EMR Integration Explained: How to Seamlessly Connect Your Healthcare Systems
EMR integration connects disparate healthcare systems, enabling seamless data flow between electronic medical records platforms. This comprehensive guide explores implementation strategies, benefits, challenges, and vendor selection criteria to optimize your healthcare technology infrastructure and improve patient care outcomes.
- 1. What is EMR Integration? Why It Matters in Modern Healthcare?
- 2. Key Benefits of EMR Integration
- 3. Common Challenges in EMR Data Integration and How to Overcome Them
- 4. 7 Steps for Successful EMR System Integration
- 5. How Much Does EMR System Integration Cost?
- 6. How to Choose the Right EMR Integration Vendor?
- 7. Custom Integrated EMR Software Solutions by AgileTech
1. What is EMR Integration? Why It Matters in Modern Healthcare?
Electronic Medical Records (EMR) integration refers to the process of connecting various digital systems used in healthcare to ensure smooth and secure data exchange. It allows disparate healthcare platforms, such as laboratory information systems, radiology software, pharmacy databases, and billing systems, to communicate with the EMR efficiently. EMR and EHR integration both aim to streamline healthcare data access and interoperability.
This connectivity fosters a more comprehensive view of a patient’s medical history, ensuring improved clinical decisions, reduced manual errors, and enhanced patient outcomes. As digital transformation accelerates in healthcare, EMR integration is no longer optional, it is essential for optimized operations.
EMR System Integration Examples
- Telehealth Platform Integration: Telehealth platform integration represents one of the most impactful EMR system integration examples in modern healthcare delivery. When telehealth systems connect seamlessly with electronic medical records, healthcare providers can access complete patient histories during virtual consultations, document encounter notes directly into the EMR, and maintain continuity of care across in-person and remote interactions. This integration proved particularly valuable during the COVID-19 pandemic, enabling healthcare organizations to maintain patient care while adhering to social distancing requirements.
- Hospital Network Integration: Hospital networks frequently integrate their primary EMR platforms with specialized departmental systems such as radiology information systems, laboratory information management systems, and pharmacy management platforms. This enables seamless data flow between departments and improved clinical workflows, including pharmacy records via a pharmacy management system.
- Ambulatory Care Integration: Ambulatory care practices often integrate their EMR systems with practice management software, patient portal applications, and telehealth platforms. This comprehensive integration allows patients to schedule appointments online, access medical records through patient portal software, and participate in virtual consultations while maintaining continuity with their primary care records.
- Telemedicine Integration Solutions: Telemedicine integration extends beyond basic video conferencing to include remote monitoring capabilities, digital diagnostic tools, and mobile health applications. Integrated telemedicine solutions allow healthcare providers to receive real-time patient data from wearable devices, monitor chronic conditions remotely, and adjust treatment plans based on continuous health metrics. This level of integration transforms traditional healthcare delivery models by enabling proactive care management and reducing the need for frequent in-person visits.
2. Key Benefits of EMR Integration
Enhanced Clinical Decision-Making
EMR integration delivers substantial advantages by providing healthcare providers with comprehensive patient information aggregated from multiple sources. This enables more informed treatment decisions as physicians can review complete medication histories, identify potential drug interactions, analyze trends in vital signs and laboratory results, and access specialist consultation notes within a single integrated interface.
Improved Care Coordination
Healthcare teams gain real-time access to shared patient information, enabling seamless communication between primary care physicians, specialists, nurses, therapists, and other healthcare professionals. EMR data integration enables effective collaboration on treatment plans, collective monitoring of patient progress, and consistent implementation of care protocols across different departments and care settings.
Operational Efficiency Improvements
Integrated EMR systems eliminate duplicate data entry requirements, automate routine tasks, and standardize processes across departments. Healthcare staff spend less time searching for patient information and more time focused on direct patient care activities. Administrative processes such as insurance verification, prior authorization requests, and billing submissions become more efficient through automated data sharing. Integrated with electronic medication administration record software (eMAR), EMRs enhance real-time med tracking and reduce errors.
