CRM in Healthcare: Everything You Need to Know
CRM in healthcare enables providers to deliver better patient care, streamline communication, and build long-term trust. In a landscape where patient expectations are rising and digital transformation is reshaping care delivery, CRM systems are no longer optional; they are essential. These platforms do more than organize contact information. They drive engagement strategies, facilitate care coordination, reduce administrative workload, and empower healthcare organizations with real-time insights. By bridging gaps in communication and aligning clinical and non-clinical functions, CRM systems enable providers to foster deeper patient relationships and improve outcomes. This article explores the complete landscape of CRM in the healthcare industry, how it works, its key features and benefits, associated costs, and how to implement it successfully.

1. Understanding CRM in the Healthcare Industry
1.1. What Is Healthcare CRM and How Does It Work?
Customer relationship management in the healthcare industry refers to specialized platforms designed to manage interactions with patients and optimize internal processes. Unlike generic CRM tools, healthcare CRM systems are tailored to support medical workflows, from patient onboarding to post-treatment follow-ups. These systems aggregate patient information, communication history, appointment scheduling, and marketing efforts in one interface. The ultimate goal is to deliver more personalized, responsive care across every touchpoint.
CRM for healthcare providers is often cloud-based and designed to ensure high availability, security, and compliance with healthcare regulations. These systems operate by collecting data through touchpoints like online forms, in-person visits, call center interactions, and digital engagement tools. Information is then organized and used to create detailed patient profiles that guide decisions and actions.
1.2. Key Use Cases Across Healthcare Segments
Healthcare CRM systems are used in various medical settings. Private practices use CRM to manage appointment scheduling and patient reminders. Hospitals apply CRM to streamline cross-department communication, while telehealth providers rely on CRM to maintain virtual engagement and continuity of care. Wellness platforms often use CRM for marketing automation and personalized health content. Each segment requires different functionalities, but the shared purpose is enhancing the provider-patient relationship.
Health insurance companies are also investing in CRM solutions to handle policyholder inquiries, track claims, and segment members for targeted wellness programs. In medical research, CRM tools help manage study participants and improve engagement throughout trial phases. Public health departments use healthcare CRM systems to run educational campaigns and facilitate vaccination drives.
2. Key Features of Healthcare CRM Systems
2.1. Patient Information Management
Patient data is the foundation of any healthcare CRM system. These platforms serve as a central hub, aggregating patient demographics, contact information, medical history summaries, interaction logs, appointment details, and more. By consolidating these data points into a unified profile, healthcare CRM systems allow providers to build a 360-degree view of every patient.
For instance, a front-desk coordinator can instantly see if a patient missed their last appointment, while a doctor can view notes from a previous consultation and send a follow-up plan, all without switching platforms. Data accuracy and completeness are also improved through standardized data entry fields, real-time syncing with EHRs, and automation.
Advanced features like timeline views, activity histories, and customizable tags make it easier to prioritize urgent cases or track patients with chronic conditions. The ability to group patients by shared attributes, such as those needing post-surgery care or undergoing long-term therapies, enables more effective communication and treatment planning.
2.2. Engagement and Communication Tools
Modern patients expect transparency, convenience, and responsiveness. Healthcare CRM systems are equipped with tools that automate and personalize communication. These include automated appointment reminders, patient satisfaction surveys, educational content, and health alerts.
Two-way messaging allows patients to confirm appointments, ask questions, or request prescription refills. In addition, some CRM platforms integrate with mobile apps and patient portals, creating omnichannel engagement opportunities. For example, a pregnant patient might receive a personalized content series about prenatal care based on her due date and health history.
CRMs also support outreach via SMS, email, voice calls, and even WhatsApp in some global markets. These messages can be triggered by events (e.g., appointment scheduled) or timed campaigns (e.g., seasonal vaccination reminders). All interactions are recorded, giving the care team full visibility into the communication history and improving coordination.
2.3. Marketing Automation and Patient Segmentation
Marketing capabilities in healthcare CRM systems go beyond mass emails. Through intelligent segmentation, providers can divide their patient base by age, gender, medical conditions, behavior patterns, or engagement levels.
For example, patients who have not visited in over a year might be grouped into a reactivation campaign with a personalized message from their doctor. Similarly, a CRM can identify diabetic patients for targeted nutrition webinars or follow-up lab testing reminders.
Marketing automation enables the scheduling, delivery, and monitoring of multi-step campaigns. Campaign performance metricssuch as open rates, click-through rates, and appointment conversions be tracked and optimized. This ensures that outreach efforts are not only efficient but also data-driven and outcome-focused.
