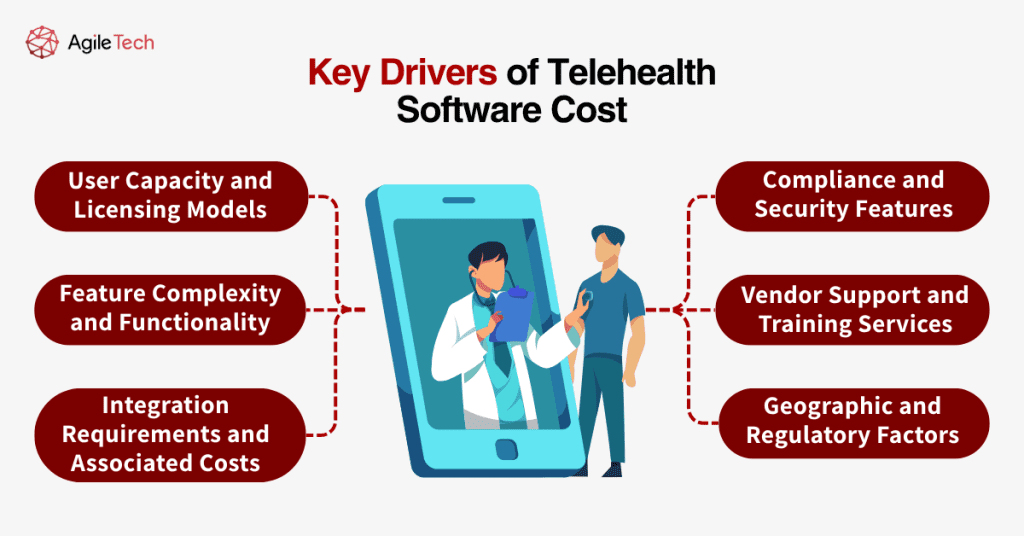
Integration Requirements and Associated Costs
Integration requirements represent a major cost driver that organizations often underestimate. Telehealth platforms that connect with multiple existing systems require custom development work, API licensing fees, and ongoing maintenance contracts. Simple integrations might add 10-20% to base software costs, while complex multi-system integrations can double or triple implementation expenses. Organizations should budget for integration costs early in their planning process.
Compliance and Security Features
Compliance and security features essential for healthcare applications add significant value but increase telehealth software costs. HIPAA-compliant platforms, advanced encryption capabilities, audit logging systems, and regulatory reporting tools command premium pricing compared to general-purpose video conferencing solutions. Healthcare organizations cannot compromise on these features, making compliance-ready platforms a necessary investment despite higher costs.
Vendor Support and Training Services
Vendor support and training services influence total cost considerations. Some vendors include comprehensive training, implementation support, and ongoing technical assistance in their base pricing, while others charge separately for these services. Organizations should evaluate support offerings carefully, as inadequate training can lead to poor adoption rates and reduced return on investment regardless of software quality.
Geographic and Regulatory Factors
Geographic and regulatory factors also impact telehealth service cost structures. Platforms operating across multiple states or countries must comply with varying licensing requirements, data sovereignty regulations, and technical standards. These compliance costs are typically reflected in software pricing, particularly for organizations with multi-jurisdictional operations.
3. How Much Does Telehealth Cost Overall?
Initial Setup and Implementation Costs
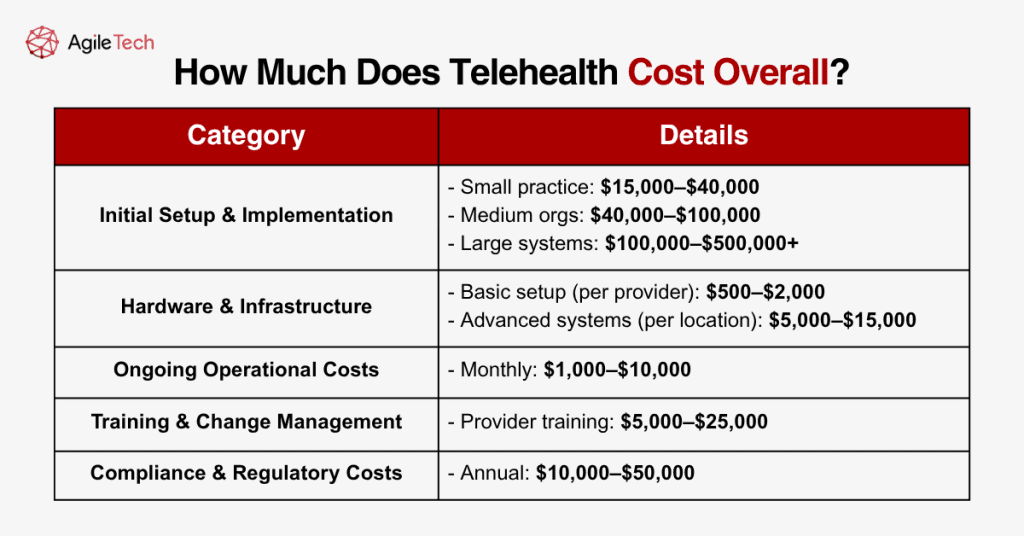
Determining comprehensive telehealth implementation costs requires examining expenses beyond software licensing fees. Healthcare organizations typically invest between $15,000 and $150,000 in their first year of telehealth deployment, with ongoing annual costs ranging from $10,000 to $100,000, depending on scale and sophistication levels.