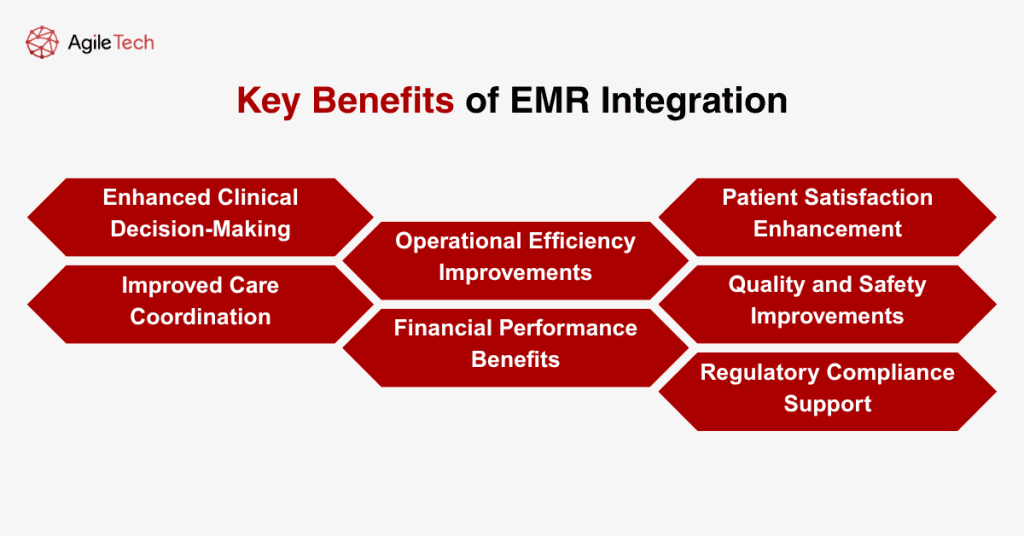
Financial Performance Benefits
EMR integration supports improved revenue cycle management and cost reduction opportunities. Healthcare organizations experience more accurate coding and billing processes, faster claims processing, reduced claim denials, and improved cash flow through automated billing workflows. Additionally, integrated systems help identify cost-saving opportunities through reduced duplicate testing and optimized resource utilization.
Patient Satisfaction Enhancement
Patients benefit from enhanced care experiences and better communication through integrated EMR systems. Healthcare providers can spend more quality time with patients rather than managing disparate systems. Patients experience reduced wait times, fewer redundant questions about medical history, and more coordinated care experiences through unified digital platforms.
Quality and Safety Improvements
Integrated EMR systems implement automated alerts for potential medication interactions, allergy warnings, and clinical guideline reminders. Healthcare organizations can monitor quality metrics more effectively, identify trends in patient outcomes, and implement targeted improvement initiatives based on comprehensive data analysis. Emerging tech like computer vision in healthcare supports visual diagnostics directly within EMRs.
Regulatory Compliance Support
Healthcare organizations can generate required quality reports, track meaningful use metrics, and demonstrate compliance with various regulatory requirements through automated data collection and analysis. Integrated systems support audit preparation and help organizations maintain consistent documentation standards across all departments.
3. Common Challenges in EMR Data Integration and How to Overcome Them
Data Standardization Challenges
Healthcare organizations often operate legacy systems that use different data formats, coding systems, and terminology standards. Clinical information may be stored using various medical coding systems such as ICD-10, CPT, SNOMED CT, or proprietary classification schemes.
Overcoming data standardization challenges requires comprehensive data mapping exercises, implementation of healthcare interoperability standards such as HL7 FHIR, and development of data transformation protocols that ensure consistent information representation across integrated systems.
System Compatibility Issues
Legacy healthcare systems may lack modern application programming interfaces or use outdated communication protocols that complicate integration efforts. Healthcare organizations can address compatibility challenges by implementing middleware solutions that serve as translation layers between disparate systems, upgrading legacy systems to support modern integration standards, or partnering with experienced EMR integration software vendors who specialize in connecting diverse healthcare technologies.
Security and Privacy Concerns
EMR integration projects must maintain strict compliance with HIPAA regulations, state privacy laws, and other healthcare data protection requirements while enabling appropriate information access for authorized users.
Healthcare organizations should implement comprehensive security frameworks that include data encryption, access controls, audit logging, and regular security assessments. Establishing clear data governance policies and providing ongoing staff training on privacy protection requirements helps maintain regulatory compliance.