Some CRMs use AI-powered tools to predict when a patient is likely to need care, allowing for proactive outreach that can improve retention and reduce costly complications.
2.4. Reporting and Analytics
One of the most valuable features of healthcare CRM systems is their robust reporting and analytics capabilities. These tools provide both high-level overviews and granular breakdowns of key performance indicators (KPIs). Stakeholders can measure patient engagement trends, marketing campaign outcomes, operational bottlenecks, and care quality indicators.
For example, a healthcare marketing team may use CRM analytics to identify that open rates for appointment reminders are higher via SMS than email. As a result, they may shift their communication strategy accordingly. Administrators may notice peak scheduling times or identify service gaps by reviewing appointment trends over weeks or months.
Advanced CRM tools also include predictive analytics, which apply machine learning algorithms to historical data. This functionality helps anticipate patient no-shows, identify at-risk individuals, and forecast care demand based on seasonal trends or previous behaviors. By using these insights proactively, healthcare providers can allocate resources efficiently and improve outcomes.
2.5. Integration With Third-Party Systems
Modern healthcare CRM platforms are not designed to operate in isolation. They must integrate seamlessly with a variety of third-party systems, such as EHRs (Electronic Health Records), laboratory information systems, medical billing software, telemedicine platforms, and scheduling applications.
These integrations enable data flow between departments and eliminate redundancies. For example, when a patient schedules an appointment through a CRM-integrated app, the details automatically reflect in the hospital’s central scheduling system. After the visit, clinical updates from the EHR can trigger a follow-up campaign from the CRM to ensure continuity of care.
Such interoperability also supports population health initiatives, where data from various sources is unified to monitor public health trends, manage chronic conditions, and launch preventive campaigns. The more integrated a CRM system is, the more value it brings across the care ecosystem.
Read more: Healthcare LMS Implementation: How to Create Hospital Training Software
3. CRM Benefits for Healthcare Providers
3.1. Enhanced Patient Experience and Trust
In today’s healthcare landscape, patient experience is a critical metric. Healthcare CRM systems are designed to deliver experiences that feel personalized, seamless, and responsive. With tools to automate reminders, send timely follow-ups, and offer educational content tailored to patient needs, CRMs empower providers to maintain consistent communication.
Patients no longer need to chase information or make repeated phone calls for updates. For instance, after an initial visit, a patient can receive a follow-up email with aftercare instructions and a link to schedule their next appointment. This level of attentiveness boosts patient confidence and loyalty.
Healthcare CRM systems also enable better coordination between departments, ensuring that patients receive accurate information without conflicting messages. When patients trust their providers, they are more likely to follow treatment plans, ask questions, and engage actively in their care journeys.
3.2. Operational Efficiency
CRMs reduce the burden of manual tasks. Repetitive actions like data entry, schedule confirmations, and internal notifications can be automated, freeing up staff time for more meaningful interactions. As a result, healthcare organizations experience faster turnaround times, fewer administrative errors, and greater staff satisfaction.
Operational dashboards offer managers a real-time overview of patient volumes, staff workload, and scheduling gaps. This data enables healthcare facilities to optimize resource allocation, ensure timely patient handovers, and reduce waiting times.
Beyond front-desk operations, CRM systems streamline referral management, discharge planning, and insurance pre-authorization processes. These improvements contribute to smoother workflows and more coordinated care delivery across all touchpoints.
3.3. Smarter Decision-Making With Centralized Data
Data-driven decisions are at the heart of modern healthcare. By centralizing patient engagement data, healthcare CRM systems provide actionable insights into patient behavior, treatment adherence, and population health trends.
With customizable reports and real-time analytics, healthcare leaders can track key performance indicators (KPIs), such as no-show rates, campaign ROI, and patient satisfaction scores. These metrics help identify opportunities for process improvements and pinpoint underperforming areas.
Predictive analytics modules in advanced CRMs can forecast patient churn risk, anticipate appointment demand, and even flag potential complications based on previous interactions. This foresight allows for timely interventions, ultimately improving outcomes and resource efficiency.
3.4. Better Resource Planning and Staffing Decisions
CRM platforms help healthcare administrators identify service bottlenecks and manage resources more strategically. By analyzing appointment patterns, no-show rates, and staff availability, the system can support better shift planning and capacity forecasting.
For example, if CRM reports reveal that cardiology appointments have a consistently high cancellation rate on Friday afternoons, management can adjust clinic hours or reassign staff accordingly. Similarly, if patient satisfaction scores are lower on certain days, further investigation can identify staffing shortfalls or operational inefficiencies.