Initial setup costs encompass software licensing, hardware procurement, network infrastructure upgrades, and implementation services. Small practices might spend $15,000 to $40,000 on initial telehealth deployment, including basic software licenses, tablets or computers for providers, and professional implementation assistance. Medium-sized organizations typically invest $40,000 to $100,000, while large health systems often require $100,000 to $500,000 or more for comprehensive telehealth implementations.
Hardware and Infrastructure Requirements
Hardware expenses vary significantly based on existing infrastructure and quality requirements. Basic telehealth setups require high-definition cameras, quality microphones, and reliable internet connections, typically costing $500 to $2,000 per provider workstation. Advanced implementations might include specialized medical devices, diagnostic equipment, and professional-grade audio-visual systems that can cost $5,000 to $15,000 per clinical location.
Ongoing Operational Expenses
Ongoing operational costs include software subscription fees, technical support contracts, bandwidth expenses, and staff time for system administration. Monthly operational expenses typically range from $1,000 to $10,000 for most healthcare organizations, depending on user volumes and service levels. These recurring costs accumulate to substantial annual expenses that organizations must budget for sustainable telehealth operations.
Training and Change Management Investments
Training and change management represent often-overlooked cost components that significantly impact implementation success. Comprehensive provider training programs cost $5,000 to $25,000, depending on organization size and complexity. Patient education initiatives, workflow redesign projects, and staff adoption programs add additional expenses but prove essential for maximizing telehealth investment returns.
Compliance and Regulatory Costs
Compliance and regulatory costs add another layer to overall telehealth expenses. Organizations must invest in privacy impact assessments, security audits, policy development, and ongoing compliance monitoring. These activities typically cost $10,000 to $50,000 annually but remain necessary for maintaining regulatory compliance and avoiding costly violations.
Return on Investment Considerations
Lost productivity during implementation phases represents an indirect but significant cost factor. Healthcare organizations typically experience temporary efficiency reductions as staff learn new systems and adjust workflows. Planning for 10-20% productivity impacts during the first three to six months helps organizations set realistic expectations and budget for transition periods.
The return on investment timeline for telehealth implementations varies considerably based on deployment scope and organizational efficiency. Most healthcare organizations begin seeing positive returns within 12 to 24 months through increased patient access, reduced no-show rates, and improved provider efficiency. Organizations with well-planned implementations and strong change management programs often achieve break-even points within 6 to 12 months.
4. Hidden Cost of Telehealth Implementation
Security and Compliance Infrastructure
Healthcare organizations frequently encounter unexpected expenses that significantly impact their total cost of telehealth implementation. These hidden costs can increase project budgets by 30-50% if not properly anticipated and planned. Understanding common hidden expenses enables organizations to develop more accurate budgets and avoid costly surprises during implementation.
Data security and compliance infrastructure represent a major hidden cost category. Organizations must invest in advanced cybersecurity measures, including endpoint protection, network monitoring, and incident response capabilities specifically designed for healthcare environments. These security investments typically cost $10,000 to $50,000 annually but remain essential for protecting patient data and maintaining regulatory compliance.
Network Infrastructure and Bandwidth Requirements
Bandwidth and network infrastructure upgrades often require substantial unexpected investments. High-quality video conferencing demands significant internet bandwidth, and many healthcare facilities discover that their existing connections cannot support multiple concurrent telehealth sessions. Network upgrades, redundant internet connections, and quality-of-service configurations can cost $20,000 to $100,000, depending on facility size and current infrastructure state.
Staff Productivity and Transition Costs
Staff productivity losses during transition periods represent another significant hidden cost. Healthcare providers typically require 3-6 months to achieve full proficiency with new telehealth systems, during which patient throughput and efficiency may decline. Organizations should budget for temporary productivity reductions and consider additional staffing or extended hours to maintain patient care levels during transition periods.
Integration Complexities
Integration complexities frequently exceed initial estimates, particularly for organizations with multiple existing systems. Custom API development, data migration projects, and workflow synchronization efforts often require additional consulting services and extended timelines. These integration costs can add 25-100% to original software licensing expenses, depending on system complexity.