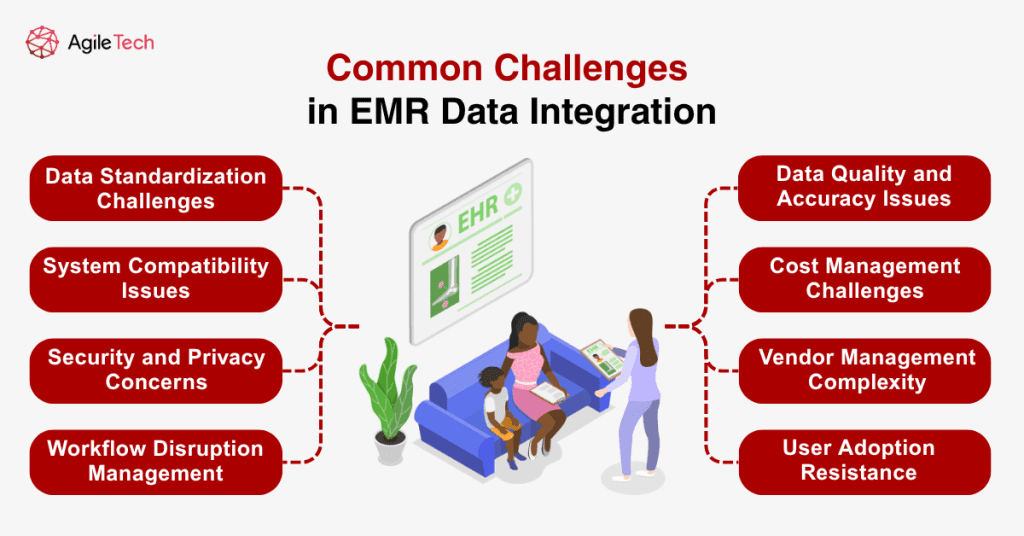
Workflow Disruption Management
Healthcare providers may experience temporary system downtime, modified workflows, or learning curves associated with new integrated interfaces. Successful organizations minimize workflow disruption through phased implementation approaches, comprehensive staff training programs, and the development of contingency plans for system failures. Change management strategies that involve frontline staff in integration planning help ensure smooth transitions to integrated EMR environments.
Data Quality and Accuracy Issues
Inconsistent data entry practices, incomplete records, or outdated information can compromise the reliability of integrated EMR systems. Healthcare organizations should implement data quality assessment processes, establish data governance committees, and develop data cleansing procedures to improve information accuracy before and after integration. Regular data quality audits and standardized data entry protocols help maintain high-quality information.
Cost Management Challenges
Healthcare organizations must budget for software licensing, hardware infrastructure, professional services, staff training, and ongoing maintenance costs. Developing detailed project budgets, exploring phased implementation approaches, and evaluating return on investment projections help organizations manage integration costs effectively. Partnering with experienced vendors who offer transparent pricing models can help control project expenses.
Vendor Management Complexity
Coordinating activities between different vendors, managing contract terms, and ensuring accountability for project deliverables requires sophisticated project management capabilities. Healthcare organizations should establish clear vendor management processes, define specific performance metrics and service level agreements, and maintain regular communication channels with all project stakeholders.
User Adoption Resistance
Healthcare staff may resist changes to established workflows or express concerns about increased complexity. Successful organizations address user adoption challenges through comprehensive change management programs that include stakeholder engagement, user-centered design principles, and ongoing support resources. Involving end users in system design decisions and providing adequate training opportunities help build organizational support for integrated EMR systems.
4. 7 Steps for Successful EMR System Integration
Implementing a successful EMR system integration requires a systematic approach that addresses technical, organizational, and strategic considerations throughout the project lifecycle. Healthcare organizations that follow structured implementation methodologies achieve better outcomes, reduced costs, and smoother transitions to integrated EMR environments.
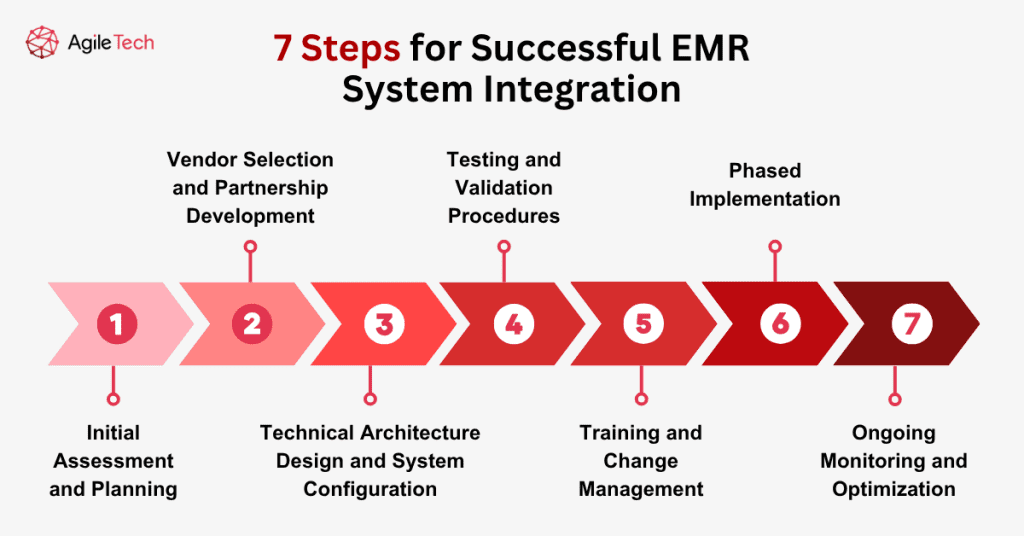
Step 1: Initial Assessment and Planning
The initial assessment and planning phase establishes the foundation for successful EMR integration by identifying current system capabilities, defining integration objectives, and developing comprehensive implementation strategies. Healthcare organizations should conduct thorough inventories of existing systems, document current workflows, and assess technical infrastructure capabilities. This assessment phase should include stakeholder interviews, workflow analysis, and gap identification to understand integration requirements fully.