Over time, this data-driven approach enables healthcare providers to maximize productivity, improve care access, and ensure high levels of patient satisfaction.
4. Choosing the Right Healthcare CRM System
4.1. Essential Features to Look For
When selecting a CRM for healthcare providers, prioritize HIPAA compliance to ensure patient data security. The system should also be scalable to match your organization’s growth, intuitive for users with varied tech expertise, and capable of integrating with existing tools like EHRs, billing platforms, or patient portals.
Advanced healthcare CRM systems should support real-time data sync, offer AI-enhanced reporting, and accommodate mobile access for on-the-go staff. Look for CRM vendors with healthcare-specific expertise, as they better understand regulatory requirements and industry nuances.
4.2. Questions to Ask CRM Vendors
Before committing to a healthcare CRM system, ask vendors about customization capabilities, onboarding assistance, and training resources. Inquire about their update cycles and customer support response times. A transparent vendor relationship ensures long-term reliability and adaptability.
It’s also crucial to ask for reference clients in the healthcare space. Understanding how the CRM has performed in similar organizations gives better insight into expected ROI and support quality. Trial access or demos should be evaluated across departments for hands-on experience before purchase.
4.3. Common Implementation Mistakes to Avoid
Avoid rolling out a CRM platform without a clear adoption strategy. Ensure internal teams understand its benefits and are trained on system usage. Failing to align the CRM’s data structure with current processes can result in poor user engagement and inefficiencies.
Another common mistake is underestimating integration complexity. CRM systems must work seamlessly with existing infrastructure. Conducting a systems audit before implementation helps identify gaps and avoid disruptions. Allocate a change management team to monitor and guide internal adoption.
5. How Much Does CRM in Healthcare Cost?
5.1. Factors That Influence Pricing
The cost of CRM in healthcare depends on multiple variables. These include the number of users, deployment type (cloud-based vs on-premises), system complexity, and the level of customization required. Integration with existing platformssuch as EHRs, billing tools, and telehealth appsalso adds to the total investment.
Support needs, data migration requirements, and training services further influence pricing. For organizations prioritizing compliance, costs may increase to accommodate third-party audits and data encryption services.
5.2. Average Pricing Models
There are two primary pricing models for healthcare CRM systems: subscription-based and custom-built. Subscription-based CRMs, often offered as SaaS (Software as a Service), typically cost between $30 and $200 per user per month. These platforms are ideal for small to mid-sized practices needing rapid deployment and minimal upfront investment.
In contrast, custom-built CRM solutions are suited for large organizations with complex needs. Initial development costs can range from $50,000 to over $250,000, depending on scope, features, and integrations. However, these systems offer unmatched flexibility and scalability for long-term growth.
5.3. Open-Source vs Enterprise CRM
Open-source CRM platforms like SuiteCRM or Vtiger provide a cost-effective alternative for tech-savvy healthcare teams. These solutions are free to use but require significant internal IT resources for deployment, maintenance, and updates.
Enterprise-level CRMs such as Salesforce Health Cloud and Microsoft Dynamics 365 offer robust security, analytics, and vendor support. While more expensive, they come with compliance assurance and ongoing product improvements. The decision between open-source and enterprise depends on your organization’s size, tech maturity, and long-term goals.
5.4. Cost Breakdown by Organization Size
The financial impact of a healthcare CRM varies by the size and needs of the organization:
- Small Clinics and Practices: May spend $3,000–$10,000 annually on a basic SaaS CRM with essential features.
- Medium-Sized Facilities: With growing patient bases and more complex workflows, mid-tier CRMs range from $15,000–$50,000 annually, depending on user volume and integrations.
- Large Hospitals and Health Networks: Enterprise solutions can exceed $100,000 per year when factoring in advanced analytics, support contracts, and custom development.
Understanding these tiers helps organizations plan their CRM strategy according to budget and growth stage.
5.5. Value Over Time
The total cost of ownership (TCO) for a CRM system includes more than licensing. Over time, operational savings and revenue growth can outweigh the initial investment. For example, a system that reduces administrative workload by 20% may allow a clinic to serve more patients without hiring new staff.
Healthcare providers should consider a five-year financial model when evaluating CRM adoption. This model should include training, maintenance, system upgrades, and expected ROI from improved retention, better patient outreach, and streamlined workflows.
6. How to Successfully Implement a Healthcare CRM
Implementing a CRM system in the healthcare industry is a multi-phase process that requires careful planning, collaboration, and oversight.