Patient Support and Technology Assistance
Patient technology support creates ongoing operational expenses that organizations often overlook. Many patients require assistance with telehealth platform access, device configuration, and troubleshooting technical issues. Establishing patient support capabilities typically requires dedicated staff time or outsourced call center services costing $5,000 to $20,000 annually.
Multi-Jurisdictional Licensing and Compliance
Licensing and regulatory compliance across multiple jurisdictions adds complexity and cost for organizations serving diverse geographic areas. Each state or country may have different telehealth licensing requirements, creating ongoing compliance costs and administrative overhead. Legal consulting fees for multi-state compliance typically range from $10,000 to $50,000 annually.
Technology Refresh and Maintenance
Device replacement and technology refresh cycles represent long-term hidden costs. Telehealth hardware typically requires replacement every 3-5 years, and software platforms may require periodic upgrades or migrations. Organizations should budget 15-20% of initial hardware costs annually for maintenance and replacement to ensure reliable telehealth operations.
Quality Assurance and Performance Monitoring
Quality assurance and performance monitoring systems add operational complexity and cost. Healthcare organizations must implement systems to monitor call quality, track technical issues, and ensure consistent patient experiences. These monitoring capabilities typically cost $5,000 to $15,000 annually but prove essential for maintaining service quality standards.
Organizational Change Management
Change management and organizational transformation initiatives represent substantial hidden investments. Successful telehealth implementations require cultural changes, new workflow development, and ongoing staff engagement programs. These change management activities often cost $15,000 to $75,000 but significantly impact implementation success rates.
5. Smart Ways to Cut Down Telehealth Implementation Costs
Phased Implementation Strategies
Healthcare organizations can substantially reduce their cost of telehealth implementation through strategic planning and smart procurement approaches. Implementing cost-reduction strategies from the beginning helps organizations maximize their telehealth investment while maintaining quality patient care capabilities.
Phased implementation approaches enable organizations to spread costs over time while building telehealth capabilities progressively. Starting with basic video conferencing for a subset of providers allows organizations to learn and refine their approaches before investing in comprehensive platforms. This phased approach typically reduces first-year costs by 40-60% while providing valuable implementation experience.
Leveraging Existing Infrastructure
Leveraging existing technology infrastructure eliminates significant hardware and network investment requirements. Organizations should conduct thorough technology assessments to identify reusable equipment, adequate bandwidth capacity, and compatible systems. Maximizing existing infrastructure utilization can reduce implementation costs by 20-40% compared to complete technology refresh approaches.
Strategic Vendor Negotiations
Negotiating volume discounts and multi-year contracts with telehealth software vendors provides substantial cost savings opportunities. Healthcare organizations can often secure 15-30% discounts by committing to longer contract terms or purchasing licenses for multiple providers simultaneously. Group purchasing organizations and healthcare consortia offer additional negotiating leverage for smaller organizations.
Comprehensive Vendor Packages
Selecting vendors that provide comprehensive training and support services within base pricing eliminates additional consulting expenses. Some telehealth platforms include implementation services, user training, and ongoing technical support in their standard offerings, while others charge separately for these services. Choosing all-inclusive vendors can reduce total implementation costs by $10,000 to $50,000.
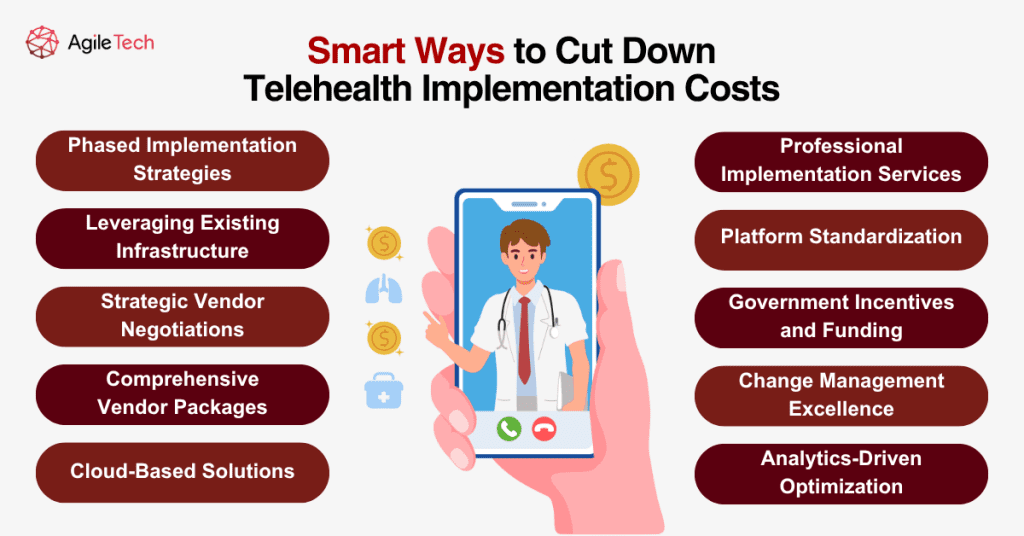
Cloud-Based Solutions
Utilizing cloud-based platforms reduces upfront infrastructure investments and ongoing maintenance costs. Cloud deployments eliminate server hardware purchases, data center requirements, and internal IT support overhead. Organizations typically save 30-50% on infrastructure costs by choosing cloud-based telehealth solutions over on-premises implementations.