During the planning phase, healthcare organizations must define specific integration objectives, establish success metrics, and develop realistic timelines for implementation. Integration goals should align with broader organizational objectives such as improved patient care, operational efficiency, or regulatory compliance. Clear success metrics enable healthcare organizations to measure integration effectiveness and identify areas requiring additional attention or optimization.
Step 2: Vendor Selection and Partnership Development
Vendor selection and partnership development represent critical steps that significantly impact integration success. Healthcare organizations should evaluate potential integration partners based on technical capabilities, industry experience, regulatory compliance expertise, and long-term viability. The vendor selection process should include comprehensive technical evaluations, reference checks, and detailed contract negotiations that establish clear expectations, deliverables, and support requirements.
Effective vendor partnerships extend beyond initial implementation to include ongoing support, system maintenance, and future enhancement capabilities. Healthcare organizations should establish clear communication protocols, escalation procedures, and performance monitoring mechanisms to ensure that vendor relationships continue to deliver value throughout the integration lifecycle.
Step 3: Technical Architecture Design and System Configuration
Technical architecture design and system configuration form the technological foundation that enables seamless data flow between integrated systems. Healthcare organizations must develop comprehensive integration architectures that account for data security, system performance, scalability requirements, and regulatory compliance. This phase includes database design, interface development, security implementation, and performance optimization.
System configuration should incorporate industry best practices for data exchange, error handling, and system monitoring. Healthcare organizations should implement robust logging capabilities, automated monitoring systems, and alert mechanisms that provide early warning of integration issues or performance problems.
Step 4: Testing and Validation Procedures
Testing and validation procedures ensure that integrated systems function correctly and meet defined requirements before full implementation. Comprehensive testing should include unit testing of individual components, integration testing of system interactions, performance testing under realistic load conditions, and user acceptance testing with actual healthcare staff.
Testing procedures should simulate realistic clinical scenarios, validate data accuracy and completeness, and verify that integrated systems maintain appropriate security and compliance standards. Healthcare organizations should develop detailed test plans, establish acceptance criteria, and document all testing results for future reference and regulatory compliance purposes.
Step 5: Training and Change Management
Training and change management initiatives prepare healthcare staff for a successful transition to integrated systems and workflows. Comprehensive training programs should address technical system usage, workflow changes, and new procedures that result from integration implementation. Training should be tailored to different user roles and include hands-on practice opportunities with integrated systems.
Change management strategies should address potential resistance, communicate integration benefits clearly, and provide ongoing support as staff adapt to new processes. Healthcare organizations should identify system champions, establish feedback mechanisms, and maintain open communication channels to address concerns and gather improvement suggestions.
Step 6: Phased Implementation
Phased implementation approaches reduce risk and allow for gradual system optimization by implementing integration capabilities incrementally rather than attempting complete system integration simultaneously. Phased approaches enable healthcare organizations to validate integration functionality, address issues promptly, and make adjustments based on real-world usage experience.
Each implementation phase should include specific objectives, success criteria, and evaluation procedures that inform subsequent phases. Healthcare organizations should maintain parallel systems during transition periods and develop rollback procedures in case integration issues require temporary system reversion.
Step 7: Ongoing Monitoring and Optimization
Ongoing monitoring and optimization ensure that integrated systems continue to deliver expected benefits and adapt to changing organizational needs. Healthcare organizations should establish performance monitoring protocols, regular system maintenance procedures, and continuous improvement processes that identify optimization opportunities.