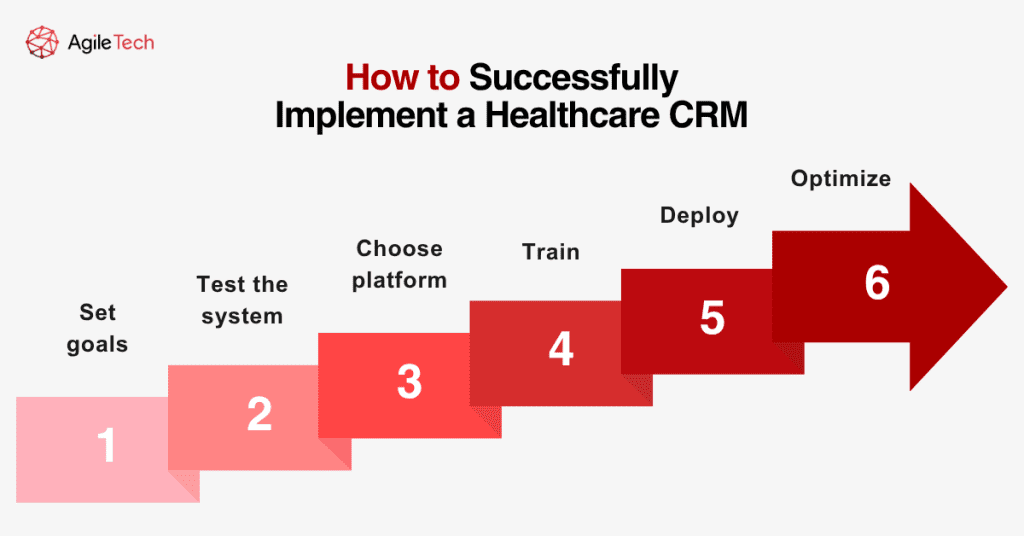
Step 1: Define clear goals and success metrics. These could include improving engagement, increasing appointment compliance, or reducing patient churn. Align goals with both clinical and business outcomes.
Step 2: Identify key stakeholders. Successful CRM implementation requires support from leadership, clinical teams, marketing staff, and IT. Form a steering committee to ensure cross-functional alignment.
Step 3: Audit current systems and processes. Map existing workflows to identify inefficiencies and integration points. Document data silos and legacy systems that could complicate CRM deployment.
Step 4: Choose a suitable CRM platform. Evaluate multiple vendors. Consider not only feature sets but also user interface, scalability, support quality, and vendor reputation in the healthcare space.
Step 5: Plan for EHR, billing, and communication tool integration. Technical compatibility with your current tech stack is crucial. Test data exchanges and interface performance before full rollout.
Step 6: Prepare data for migration. Data cleansing is often the most time-consuming task. Validate records, remove duplicates, and standardize formats. Create a secure transfer plan.
Step 7: Design onboarding and training programs. Training should be ongoing, role-specific, and supplemented with user manuals and live support. Encourage a culture of learning and experimentation.
Step 8: Establish support channels and feedback loops. Monitor user feedback through surveys and help desk analytics. Appoint internal champions to promote adoption and troubleshoot issues.
Step 9: Monitor usage and optimize workflows. Use CRM reports to measure impact. Look for adoption patterns, engagement rates, and productivity gains. Refine workflows accordingly and update training as needed.
Post-launch Phase:
After the initial rollout, continuous improvement is key. Schedule quarterly reviews with key users to assess what’s working and what needs refinement. Stay updated on new features from your vendor and adjust configurations to support evolving needs. Establish a roadmap for long-term CRM enhancements aligned with strategic goals.
With thoughtful planning and a user-centered approach, healthcare CRM implementation can unlock significant benefits, both for patient outcomes and operational excellence.
Conclusion
Healthcare CRM systems are revolutionizing how providers engage with patients and manage internal operations. From improving communication and boosting efficiency to enhancing patient loyalty, CRM is no longer optional; essential.
Understanding CRM in healthcare, how it differs from EHRs, and how to implement it strategically can help providers stay ahead in a competitive landscape. Whether you are part of a growing private practice or a large hospital network, choosing the right CRM for healthcare providers is a decision that will shape your future success.
FAQs
If you’re exploring healthcare CRM systems, take time to align features with your goals, ensure proper integration, and commit to team-wide adoption. The rewardsbetter outcomes, higher satisfaction, and greater operational control are well worth the investment.
With AgileTech Vietnam‘s custom CRM development services, you may revolutionize the way you handle client relationships. Being a top CRM development firm, we concentrate on developing unique CRM solutions that improve client interactions, expedite workflows, and spur business expansion. Our knowledgeable staff uses the newest technology to create safe, scalable CRM systems that blend in well with your business processes.