Professional Implementation Services
Partnering with experienced telehealth implementation specialists can prevent costly mistakes and accelerate deployment timelines. Professional implementation services might seem expensive initially, but they often save money by avoiding common pitfalls, reducing training time, and ensuring optimal system configuration. The cost of professional services typically pays for itself through faster implementation and improved adoption rates.
Platform Standardization
Standardizing on single-vendor solutions reduces integration complexity and ongoing support costs. Organizations using multiple telehealth platforms face higher training costs, integration expenses, and administrative overhead. Consolidating on comprehensive single-vendor solutions typically reduces total cost of ownership by 20-35% over multi-vendor approaches.
Government Incentives and Funding
Taking advantage of government incentives and funding programs can significantly offset telehealth implementation costs. Various federal and state programs offer grants, tax incentives, and reimbursement opportunities for healthcare organizations implementing telehealth capabilities. These funding sources can cover 25-75% of implementation costs for qualifying organizations.
Change Management Excellence
Implementing robust change management programs improves adoption rates and reduces productivity losses during transitions. Well-designed training programs, clear communication strategies, and strong leadership support minimize the hidden costs associated with poor adoption and extended learning curves. Investing in change management typically reduces total implementation costs by improving efficiency and reducing support requirements.
Analytics-Driven Optimization
Selecting platforms with robust analytics and reporting capabilities enables organizations to continually optimize their telehealth operations. Data-driven insights help identify usage patterns, cost optimization opportunities, and efficiency improvements that reduce long-term operational expenses. Analytics capabilities typically pay for themselves through operational improvements within 6-12 months.
6. AgileTech’s Role in Cost-Effective Telehealth Integration
Comprehensive Cost Optimization Approach
AgileTech specializes in delivering cost-effective telemedicine software development solutions that reduce total project expenses by 25-40% compared to traditional implementation approaches. Our methodology focuses on leveraging existing organizational infrastructure and systems to minimize custom development requirements and integration costs.
Modular Implementation Strategy
Our modular platform architecture enables organizations to implement telehealth capabilities progressively, spreading costs over time while building functionality incrementally. This phased approach allows healthcare organizations to start with essential features and expand capabilities as their telehealth programs mature, significantly reducing first-year implementation costs.
All-Inclusive Service Model
AgileTech’s comprehensive training and support services are included in base implementation pricing, eliminating hidden costs that often surprise healthcare organizations during telehealth deployment. Our standard service offerings include end-user training, technical documentation, implementation support, and ongoing assistance without additional consulting expenses.
Cloud-Native Architecture Benefits
Our cloud-native platform eliminates infrastructure investments while providing enterprise-grade security and compliance capabilities. This approach reduces hardware costs, maintenance requirements, and internal IT support overhead by 40-60% compared to on-premises implementations.
Seamless Integration Capabilities
The integration capabilities built into AgileTech’s platform connect with existing electronic health records, practice management systems, and billing platforms without requiring expensive custom development work. Our pre-built integrations reduce integration costs by 50-70% while accelerating implementation timelines.
Transparent Pricing and Compliance
AgileTech’s transparent pricing model eliminates surprise costs and hidden fees through fixed-price implementation packages that include software licensing, integration services, training, and ongoing support. Our dedicated healthcare compliance team ensures all implementations meet HIPAA requirements and industry security standards without requiring additional compliance consulting services.
Healthcare organizations partnering with AgileTech typically achieve 40-60% faster implementation timelines, reducing productivity losses and transition costs associated with extended implementation periods. Our streamlined deployment methodology minimizes disruption to patient care while accelerating time-to-value for telehealth investments.
7. Conclusion
As telemedicine becomes an essential component of modern healthcare delivery, understanding the true cost of telehealth implementation is crucial for strategic planning. From software development to service deployment and long-term maintenance, the expenses can vary widely based on functionality, compliance, and infrastructure choices.
However, with careful planning, such as building an MVP, leveraging cloud solutions, and outsourcing development to trusted partners like AgileTech, healthcare providers can reduce upfront investments while achieving scalable, compliant, and patient-friendly telehealth systems.
By prioritizing flexibility, integration, and user experience, organizations can not only lower telehealth software costs but also maximize returns through improved care delivery, operational efficiency, and patient engagement.