Monitoring activities should track system performance, data quality, user satisfaction, and business outcomes to ensure that integration continues to meet organizational objectives. Regular system reviews and optimization initiatives help healthcare organizations maximize integration benefits and adapt to evolving requirements.
5. How Much Does EMR System Integration Cost?
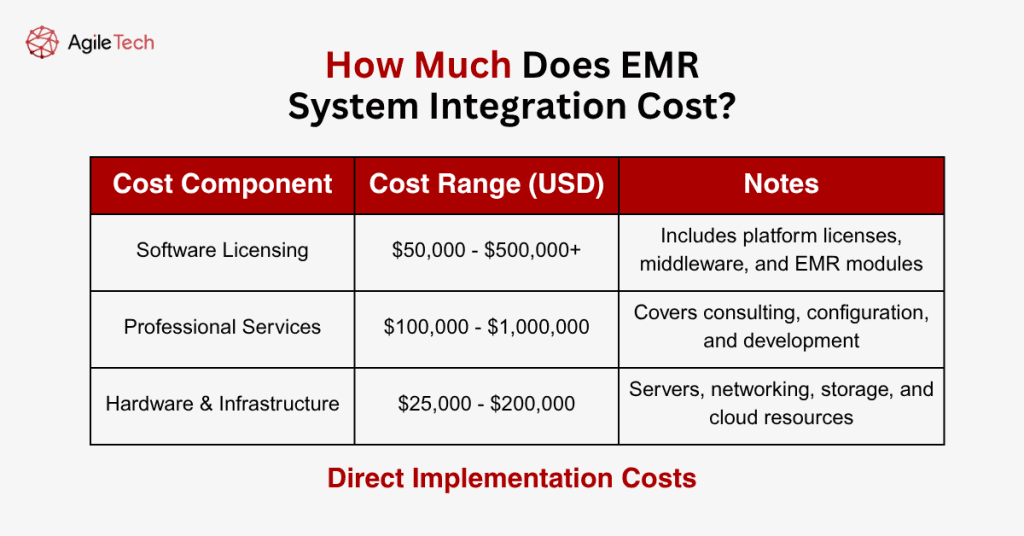
Direct Implementation Costs
- Software Licensing Expenses: Software licensing represents a major cost component for EMR integration projects, including integration platform licenses, middleware solutions, and additional EMR modules. Integration software costs typically range from $50,000 to $500,000 for mid-sized healthcare organizations, depending on the number of systems being integrated and the complexity of data exchange requirements. Enterprise-level healthcare organizations may invest $1 million or more in software licensing costs.
- Professional Services and Consulting: Professional services expenses include consulting fees for integration specialists, project management services, system configuration activities, and custom development work. Healthcare organizations typically spend $100,000 to $1 million on professional services, depending on project complexity and the level of customization required. Organizations with limited internal IT capabilities may require more extensive professional services support.
- Hardware and Infrastructure Investment: Hardware and infrastructure costs encompass servers, network equipment, storage systems, and cloud computing resources required to support integrated EMR environments. Hardware investments typically range from $25,000 to $200,000 for most healthcare organizations, depending on existing infrastructure capabilities and integration architecture requirements.
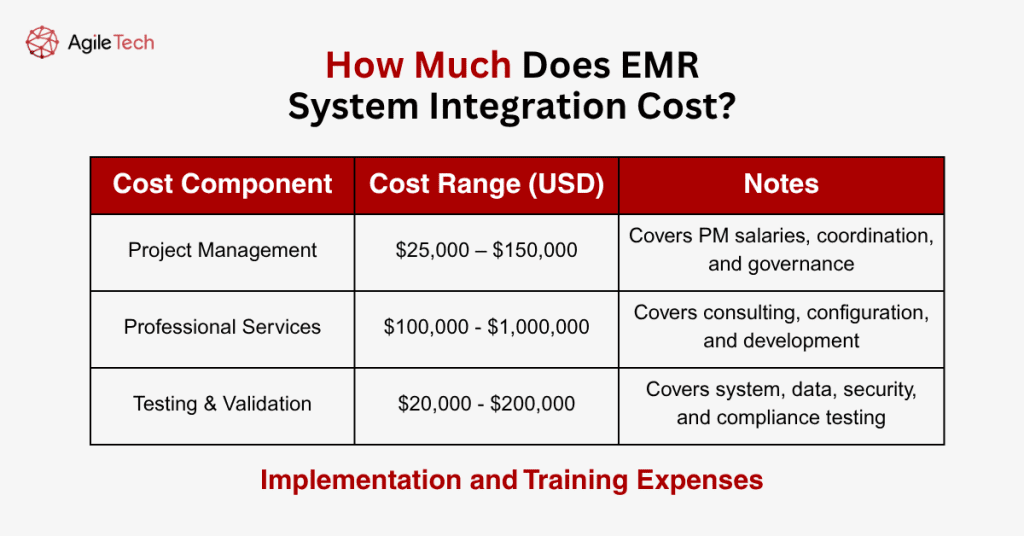
Implementation and Training Expenses
- Staff Training and Education: Training costs include expenses for educating healthcare personnel on integrated EMR workflows, system interfaces, and modified procedures. Training expenses typically range from $10,000 to $100,000, depending on organization size and the extent of workflow changes. Comprehensive training programs that include role-specific instruction and hands-on practice sessions require larger investments but generally produce better user adoption outcomes.
- Project Management Costs: Project management expenses encompass dedicated project manager salaries, governance activities, and coordination efforts required throughout integration initiatives. Healthcare organizations typically allocate 10-15% of total project budgets for project management activities, representing $25,000 to $150,000 for most integration projects.
- Testing and Validation: Testing and validation costs include expenses for system testing, data validation, security assessments, and compliance verification activities. Testing expenses typically represent 15-20% of total technical implementation costs, ranging from $20,000 to $200,000, depending on project complexity.
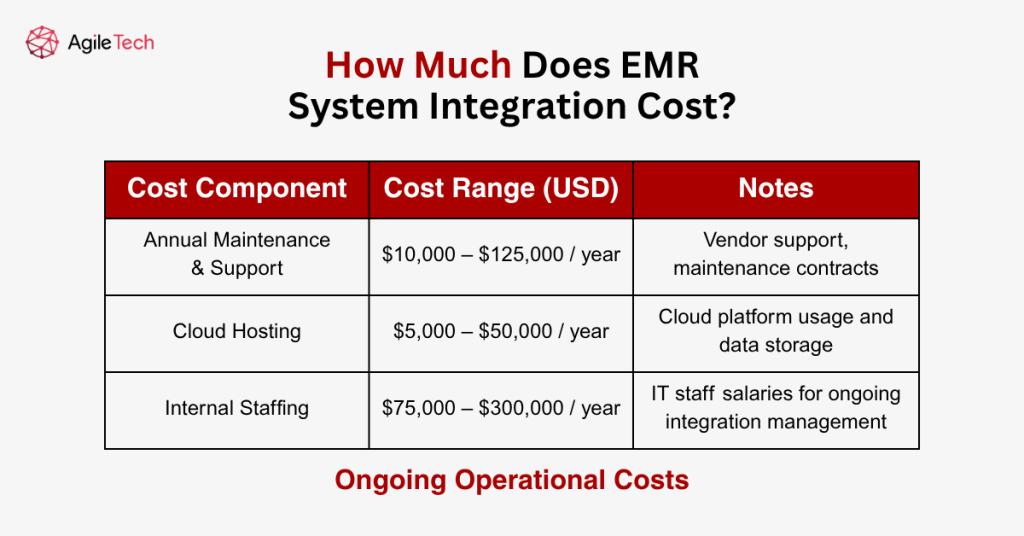
Ongoing Operational Costs
- Annual Maintenance and Support: Annual maintenance and support expenses include software maintenance fees, vendor support contracts, and ongoing technical support services. Maintenance costs typically range from 15-25% of initial software licensing fees annually, representing $10,000 to $125,000 per year for most healthcare organizations.
- Cloud Computing and Hosting: Cloud computing and hosting expenses apply to organizations utilizing cloud-based integration platforms or hosting integrated systems in external data centers. Cloud costs vary based on usage patterns and data storage requirements, typically ranging from $5,000 to $50,000 annually for mid-sized healthcare organizations.
- Internal Staffing Requirements: Internal staffing costs include salaries for IT personnel dedicated to managing and maintaining integrated EMR systems. Healthcare organizations typically require 1-3 full-time equivalent IT professionals to support comprehensive EMR integration environments, representing $75,000 to $300,000 in annual staffing costs.
6. How to Choose the Right EMR Integration Vendor?
Selecting the appropriate EMR integration vendor represents a critical decision that significantly impacts project success, long-term system performance, and overall return on investment. Healthcare organizations must evaluate potential vendors across multiple dimensions, including technical capabilities, industry experience, implementation methodologies, and ongoing support services to identify partners that align with their specific requirements and organizational objectives.
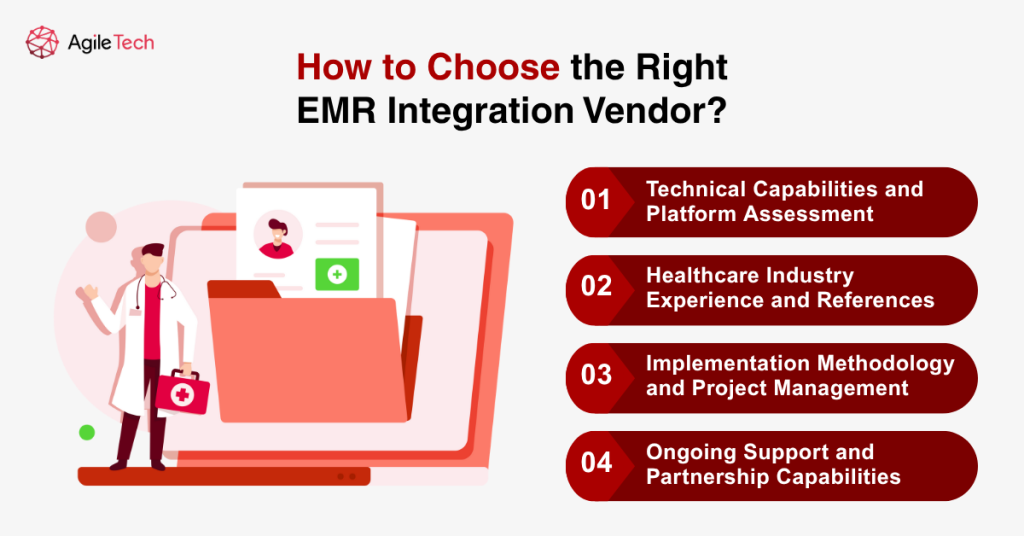
Technical Capabilities and Platform Assessment
EMR integration vendors should demonstrate comprehensive technical capabilities that address current integration requirements while providing scalability for future expansion. Healthcare organizations should evaluate vendor platforms for support of healthcare interoperability standards such as HL7 FHIR, CCDA, and DICOM, ensuring compatibility with existing EMR systems and compliance with industry best practices. Vendor platforms should offer flexible integration approaches, including real-time interfaces, batch processing capabilities, and support for various data formats and communication protocols.
API management capabilities represent essential technical requirements for modern EMR integration platforms. Vendors should provide robust API development tools, comprehensive documentation, and management interfaces that enable healthcare organizations to create, monitor, and maintain integration interfaces effectively. Advanced API management features such as rate limiting, authentication management, and usage analytics support scalable integration architectures and help organizations maintain system performance as integration complexity grows.
Data transformation and mapping capabilities enable vendors to handle the complex data conversion requirements inherent in healthcare integration projects. Vendor platforms should provide graphical mapping tools, support for complex data transformations, and validation capabilities that ensure data accuracy and consistency across integrated systems. Healthcare organizations should evaluate vendor capabilities for handling clinical terminology mapping, unit conversions, and data standardization requirements specific to their integration scenarios.
Security and compliance features represent non-negotiable requirements for healthcare integration vendors. Vendor platforms must demonstrate compliance with HIPAA regulations, support data encryption in transit and at rest, and provide comprehensive audit logging capabilities. Healthcare organizations should verify vendor security certifications, review compliance documentation, and evaluate security controls for data access, system monitoring, and incident response procedures.
Healthcare Industry Experience and References
Vendor experience within the healthcare industry provides valuable insights into their understanding of clinical workflows, regulatory requirements, and healthcare-specific integration challenges. Healthcare organizations should prioritize vendors with extensive healthcare client portfolios, demonstrated experience with similar integration projects, and a deep understanding of healthcare interoperability requirements. Vendor case studies and client testimonials provide evidence of successful integration implementations and lessons learned from previous projects to check if they can ensure compatibility with broader healthcare ERP platforms to streamline operations.
Reference checking represents a critical component of vendor evaluation, enabling healthcare organizations to validate vendor claims and gather insights from organizations with similar integration requirements. Healthcare organizations should request references from clients with comparable organizational size, technical complexity, and integration scope. Reference discussions should explore project timeline adherence, problem resolution capabilities, ongoing support quality, and overall satisfaction with vendor services.
Healthcare compliance expertise distinguishes qualified vendors from general integration providers who may lack understanding of healthcare-specific regulatory requirements. Vendors should demonstrate knowledge of HIPAA privacy and security rules, meaningful use requirements, and other healthcare regulations that impact integration design and implementation. Healthcare organizations should evaluate vendor compliance training programs, regulatory update procedures, and support for audit preparation activities.
Clinical workflow understanding enables vendors to design integration solutions that support healthcare delivery processes rather than creating additional complexity for clinical staff. Qualified vendors should demonstrate understanding of clinical workflows, patient care processes, and the role of integrated systems in supporting care coordination. Vendor solutions should minimize disruption to clinical workflows while enabling improved access to patient information and enhanced care coordination capabilities.
Implementation Methodology and Project Management
Vendor implementation methodologies provide frameworks for project planning, execution, and risk management throughout EMR integration initiatives. Healthcare organizations should evaluate vendor project management approaches, implementation phases, and quality assurance procedures to ensure alignment with organizational expectations and requirements. Structured implementation methodologies with defined milestones, deliverables, and success criteria help ensure successful project outcomes and enable effective project monitoring.
Change management capabilities represent essential vendor qualifications for healthcare integration projects that impact clinical workflows and user experiences. Vendors should provide change management expertise, user training services, and adoption support that help healthcare organizations successfully transition to integrated EMR environments. Comprehensive change management approaches address stakeholder communication, training program development, and ongoing support for user adoption challenges.
Testing and validation procedures ensure that integrated systems meet functional requirements and maintain data accuracy throughout the integration process. Vendors should provide comprehensive testing methodologies that include unit testing, integration testing, performance testing, and user acceptance testing procedures. Healthcare organizations should evaluate vendor testing capabilities, quality assurance processes, and problem resolution procedures to ensure reliable integration implementations.
Go-live support services provide critical assistance during the transition from testing to production use of integrated EMR systems. Vendors should offer dedicated support teams, escalation procedures, and rapid response capabilities during go-live periods when system issues can significantly impact healthcare operations. Healthcare organizations should evaluate vendor support availability, response time commitments, and problem resolution capabilities for go-live support services.
Ongoing Support and Partnership Capabilities
Long-term support services ensure that integrated EMR systems continue to meet organizational needs as requirements evolve and systems require updates or modifications. Vendors should provide comprehensive support services, including technical support, system monitoring, performance optimization, and enhancement development capabilities. Healthcare organizations should evaluate vendor support models, service level agreements, and escalation procedures to ensure adequate ongoing support for integrated systems.
Vendor financial stability and long-term viability represent important considerations for healthcare organizations making significant integration investments. Healthcare organizations should evaluate vendor financial health, growth trajectory, and strategic direction to ensure sustainable partnerships that support long-term integration success. Vendor acquisition history, client retention rates, and investment in research and development provide insights into long-term partnership potential.
Innovation and product development capabilities enable vendors to support evolving healthcare technology requirements and emerging interoperability standards. Healthcare organizations should evaluate vendor research and development investments, product roadmaps, and participation in healthcare standards development activities. Vendors that actively contribute to healthcare interoperability initiatives and invest in emerging technologies provide better long-term partnership value.
Partnership approach and collaboration capabilities distinguish vendors who view client relationships as long-term partnerships rather than transactional service arrangements. Healthcare organizations should evaluate vendor communication practices, collaboration tools, and willingness to adapt solutions to meet specific organizational requirements. Strong vendor partnerships enable healthcare organizations to leverage specialized expertise while maintaining control over strategic decisions and organizational priorities.
7. Custom Integrated EMR Software Solutions by AgileTech
AgileTech offers end-to-end EMR integration services that streamline healthcare operations and enhance patient outcomes. With expertise in clinical workflows, compliance, and interoperability standards, our solutions connect EMR systems with labs, radiology, pharmacy, billing, and patient engagement platforms.
Our core capabilities include:
- Custom Interface & API Development: Built with HL7 FHIR, REST, and cloud platforms.
- Data Migration & Transformation: Safe and compliant patient data transfer.
- Integration Testing & QA: Ensures secure, scalable, and high-performing systems.
- HIPAA-Compliant Architecture: Encrypted data, access control, audit trails.
We adopt a partnership-driven approach, offering dedicated support, scalable architecture, and real-time data sync to keep care delivery agile and informed. AgileTech also provides ongoing support, training, and strategic advice to maximize your EMR integration investment.
Whether modernizing legacy systems or building from scratch, AgileTech delivers secure, interoperable EMR integration software tailored to your long-term growth.
